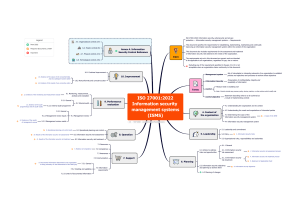
ISO 27001:2022 Implementation Step by Step ISO 27001:2022 Implementation Step by Step ● Instructor : Dr. Amar Massood ● Over 33 years of industry experience ● PhD in Computer Science, 60+ IT certifications ● ISO 27001 Auditor, Security Plus, CEH, ECSA, CISSP, and CISM ● Step by step process with templates and tools ● Easy implementation for small and medium-sized organizations Why this Course? Time effective Learn by example A lot of templates Your feedback is important ISO 27001 Foundation as a Prerequisite ● This course is about implementation of ISO 27001 ● A minimum knowledge about ISO 27001 is required ● ISO Foundation by example course is highly recommended Outline ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Obtain Management Support ● Operate the ISMS Define the scope ● Monitor the ISMS Write ISMS Policy ● Internal Audit Risk assessment ● Corrective and preventive actions Identify assets ● Management review Statement of applicability Risk Treatment Plan Define how to measure effectiveness of controls Implement the controls and mandatory procedures Implement training and awareness programs Obtain Management Support Link the ISMS to profitability (ROI) Show the benefits of ISO 27001 ● Compliance ● Retaining customers and winning new business ● Lowering expenses ● Improving processes ROI vs ROSI (Return On Security Investment) ROI = (Gain from Investment-Cost of investment)/Cost of investment. Single Loss Expectancy (SLE) : expected money lost during a single incident. Example : SLE of Loss of laptop can be $2000 or $100 000. Annual Rate of Occurrence (ARO) : Probability of security incident occurrence in a year. Annual Loss Expectancy (ALE) = ARO * SLE Example of ROSI calculation ● The Acme Corp is considering investing in an anti-virus solution. ● Acme suffers 5 virus attacks/year -> ARO=5. ● Loss of $15000 per attack -> SLE = $15000. ● Anti-virus solution is expected to block 80% of the attacks. ● Cost of $25000 : License fees $15000 + $10000 for trainings, installation Exercise Echo suffers about 10 Incident/year Cost of incident is $20000 Mitigation Ratio is 90% Cost of solution is $50000 Solution ALE = 10 x $20000 Mitigation Ratio is 90% Cost of solution is $50000 ROSI = ((10 * 20000) * 0.9 - 50,000) / 50,000 = 260% Examples of Incidents costs ● Desjardins group $53 million after exposed personal information ● Norsk Hydro : $75 million after cyberattack ● British airways, Marriott : $100 millions after falling foul of GDPR ● Target : $162 millions after a breach compromised customer’s information Define the Scope ● Locations ● Organizational units ● Processes and Services ● Assets, Technologies, Networks and Infrastructure ● Out of scope ● Validity ● Ownership Example of Scope Definition ● Locations : Second floor of company headquarters ● Organizational Units : Finance Department ● Processes and Services : Contract Management, Accounting Service ● Networks, IT Assets and infrastructure : IT Systems and network used for backend finance business ● Out of scope : cafeteria ● Validity : 1 year ● Owner : CISO A Simpler Form : Four Questions What business your company is in? How you earn your money? What assets are important? How can information security help? A Simpler Example of Scope Definition ● We are a domestic bank with a focus on retail banking. ● The storage and processing of sensitive customer data is part of our core business. ● It is therefore our duty to protect our clients data and our information assets in relation to confidentiality, integrity and availability. ● The ISMS applies to the entire organization, our employees as well as contractors.” Another Example ● As a leading company in the development, production and sales in our products ● we are highly dependent on the protection of our development and research data and the availability of our IT systems and processes. ● That is why information security is very important for our research area, our production facilities and our sales organization. Write an Information Security Policy ● Tailored to the organization ● Includes the information security objectives ● Shows the management commitment ● Must be high level policy ● Must be communicated ● Must be reviewed regularly ● Must have an owner Example of Policy of a Bank ● Objectives ○ Protect the organization’s information asset, customer data and transactions ○ Ensure Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability of Information ○ Meet Regulatory and legislative requirements ● CEO commitment and support ● Ownership : Board of directors ● Responsibilities : IT Security department, CISO, employees ● Policy is communicated by the CISO ● Should be reviewed every year Define the Risk Assessment methodology ● Methodology : A set of rules on how to calculate risks ● Why do we need a risk assessment methodology? ● ○ Required for compliance ○ Necessary for consistent way to measure risk ○ Everybody is on the same page ISO 27001 is not perspective What are Risk