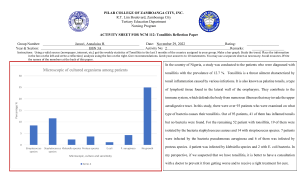
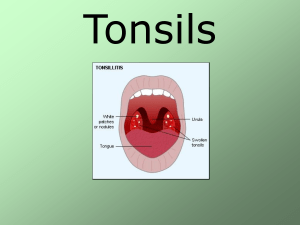
TONSILLOPHARYNGEAL INFECTIONS Tonsils are large lymphoid tissue situated in the lateral wall of the oropharynx. They form lateral part of the Waldeyer's ring. ANATOMY WALDEYER’S RING. palatine tonsils (Tonsilit) adenoids (Nasal pharyngeumdaki tonsil) Lingual tonsil Lateral pharyngeal bands. #1 #2 ACUTE TONSILLITIS Signs and symptoms: Fever Sore throat (Boğaz Ağrısı) Tender cervical lymphadenopathy Dysphagia (Yutkunamama) Erythematous tonsils with exudates (Akıntı Yapan Kanamalı Tonsiller) VIRAL TONSILLITIS/PHARYNGITIS Having additional rhinitis (burun enfeksiyonu), hoarseness (Ses Boğukluğu), conjunctivitis and cough Pharyngitis is accompanied by conjunctivitis in adenovirus infections Oral vesicles, ulcers point to viruses 7 DUE TO STREPTOCOCCI: Spreads by close contact and through air Spread more in crowded areas (KG, school, army..) Most common among 5-15 age group More frequent among lower socio-economic classes Most common during winter and spring Incubation period 2-4 days 8 SIGNS/SYMPTOMS (STREPTOCOCCI) Sore throat Anterior cervical LAP Fever > 38 C (virüslerde daha düşüktür) Tonsillar hyperemia / exudates Soft palate petechia Absence of coughing Difficulty in swallowing Öksürük Yok Headache, fatigue Absence of nose drip Muscle pain Burun Akıntısı Yok Nausea, vomiting Absence of hoarseness Öksürük +, Boğuk Sesle Ses Kısıklığı Yok Konuşma + Burun Akması + 9 CLINICAL EVALUATION Viral Lower grade fever Lower WBC, Lymphocytic shift Less tonsillar exudate Bacterial Higher WBC, Granulocytic shift More exudative / 42 LABORATORY Throat swab Rapid antigen test If negative need swab ASO (Anti Streptolysin) Gold standard Shows we came across this one in 1 year of time period. May remain + for 1 year WBC count Peripheral smear 11 / 42 AIM OF TREATMENT Prevention of complications Symptomatic improvement Bacterial eradication Prevention of contamination Reducing unnecessary antibiotic use 12 / 42 GABHS (GROUP A BETA HEMOLYTIC STREPTOCCUS) Control culture after full dose treatment? NO If history of ARF: Take control culture after treatment No need to screen or treat carriers 13 / 42 TREATMENT Many different antibiotics can eradicate GABHS from pharynx Starting treatment within 9 days is enough to prevent ARF (Acute Rhemuatic Fever) 14 COMMON DISEASES OF THE TONSILS AND ADENOIDS Acute tonsillitis Chronic tonsillitis Recurrent tonsillitis Obstructive tonsillar hyperplasia Acute adenoiditis Chronic adenoiditis adenoid hypertrophy ACUTE TONSILLITIS Etiology 5-30% bacterial; of these 39% are beta-lactamaseproducing (BLPO) Anaerobic BLPO GABHS most important pathogen because of potential sequelae Throat culture Treatment CHRONIC TONSILLITIS Chronic sore throat Malodorous (kötü kokulu) breath Presence of tonsillithis Peritonsillar erythema Persistent tender cervical lymphadenopathy Lasting at least 3 months CHRONIC TONSILLITIS No true consensus (fikir birliği) on the definition. Symptoms greater than 4 weeks RECURRENT ACUTE TONSILLITIS Same signs and symptoms as acute Occurring in 7 separate episodes per year 5 episodes per year for 2 years 3 episodes per year for 3 years OBSTRUCTIVE ADENOID HYPERPLASIA Adenoidler bir araya değecek kadar büyür ve tıkanıklığa sebep olur. Signs and Symptoms Obligate mouth breathing Hyponasal voice Snoring and other signs of sleep disturbance ADENOID HYPERPLASIA Triad Hyponasality Snoring Open mouth breathing Purulent rhinorrhea, post nasal drip, chronic cough, and headache ADENOID DISEASES Common in young children Adenoid hypertrophy caused by: infections, allergy, environmental.. Symptoms Otitis media and sinusitis Dx: palpation, X-ray, endoscopy Tx: Surgery OBSTRUCTIVE TONSILLAR HYPERPLASIA Snoring and other symptoms of sleep disturbance Muffled voice Dysphagia MALIGNANT NEOPLASMS Most common is lymphoma Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma Rapid unilateral tonsillar enlargement associated with cervical lymphadenopathy and systemic symptoms INDICATIONS FOR TONSILLECTOMY 1.Infection Recurrent, acute tonsillitis (more than six episodes per year or three episodes per year for 2 years) Chronic tonsillitis: halitosis, persistent sore throat, tender cervical adenitis Peritonsillar abscess 2. Obstruction Excessive snoring and chronic mouth-breathing Obstructive sleep apnea or sleep disturbances 3. Neoplasia Asymmetric tonsillar hypartrophy ADENOTONSILLECTOMY Most commonly performed procedure in the history of surgery $500 million annually in healthcare expenditures INDICATIONS FOR ADENOIDECTOMY Obstruction: Chronic nasal obstruction or obligate mouth breathing OSA with FTT, cor pulmonale Dysphagia Speech problems Severe orofacial/dental abnormalities Infection: Recurrent/chronic adenoiditis (3 or more episodes/year) Recurrent/chronic OME (+/- previous BMT) PERITONSILLAR ABSCESS “Hot potato voice” (Vö Vö Vö Vö) Trismus and difficulty speaking Asymmetric tonsillar enlargement Uvula pushed away from abscess Fluctuant mass frequently palpable INCISION AND DRAINAGE Needed for incomplete needle aspiration Vertical incision through mucosa Curved hemostat to break up loculations Swab inside of abscess for culture TREATMENT Preferably admitted to hospital and treated with analgesics and antibiotics. In a patient with an early peritonsillar abscess which is really a peritonsillar cellulitis incision and drainage are not recommended.