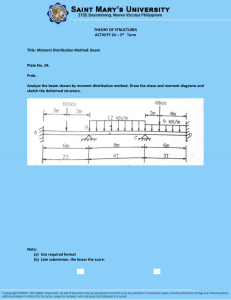
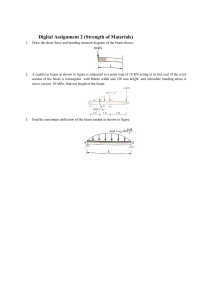
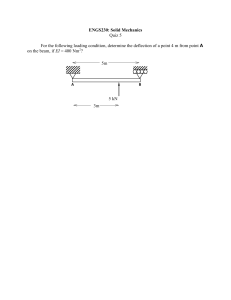
CECC483 – CE COMPREHENSIVE COURSE 2 (CC2) MIDTERM EXAM 1. A solid circular brass 25 mm in diameter is subjected to an axial tensile force of 50 kn. Determine the decrease in the diameter of the bar due to this load. For brass, E = 90 GPA and Poisson’s Ratio = 0.28 2. A 500-mm-long, 16-mm-diameter rod made of a homogenous, isotropic material is observed to increase in length by 300 μm, and to decrease in diameter by 2.4 μm when subjected to an axial 12-kN load. Determine the modulus of elasticity and Poisson’s ratio of the material. CECC483 – CE COMPREHENSIVE COURSE 2 (CC2) 3. Two shafts 'A' and 'B' transmit the same power. The speed of shaft A is 300 r.p.m. and that of shaft B is 200 r.p.m. Answer: Shaft B has greater diameter 4. The homogeneous 600-N plate is suspended from three cables as shown. a. Compute the tension of cable at A in Newtons. b. Compute the tension of cable at B in Newtons. c. If the tensile stress of a 5 mm diameter cable at C is limited to 50 MPa, compute the maximum weight (in Newtons) of the plate. 5. The buckling load will be maximum for a column, if Answer: Both ends of the column are clamped CECC483 – CE COMPREHENSIVE COURSE 2 (CC2) 6. The entrance of a warehouse has a roof that supports a roof load of 20kN/m. The supports B and C are considered as simply supported. a. Determine the vertical reaction at C in KiloNewtons. b. Determine the maximum negative moment at BC in kilonewton-meter. c. Which of the following gives the location of the maximum moment from point A. 7. The 4-mm diameter cable BC is made of steel with E = 200 GPa. Knowing that the maximum stress in the cable must not exceed 190 MPa and that the elongation of the cable must not exceed 6mm, find the maximum safe value of P in kiloNewtons. Length of the cable is 7.58 meters. CECC483 – CE COMPREHENSIVE COURSE 2 (CC2) 8. A 6-meter simply supported beam is loaded with triangular loading varies 20 kN/m at the right support to 0 kN/m at the left support. a. Compute shear force in kiloNewtons at the midspan. b. Compute moment value in kiloNewton-meter at the midspan. c. Compute the location of the maximum moment from the right support. 9. A 15-meter-simple beam is loaded with two concentrated loads P1 and P2 P1 is applied 5 m from left support and P2 is located 7 meters from P1. If P1 = P2 = 120 KN a. Which of the ff. most nearly gives the slope at the left support if El is constant b. Compute the location of the maximum deflection of the beam in meters from the left support CECC483 – CE COMPREHENSIVE COURSE 2 (CC2) 10. A 15-meter-simple beam is loaded with clockwise moment M at one of the supports. If M = 60 kN-m a. Which of the ff. most nearly gives the location of the maximum deflection of the beam from the point of application of M if El is constant (in meters). b. Compute the maximum deflection (in mm) of the beam if its flexural rigidity is 49 840 kN-m^2. 11. A 25-m long girder of the bridge is simply supported at the right end at 3 m from the left end. Given highway live load, W1 = 19.6 kN and W2 = 78.4 kN Answer: (see problem 15 in Quiz 2) CECC483 – CE COMPREHENSIVE COURSE 2 (CC2) 12. A tee section is made up of a 30 mm x 150 mm flange and a 30 mm x 160 mm web. Determine the location of the neutral axis above the lowest fiber of the section in mm. 13. A rectangular beam 60 mm wide and 100 mm deep is used as a cantilever 2 m long. A 40 kg mass falls through a height of 0.2 m before striking the free end and sticks at the free end of the beam. Calculate the maximum deflection caused by impact. Neglect the weight of the beam. CECC483 – CE COMPREHENSIVE COURSE 2 (CC2) 14. For the figure shown below, the hinge support at A is in double shear connection while the support at B is in single shear connection. Forces P is applied at C and F is an axial force produced from a member BD connected at B. Given data are as follows: x = 2 m, y = 3 m, z = 4 m, and angle = 30 degrees. a. Solve