Assessment Methodologies? ● ● Asset Based Risk Assessment ○ Asset register ○ Asser owner ○ Identify threats and vulnerabilities Event Based Risk Assessment ○ ● Identify risks based on security events Threat Risk Assessment ○ Analyse IT systems for vulnerabilities ○ Remove potential threats IT Assets Based Risk Assessment 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Identify and Prioritize Assets Identify Threats and vulnerabilities Identify risk owners Analyse controls Determine the likelihood of incident Assess the Impact a Threat Could Have Prioritize the Information Security Risks Risk Acceptance Criteria Document the Results Identify and Prioritize Assets ● ● Assets valuable to the business Example of assets ○ ○ ○ ● ● Seevers, routers, switches … Customer data, partners documents, trade secrets … People Identify asset owners Prioritize assets according to ○ ○ ○ The monetary value of the asset Legal standing Importance to the organization Identify Vulnerabilities and Threats ● ● Vulnerability : Weakness that can be exploited Identified through ○ ○ ○ ○ ● Vulnerability analysis Audit reports Penetration testing Scanning tools Threat : Anything that can exploit a vulnerability ○ ○ ○ ○ Hackers Natural disasters System failure Accidental human interference Example of Threat and Vulnerability Asset : Paper Document Threat Vulnerability Risk Theft Unlocked cabinet Loss of confidentiality and availability of the information Fire There is no fire suppression system Loss of availability of the information Water damage Leaky roof Loss of availability Another Example of Threat and Vulnerability Asset : System Administrator Threat Vulnerability Risk Unavailability There is no replacement for potential loss of availability this position Frequent errors; lack of training potential loss of integrity and availability Identify Risk Owners Risk owner : a person or entity with the accountability and authority to manage a risk. Example : Asset owner of a server : System administrator Risk owner : Head of IT department Analyse the Current Controls ● ● ● Controls ○ In place ○ Or planned Two types of controls ○ Technical ○ Non technical Should be mapped to Annex A controls when possible Example Asset : E-Mail system Vulnerability : weak password policy Risk : Loss of confidentiality and availability Controls : Two factor authentication, password updates, awareness trainings Annex A : A.5.16 Identity Management, A.5.14 Information transfer Assess the Likelihood of Incident Low likelihood 0 The existing security controls are strong enough, adequate and provide the required level of protection. We do not expect new incidents to occur in the future. Medium likelihood 1 The existing security controls are moderate and have mostly provided the required level of protection. New incidents are possible, but not highly likely. High likelihood 2 The existing security controls are poor or ineffective. Incidents have a high probability of occurring in the future. Assess Impact of Incident Low impact 0 Loss of confidentiality, availability or integrity does not affect the organization's mission, reputation, or interest; it does affect cash flow, legal or contractual obligations and may not result in the loss of tangible assets or resources; Medium impact 1 Loss of confidentiality, availability or integrity incurs costs and has a low or moderate impact on legal or contractual obligations, or the organization's reputation, mission or interest.. High impact 2 Loss of confidentiality, availability or integrity has considerable and/or immediate impact on the organization's cash flow, operations, legal or contractual obligations, or its mission and reputation. Risk Calculation Matrix and Acceptance Criteria Risk = Impact + Likelihood Impact 2 2 3 4 1 1 2 3 0 0 1 2 0 1 2 Likelihood Risk Calculation Matrix and Acceptance Criteria (2) Impact High Medium High High Medium Low Medium High Low Low Low Medium Low Medium High Likelihood Document the Results No Asset name Asset owner Vulnerability Threat Likelihood Impact Risk Rating 1 Data Center Network Administrator Location sensitive to Earthquakes 2 Accounting Software Support Manager 3 Accountant Computers 4 5 Risk Owner Existing controls Damage High 2 High 2 High 4 Network Administrator None Undocumented Software Developers Resignation High 2 High 2 High 4 Support Manager None Accountants Single copy of data Loss of data Low 0 High 2 Medium 2 Accountants Occasional backup Accounting Software Support manager No deactivation of user accounts Unauthorized access to sensitive data Medium 1 Medium 1 Medium 2 Support manager Ad hoc Servers System Administrator Air conditioning systems is 12 years old System failure — Overheating in server room High High 2 High 2 High 4 System Administrator Old A/C systems Example of Statement of Statement of Applicability Control Description Applicable Justification A.5.29 Implementing Information Security Continuity through Physical or technical controls Yes Risk 1: Disaster recovery site