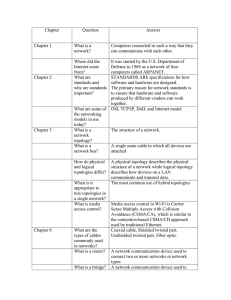
Data Communication Group 2 Introduction Network routing is the process of selecting a path across one or more networks. The principles of routing can apply to any type of network, from telephone networks to public transportation. In packet-switching networks, such as the Internet, routing selects the paths for Internet Protocol (IP) packets to travel from their origin to their destination. These Internet routing decisions are made by specialized pieces of network hardware called routers. Overview 1. Keywords from the video 2. Definition of Network Topology 3. Physical Topology & Logical topology 4. Comparison between the two Keywords: 1. Routing Protocol 11. Route Aggregation 2. Network Topology 12. Route Filtering 3. Link State Protocol 13. Load Balancing 4. Distance Vector Protocol 14. Metric 5. Path Vector Protocol 6. Autonomous System (AS) 7. Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) 8. Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP) 15. Hop Count 16. Administrative Distance 17. Split Horizon 9. Routing Table 18. Poison Reverse 10. Route Advertisement 19. Triggered Updates 20. Convergence Network Topology Network topology is the arrangement of the various elements (links, nodes, etc.) of a computer network. It can be used to define or describe the arrangement of various types of telecommunication networks, including command and control radio networks, industrial fieldbuses and computer networks. Network topology can be used to define physical or logical topologies. Physical Topology Logical Topology Physical topology refers to the logical topology is a concept in networking that interconnected structure of a local area defines the architecture of the communication network (LAN). The method employed to mechanism for all nodes in a network. Using connect the physical devices on the network equipment such as routers and switches, network with the cables, and the type of the logical topology of a network can be cabling used, all constitute the physical dynamically maintained and reconfigured . topology. Common physical topologies Common logical topologies include bus, star and include bus, star, ring and mesh. tree. Comparison PHYSICAL TOPOLOGY LOGICAL TOPOLOGY The physical topology shows the layout of the network. Shows the logic of the network transmission of data. The layout can be modified depending on the needs. There is no interference or manipulation involved. related to the Physical topologies can be organized into star, ring, Topologies could be bus and ring topologies. mesh, and bus topologies. This has a major impact on the cost, scalability, and This has a big impact on the speed and delivery of data bandwidth capacity of the network depending on the packets. It also handles flow control and distribution of equipment election and availability. data packets. This is the actual route of transmission. It is a high-level representation of the data flow. Conclusion These are the result of my research and understanding of the definition of Network topology. I hope that Professor satisfied with our work and thank you everyone for your patients. Questions & answers Invite questions from the audience.