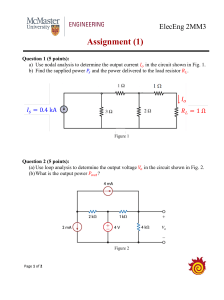
Fig. P8.132. 6 0° V 6 0° V + − + − 1Ω 4 0° A 1Ω 1Ω 2 0° A −j1 j1 Ω Ω –j1 Ω I4o 0° A 12 0° V −+ 1Ω 1Ω THE UNIVERSITY OF LAGOS 1Ω 1Ω + 1Ω Vo 12 0° V V +− + − 12 0° V DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING − − −j1 Ω 1Ω −j1 Ω o j1 Ω 2V x + – 21 Ω 0° A 1Ω 1Ω 1Ω EEG301: CIRCUITS SESSION 3 0° A AND SYSTEMS 1 -2017/18 j1 Ω ACADEMIC 1Ω TUTORIAL QUESTIONS SET V: STEADY-STATE PHASORS & SINUSOIDS Figure AC: P8.149 o Fig. P8.136. 2V x − + − V x + −j1 Ω Io Io 1Ω V 1Ω 1Ω −+ 1Ω + 2Ix 12 0° V + 6 0° V − j1 Ω j1 Ω 1Ω x 1Ω 1Ω QUESTION TWO − Ix Figure P8.153 a) Evaluate the current symbolized by I in the circuit of Fig. Q2(a), using Norton’s + 12 0°0V 1Ω −using either of the nodal or loop analysis methods. theorem. And very your result 8.154 Use both nodal analysis and loop analysis to find Io in the Figure P8.154 Io network in Fig. P8.154. Figure P8.150 8.150 Find Vo in the circuit in Fig. P8.150. 8.155 Find Io in the network in Fig. P8.155. 8.151 Find QUESTION ONE the node voltages in the network in Fig. P8.151. Figure P8.136 Figure 1Ω a) For the circuit of Fig.P8.132 Q1(a), determine −j1 Ω i. The voltage V0 across the 2-Ohm resistor 2 0° A Ω Fig. P8.137 using Thévenin’s 8.137 Find Vo in the network 1in −j1 Ω 8.133 Use Thévenin’s theorem find Voload in the network 6 0° Vto + 2 in 0° A 1Ω 1Ω ii. The maximum power deliverable to any that replaces that − theorem. 1Ω 1Ω Fig. P8.133. resistor 12 0° V TEADY-STATE ANALYSIS 1Ω 1 Ω Io −j1 Ω 2Ω 2 0° A 12 0° V 6 0° V −+ 1 Ω −j1 Ω 12 0° V +− find Vo in the network in 8.135 Use Thévenin’s theorem to find Vo in the network in + − +− + 12+0° V Fig. P8.135. 1Ω + − 1Ω + j1 Ω 4 0° A 1Ω V x 2V x − + 1Ω j1 Ω + j1 Ω 2 0° V 1 Ω 1Ω 1Ω 1Ω Vo 2 0°1 AΩ 2 0° A 1Ω − Ix 4 0° A −j1 Ω V 1 Ω 1 Ω 2V V 6 0° A x x o −j2 Ω 2Ω − −j1 12 Ω 0° V + DUE ON TUESDAY, MARCH 06, 2018 − 1Ω + + V x − −j1 Ω Figure P8.150 1Ω − Figure P8.154 + V o find Vo in the network in 1Ω Io j1 Ω j1 Ω − Figure Question 2(a). Figure P8.155 + 8.155 Find Io in the network in Fig. P8.155. Figure P8.137 Ω node voltages 2Ω the in the P8.151. 8.151 +Findj2 V o network in Fig. + b) Repeat Find ‘2a)’ for Fig. Q2(b) 8.156 Io circuit in the ofnetwork in Fig. P8.156. 1Ω Vo − Figure P8.151 2V x – 1Ω − 6 0° V 8.138 Find the Thévenin’s equivalent for the network in − − Fig. P8.138 at terminals A–B. −j1 Ω 8.152 Determine Vo in the network in Fig. P8.152. 1Ω 1Ω Figure P8.135 Figure P8.133 Figure Question 1 (a) 1Ω 1Ω −j1 Ω 2 Ω 2 0° A 12 0° V 6 0° V find Io in the network in A Use1(a) Thévenin’s findQ1(b), Io in the network in for the 2Ix + b) Repeat8.136 for the theorem circuit oftoFig. but this time, 8.134question UseFig. Thévenin’s theorem to determine I in the circuit in o P8.136. I − + + − j1 Ω + resistor through which the current symbolized by I flows. x Io 1 Ω 0 1Ω 1Ω 30° V 2 0° A −j1 Ω Fig. P8.134. Vx − 4 12 0° A 1Ω 1 Ω 6 0° V j1 Ω 1Ω 1Ω −j1 Ω − 2 0° A 1Ω 2 0° A 4 0° A –j1 Ω 1Ω 1Ω −+ + 6 0° V −j1 Ω + 1 Ω 12 0° V 1 Ω V + −j2 Ω 2 Ω − 12 0° V− − x + −+ 1Ω 1Ω −j1 Ω j1 Ω 1Ω 1Ω 2V x j1VΩo + Figure P8.155 + 12 0° V 1Ω 2V x−+ 1Ω – − 1Ω Figure P8.156 BFigure Question 2(b) − −j2IoΩ 8.156 Find Io in the network in Fig. P8.156. 6 0° V Figure P8.151 Figure 4 0° A 1Ω 1 Ω P8.152 1 Ω Figure P8.138 Figure P8.136 Figure Question 1(b) V in the network in Fig. P8.152. 8.152 Determine o Io 1Ω 2Ix 1Ω 4 0° A 8.137 Find Vo in the network in Fig. P8.137 using Thévenin’s 1Ω theorem. Figure P8.134 1 Ω 12 0° V +− 6 0° V c08ACSteady-StateAnalysis.indd 360 j1 Ω 1Ω 2 0° A + + 12 30° V − 1Ω j1 Ω Ix 1Ω 1Ω Io − + 1Ω j1 Ω 4 0° V 1Ω 2Ix Io 1Ω 19/11/14 2:41 PM