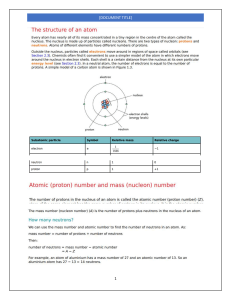
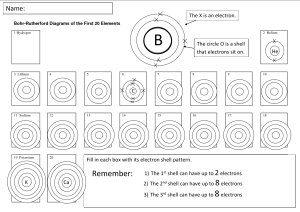
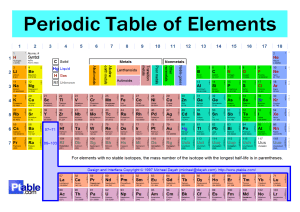
Names _____Jon Marinus_______ Chem1180 Chapter 7 Group Quiz 1. Electrons in the 2nd shell experience a greater attraction to the atom’s nucleus than to electrons in the 3rd shell. Which of the following statements explains this fact? Choose ALL that apply. (3 points) a. Electrons in the 2nd shell are, on average, closer to the nucleus b. Electrons in the 3rd shell are screened by electrons in the 2nd shell c. The 3rd shell has more orbitals than the 2nd shell d. Orbitals in the 3rd shell are shaped differently from orbitals in the 2nd shell 2. Which statement best explains the large difference between the size of atoms in group 1 and the corresponding noble gas (the noble gas with 1 less proton than the group 1 element, ex. sodium and neon)? (3 points) a. The group 1 element has more electrons b. The group 1 element has more protons c. One of the electrons in the group 1 element is in a higher energy shell relative to the noble gas. d. Group 1 elements form +1 ions 3. Neutral atoms from what part of the periodic table want an electron most strongly, which do not? (3 points) Neutral atoms from the top of group 17 (p5) i.e. Flourine, want an electron most strongly. While atoms from the bottom group 1 (s1) i.e. Francium, strongly don't want an electron. 4. Arrange the following atoms in order of increasing distance of the n=3 electron shell from the nucleus: K, Mg, P, Rh, and Ti.(3 points) Mg, P, K, Ti, Rh 5. Ionization energies generally increase from left to right across the periodic table. Why then do group 5 elements generally have higher ionization energies than group 6 elements? (4 points) This is due to the spin of electrons when they fill a shell. In group 6, there are two electrons that are closer together. These two electrons repel each other, this is why the ionization energy for group 6 is slightly lower. 6. Explain (briefly) why the second ionization energy for sodium is so much larger than the second ionization energy for magnesium. (4 points) The second ionization energy of sodium drops a core electron in favor of being valently harmonious, while magnesium's second energy only brings it down to the s1 subshell.