for the diameter of pin at B in mm if P = 50 kN and the shear capacity of the point B is at 140 MPa. b. Solve for the maximum value of P in kN if the shearing stress of 16-mm diameter pin at A is 120 MPa. The horizontal distance between point A and B is 0.75x. c. If the axial stress of BD is limited to 180 MPa, wherein BD is made of 40-mm square tubing with thickness is one-tenth of its dimension, solve for the shearing stress of the 16-mm diameter pin at A in MPa. Answer: (see problem 2 of Quiz 2) CECC483 – CE COMPREHENSIVE COURSE 2 (CC2) 15. A beam is said to be of uniform, if bending stress is the same throughout the beam. 2 ML 16. The deflection due to couple M at the free end of a cantilever length L is 2EI 17. A hollow steel bar (G = 80 GPa) is twisted by torques T (see figure). The twisting of the bar produces a maximum shear strain γmax = 640 × 10−6 rad. The bar has outside and inside diameters of 150 mm and 120 mm, respectively. a. Determine the maximum tensile strain in the bar. b. Determine the maximum tensile stress in the bar. c. What is the magnitude of the applied torques T? 18. A shaft is initially subjected to bending moment and then to torsion. In that case, if the magnitude of bending moment is found to be the same as that of torque, then the ratio of maximum bending stress to shear stress would be 2.0. 19. A propped beam with span L carries a concentrated moment M at the simple end. a. Compute the location of the maximum deflection from the free end. b. Compute the maximum deflection of the beam is EI is constant. c. Compute the slope at the midspan if IE is constant. CECC483 – CE COMPREHENSIVE COURSE 2 (CC2) 20. A bar of cross-section 10 mm x 10 mm is subjected to an axial pull of 8000 N. The lateral dimension of the bar is found to be changed to 9.9985 mm x 9.9985 mm. If the modulus of rigidity of the material is 800 000 N/mm2. Calculate the Poisson’s Ratio. 21. Refer to a robot shown, if P = 200 N, solve for (a) vertical component of the force P (in N), (b) moment at point O (N.m), and (c) moment at point A (in N.m). CECC483 – CE COMPREHENSIVE COURSE 2 (CC2) 22. A 10-m long beam is simply supported at the left end and at 2 m from the right end. The beam will be analyzed for the maximum moment at the midspan that can be induced by a moving load. What is the ordinate of the influence diagram at the midspan? 23. If a member, whose tensile strength is more than two times the shear strength, is subjected to an axial load up to failure, the failure of the member will occur by maximum shear stress. 24. Given the parallel forces shown in figure MTE-STAT-003: P = 20 kN. Q = 30 KN, S = 25 kN, T = 50 kN, a = 3m, b = 4m, c= 5m, d=2, e= 5m, f= 3m. Compute the z-coordinate of the resultant force. CECC483 – CE COMPREHENSIVE COURSE 2 (CC2) 25. A 12-meter span non-symmetrical parabolic cable carries a uniform horizontal load of 40 kN/m. The left support is 6 m higher than the right support and 9 m above the lowest sag, Determine the maximum tension of the cable. (Quiz 1 Problem 2) 26. A 9-meter, propped beam is loaded with 20 kN/m uniformly distributed load applied at the right twothirds of the span and a concentrated load of 50 kN at the midspan. Determine the moment at the fixed support at the left in kiloNewton-meter. CECC483 – CE COMPREHENSIVE COURSE 2 (CC2) 27. A load of "x" lbs is hung from the middle of a rope which is stretched between two rigid walls 20 ft apart. Due to the load, the rope sags 2 ft in the middle. if the tension of the rope is 100 lbs, compute the value of x. 28. Which of the following nearly gives the centroidal polar moment of Inertia (mm^4) of a steel T-section with 300 mm x 20 web and 200 mm x 20 mm 29. If the area of cross-section of a wire is circular and If the radius of this wire decreases to half of its original value due to stretch to the wire by a load, then modulus of elasticity of the wire will be. CECC483 – CE COMPREHENSIVE COURSE 2 (CC2) 30. Refer to the figure shown, if F = 855 kN, solve for (a) moment of the force about x-axis (in