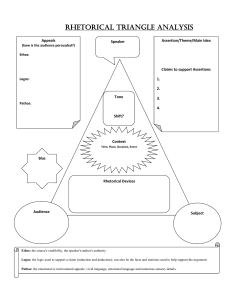
HOW TO ANALYSE SPEECHES A lot to look for in speeches Topic Speaker Audience Circumstance Structure Beginning – middle – end Language Formal or informal Vocabulary Imagery Short or long sentences Rhetorical, stylistic, literary devices Intention Inform, discuss, persuade, entertain, provoke etc. ETHOS, LOGOS, PATHOS Three modes of appeal How the speaker persuades to the audience They do not exist alone LOGOS Appeals to logic and reason(logic comes from logos) The speaker mainly uses logic and argumentation to prove the point. Describes facts and figures ETHOS Appeals to the speaker’s own character. The speaker tries to present him/herself as trustworthy and qualified. People with a strong ethos do no have to use as many arguments as people with a weaker ethos Trust= key (e.g. doctor) PATHOS Appeals to emotions. The speaker relies on feelings to get the point across. The speaker also tries to speak to the listener’s feelings DIFFERENT ANALYTICAL DEVICES Alliteration The use of the same sounds, especially consonants, to make you remember. Antithesis Using contrasts directly after one another Used for a variety of reasons. To ease tension, to relate to the audience etc. Hyperbole The repetition of a word or a sequence of words as in Martin Luther King’s famous speech “I have a dream” Humour and Irony An indirect reference to another text e.g. the bible Anaphora It was the spring of hope and the winter of despair Allusion ”Let every nation know, whether it wishes us well or ill, that we shall pay any price, bear any burden” – John F. Kennedy, 1961 Exaggerating words and phrases fx “over my dead body” Oxymoron A paradoxical antithesis with only two words Falsely true, dark light CONT. Listing Especially with three items, trying to build a climax. Metaphor Using an implied comparison Her love was like a red rose. Rhetorical questions Asking questions which need not be answered or suggesting answers. There are plenty of fish in the sea. Simile/comparison: When two objects are compared to each other: ”The truth, the whole truth, and nothing but the truth”. Do we really want to put our kids at risk? No we do not! Pauses Used to build tension or to let something sink in THE RHETORICAL PENTAGON