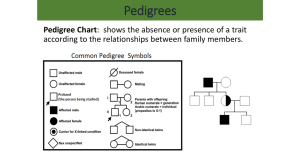
Non-Mendelian and Pedigrees Elston Eusores, MBio Incomplete Vs. Co-dominance • Codominance - A form of inheritance in which both alleles are equally shown. • Incomplete dominance - A form of inheritance in which the heterozygous alleles are both expressed, resulting in a combined phenotype. – Most commonly found in plants. • A red and a white allele gives pink. If it were codominance, you would see the red and white colors. Human Genetics: Karyotypes 46 TOTAL 23 homologous pairs 46 TOTAL Chromosomes 23 homologous pairs What is the difference between an Autosome and a Sexchromosome? • Autosomes are the first 22 homologous pairs of human chromosomes that do not influence the sex of an individual. • Sex Chromosomes are the 23rd pair of chromosomes that determine the sex of an individual. Autosomal Traits • Genes located on Autosomes control Autosomal traits and disorders. 2 Types of Traits: • Autosomal Dominant • Autosomal Recessive Autosomal Recessive Traits • In order to express the trait, two recessive alleles must be present. • What would be the genotype of an individual with an autosomal recessive trait? (A = dominant) – aa • What would be the genotype of an individual without the autosomal recessive trait? – AA or Aa – Aa – called a Carrier because they carry the recessive allele and can pass it on to offspring, but they do not express the trait. Albinism Defect of melanin production that results in little or no color in the skin, hair, and eyes Albinism Albinism How does it happen? Affected Genotype: aa Cystic Fibrosis Disease that causes the body to produce unusually thick, sticky mucus that: •Clogs the lungs and leads to lung infections • Obstructs the pancreas • Stops natural enzymes from helping the body break down and absorb food How does it happen? Affected Genotype: cc Sickle Cell Anemia Caused by an abnormal hemoglobin shape which causes the red blood cells to have a crescent shape. Red blood cells carry oxygen. How does it happen? Affected Genotype: ss Tay–Sachs disease • Symptoms: – a build up of lipids in the brain – Seizures – blindness • Mainly occurs in Jewish people Tay-Sachs Disease PKU (phenylketournia) • symptoms; – cannot break down the specific amino acid (phenylalanine found in foods like milk) – results in brain damage • Mainly occurs in people of European descent Autosomal Dominant Traits • If dominant allele is present on the autosome, then the individual will express the trait. • What would be the genotype of an individual with an autosomal dominant trait? – AA and Aa (Heterozygotes are affected) • What would be the genotype of an individual without the autosomal dominant trait? – aa Huntington’s Disease Causes the break down of brain cells, (neurons) in certain areas of the brain. Causes uncontrolled movements, loss of intellectual faculties, and emotional disturbance. How does it happen? Affected Genotype: HH or Hh Progeria • Drastic premature aging, rare, die by age 13. Symptoms include limited growth, alopecia, small face and jaw, wrinkled skin, atherosclerosis, and cardiovascular problems but mental development not affected. Sex-Linked Traits • Sex-linked traits are produced by genes only on the X chromosome. – They can be Dominant or Recessive. • What would be the genotypes of a male and female that have a Sex-linked Dominant trait and do not express the trait? • Expresses Trait: Male - XA Y Female - XA XA or XA Xa • No Expression: Male - Xa Y Female - Xa Xa • What would be the genotypes of a male and female that have a Sex-linked Recessive trait and do not express the trait? • Expresses Trait: Male - Xa Y Female - Xa Xa • No Expression: Male - XA Y Female - XA XA or XA Xa (Carrier) • Most Sex-linked traits are Recessive! Color Blindness Inability to see colors in the normal way How does it happen? Affected Genotypes: XbXb XbY Hemophilia Inability of the blood to clot properly How does it happen? Affected Genotypes: XhXh XhY Pedigree Analysis • A pedigree shows the relationship between parents and children over the generations and how a trait is passed down from one generation to the next. How to Construct a Pedigree? • A Pedigree is a visual showing the pattern of inheritance for a trait. (Family tree) • • • • Symbols and Rules: Male = Female = Affected = Unaffected = Carrier = Link parents together with a line and then make a vertical line to connect to offspring. Autosomal Dominant Pedigree • Draw a Pedigree showing a cross between Heterozygous parents that have 2 boys and 2 girls. (Show all possibilities) Genotypes of Affected and Unaffected: • AA and Aa = Affected aa = Unaffected Aa aa Aa Aa Aa AA Autosomal Recessive Pedigree • Draw a Pedigree showing a cross between Heterozygous parents that have 2 boys and 2 girls. (Show all possibilities) Genotypes of Affected and Unaffected: • AA=Unaffected Aa=Carrier, Unaffected aa=Affected Aa aa Aa Aa Aa AA Sex-Linked Recessive Pedigree • Draw a Pedigree showing a cross between a normal male and a Carrier Female. • Genotypes of Parents: • Male = Xh Y Female = XH Xh XRY XRY XR Xr XrY XRXR XRXr