kN.m), (b) moment of the force about zaxis (in kN.m), and (c) angle in degrees between the force and the z-axis. 31. A simply supported beam, 150 mm wide by 350 mm high and 8 m long is subjected to a concentrated load of 50 kN at a point 5 meters from one of the supports. Solve for (a) maximum fiber stress (in megaPascals) and (b) the stress in a fiber located 20 mm from the topmost fiber of the beam (in megaPascals). CECC483 – CE COMPREHENSIVE COURSE 2 (CC2) 32. A three-legged stool is subjected to the load "P" as shown, P = 200, solve for (a) value of the vertical force reaction under leg A, (b) value of the vertical force along leg B, and (c) value of the vertical force along leg C. CECC483 – CE COMPREHENSIVE COURSE 2 (CC2) 33. A 4-meter-wide flange is simply supported at each end and supports the concentrated load at the midspan W and a total uniformly distributed load (loaded throughout the span) of 2W. Properties of section: bf = 200 mm d = 220 mm tf = tw = 20 mm a. Which of the following most nearly gives the value of W that will not exceed the flexural stress of 10 MPa. b. Which of the following most nearly gives the value of W that will not exceed the shearing stress of 1.4 MPa. CECC483 – CE COMPREHENSIVE COURSE 2 (CC2) 34. Beam ABC is on fixed supports at A and C. It’s on roller support at B. The beam carries a uniformly distributed load W, throughout the 2 spans (L1 and L2). If W = 36 kN/m, L1 = L2 = 8 meters. a. What is the degree of indeterminacy of the beam ABC? b. Due to W, the resulting reaction at B = 288 kN, what is the maximum shear at span AB? c. Find the maximum positive moment (kN-m) if the roller support Is removed at the support B. CECC483 – CE COMPREHENSIVE COURSE 2 (CC2) 35. Determine the ratio of the shear modulus to the modulus of elasticity of a material whose Poisson's ratio is 0.25. 36. A steel tube with diameters d2 = 84 mm and d1 = 52 mm is twisted by torques at the ends. The diameter of a solid steel shaft that resists the same torque at the same maximum shear stress is nearest to: 37. A steel pipe of length L = 4 ft, outside diameter D = 6 in, and inside diameter d = 4.5 in. is compressed by an axial force P = 140 kips. The material has modulus of elasticity E = 30,000 ksi and Poisson's ratio = 0.30. Determine the increase in the wall thickness in inches. CECC483 – CE COMPREHENSIVE COURSE 2 (CC2) 38. A body is subjected to a tensile stress of 1200 MPa on one plane and another tensile stress of 600 MPa on a plane at right angles to the former. It is also subjected to a shear stress of 400 MPa on the same planes. The maximum normal stress nearly equal to: 39. The length of a solid bar is 1.20 m and is twisted torques, T acting at the ends. It has a diameter of 30 mm and of a shear modulus G = 28 GPa. a. Determine the torsional stiffness of the bar. b. Determine the maximum shear stress if the angle of twist of the bar is 1/90 of the complete revolution in megaPascals. c. Determine the maximum shear strain in radians. CECC483 – CE COMPREHENSIVE COURSE 2 (CC2) 40. A simple beam with span L is applied with concentrated moment M at the midspan. Compute its maximum moment. CECC483 – CE COMPREHENSIVE COURSE 2 (CC2) 41. A 4-meter cantilever beam supports a uniform load of 25 kN/m throughout its length. The beam deflects 20 mm at the free end. Flexural rigidity is equal to 50 000 kN-m2 a. What force at the free end is required to eliminate the deflection at that end in kiloNewtons? b. What force at the midspan is required to reduce the deflection at the free end by 16 mm in kiloNewtons? c. What force at the free end is required to reduce the deflection at that end to 8 mm in kiloNewtons? CECC483 – CE COMPREHENSIVE COURSE 2 (CC2) 42. A triangular section has base of 150 mm and depth of 300 mm. What is its moment of inertia about its base in mm⁴? 43. The slope at the free end of a cantilever beam of length, L = 1 meter is 1 degree. If the cantilever beam carries a uniformly distributed load over the whole length, then the deflection at the free end is approximately equal to