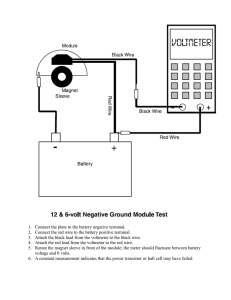
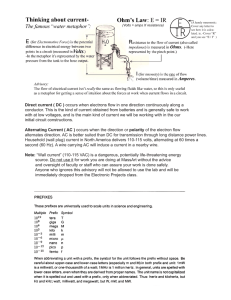
Electric Current
advertisement
Electric Current Types of Electric Current Electric current is a continuous flow of electric charge and is measured in Amperes (A). The two types of electric current are direct current and alternating current. Direct Current Electric charge that only flows in one direction is direct current. A battery is a device that changes chemical energy to electrical energy. A battery has a negative terminal and a positive terminal • The charge moves from the negative terminal to the positive terminal. Alternating Current A flow of electric charge that regularly reverses its direction is known as alternating current. AC offers an advantage in transporting electric current over long distances. • AC electricity in the US changes direction 60 times each second. “War of Currents” AC: Tesla/Westinghouse DC: Edison/General Electric AC wins due to long range transmission and transformers Conductors A conductor is a material through which charge can easily flow. • Metals, such as, copper, silver, and aluminum are good conductors. Insulators A material through which charge cannot easily flow is called an insulator. • Wood, rubber, and Styrofoam are good insulators. Resistance Resistance is the opposition to movement of charge through a material. Measured in units called ohms (Ω) What effects resistance of a material • Its size (thick wire < thin wire) • Shape (long wire > short wire) • Temperature (hot wire > cool wire) Voltage Electric current flows because of differences in electric potential, called voltage. Electric Potential: The electric energy per charge. Potential Difference: Difference in electric potential between two places in an electric field. Voltage Source Electric Current requires continuous voltage Ohm’s Law V=IR (v=voltage, I=current, R=resistance) Labels: Voltage (volts), Current (amps), and Resistance (ohms)