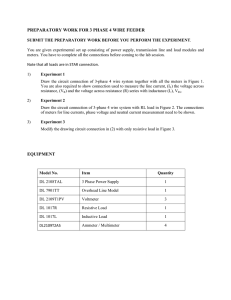
1. Explain the procedure steps used in this practice to get the experimental values. Part I Series Circuits 1. Connect the Current Probe to Channel 1 and the Differential Voltage Probe to Channel 2 of the interface. 2. Open the file “23a Series Parallel Circ” in the Physics with Vernier folder. Current and voltage readings will be displayed in a meter. 3. Connect together the two voltage leads (red and black) of the Voltage Probe. Click, then click to zero both sensors. This sets the zero for both probes with no current flowing and with no voltage applied. 4. Connect a 10 , a 51Ω, and a 68Ω resistors in series with each other and with the power supply, to do this follow these steps: • • • • • • Place the switch SW1 in the middle position, external. Connect a wire from 1 to 2. Connect a wire from 3 to 6. Connect a wire from 7 to 10. Connect a wire from 11 to the red of the current probe. Connect a wire from the black of the current probe to 35. 5. Set the power Supply to 5 volts, connect the differential voltage probe across 1 and 35 to measure the total voltage, record it in Table I, record the Total Current. 6. Measure the voltage across each resistor by connecting the voltage probe across each, record your findings in Table I. 7. Measure the current through each resistor to do this follow these steps: • • • • Replace the current probe with a wire, connecting 11 to 35. Place the current probe between 1 and 2, replace the wire; record in table I; Place the wire back and place the current probe between 3 and 6, replace the wire, record in Table I Place the wire back and place the current probe between 7 and 10, replace the wire, record in Table I 8. Determine the Equivalent Resistance of the series circuit using Ohm’s Law. Measure the Total current for different values of the total voltage. • • • • • Set the configuration according to steps 5 and 6. Open the filed “22 Ohm’s Law” in the Physics with Vernier folder. Increase your voltage by about 0.5 V from 0 to 4.5 V for a total of 10 data points. Record your values in Table II; Obtain the linear regression. Part II Parallel circuits 9. Connect a 10 , a 51Ω, and a 68Ω resistors in parallel with each other and with the power supply, to do this follow these steps: • Place the switch SW1 in the middle position, external. • Connect a wire from 1 to 2. • Connect a wire from 2 to 6. • Connect a wire from 6 to 10. • Connect a wire from 3 to 7. • Connect a wire from 7 to 11. • Connect the current probe between 11 and 35. 10. Set the power Supply to 5 volts, connect the differential voltage probe across 1 and 35 to measure the total voltage, record it in Table III, record the Total Current. 11. Measure the voltage across each resistor by connecting the voltage probe across each, record your findings in Table III. 12. Measure the current through each resistor to do this follow these steps: • • • • Replace the current probe with a wire, connecting 11 to 35. Place the current probe between 3 and 7, replace the wire; record in table III. Connect current probe to 7 (red end) and connect two wires to the black end, connect one wire to 3 and the other to 11, record in Table III. Make sure that a wire connects 3 with 7. • Connect current probe to 11 (red end) and connect two wires to the black end, connect one wire to 7 and the other to 35, record in Table III. 13. Determine the Equivalent Resistance of the series circuit using Ohm’s Law. Measure the Total current for different values of the total voltage. • • • • • Set the configuration according to steps 9 and 10. Open the filed “22 Ohm’s Law” in the Physics with Vernier folder. Increase your voltage by about 0.5 V from 0 to 4.5 V for a total of 10 data points. Record your values in Table IV. Obtain the linear regression. 2. Compute the equivalent resistance between two resistances in parallel. Demonstrate.