is needed because of probability of earthquake Not implemented A 8.32 System Change Control Procedures : To avoid compromising systems by the implemented change through poor development Yes Risk 2 : The undocumented accounting software is due to lack of poor change control Not implemented Back-up copies of information and software shall be taken and tested regularly in accordance with the agreed backup policy. Yes Risk 3: Single copy of data, risk of data loss. Implement through backup procedure Not implemented Access rights should be removed upon termination or adjusted upon change of roles. Yes Risk 4: User accounts on accounting software are not removed or deactivated according to clear procedure Implemented through access right revocation procedure Not implemented A.8.13 A 5.15 Implementation Method Status ISO 27001 Annex A Controls This course is on ISO 27001 Implementation Check our course dedicated to ISO 27001 Annex A Controls Total of 7 hours 114 Controls with guidelines and examples Risk Treatment Plan Risk Treatment Plan has to be implemented and documented ● Which controls to implement ● Who is responsible for them ● What are the deadlines ● Which resources are required Risk Treatment Options ● Decrease the Risk ○ Example : installing an antivirus on users’ PCs to protect them from malware ● Avoid the Risk ○ Example : Not allowing employees to work from home to avoid the related threats ● Transfer the Risk ○ Example : Buy an insurance policy ● Accept the Risk ○ Example : Accepting the risk that the main switch can break without having redundancy Risk Treatment Plan Control to be implemented Risk reference Responsible person Start/End Date Resources Status A.5.29 : A cloud based disaster recovery site outside the country Risk 1 : probability of earthquake Infrastructure Manager 01/08/2020 01/11/2020 Financial. To be evaluated. Not implemented A 8.32 : System Change Control Procedure Risk 2 : The undocumented accounting software Change Manager 02/05/2020 15/05/2020 10 days work Not implemented A.8.13: Create a backup policy.and documented procedure and implement it Risk 3: Single copy of data, risk of data loss. System administrator 10/03/2020 22/03/2020 Financial : buy 5 SAN disks Work :12 days Not implemented A.5.15 : Write an Access control policy and documented procedure for access right removal Risk 4: User accounts removed CISO 01/03/2020 04/03/2020 3 days work Not implemented Monitoring, Measurement, Analysis and Evaluation Organisation should provide ● ● Metrics for the ISMS performance regarding ● Compliance with standard ● Alignment with policies ● Achievement of objectives Take into consideration ■ ■ ■ ■ ● What need to be monitored and measured (e.g., Incident Management Procedure) Methods of monitoring and measurement (e.g., Reports) Frequency to perform monitoring and evaluation (e.g., Real time monitoring, Monthly reports) Who is responsible (e.g., System administrator) Performance results should be retained Examples of measurements ● Number of information security incidents ● Number of security breaches ● Duration of service interruption ● MTTRS : Meantime to restore service ● Number of security related downtimes ● Accomplishment of information security objectives Effectiveness Measurement Control Description Measurement Responsible A.5.29 Implementing Information Security Continuity through Physical or technical controls Proportion of recovery exercises that are successfully conducted Infrastructure Manager A 8.32 System Change Control Procedures : To avoid compromising systems by the implemented change through poor development Proportion of successful changes following the change control procedure Change manager Back-up copies of information and software shall be taken and tested regularly in accordance with the agreed backup policy. Effectiveness will be measured against whether the backup policy is being applied across the relevant area System administrator Access rights should be removed upon termination or adjusted upon change of roles. Proportion of removed accounts upon termination or role change CISO A.8.13 A 5.15 Reminder This is not beginner course ISO 27001 Foundation by example ISO 27001 Annex A : Information Security Controls Explained Implement Controls and Mandatory Procedures ISO 27001 is not prescriptive on grouping controls into policies and procedures Two approaches Big companies : A policy for each section of Annex A, A procedure for each control Example of policy : Asset Management Policy (A.8), Access Control Policy (A.9) Example of procedure : A.8.1.1. Asset inventory procedure, A.8.1.3.4 Asset return procedure Small companies : A policy or procedure that covers many controls in one document Example : Supplier relationship policy that covers all the five controls of section A.15 List of Mandatory Documents ● Scope of the ISMS ● Definition of security roles and responsibilities ● Information security policy and objectives ● Acceptable use of assets ● Risk assessment and risk treatment methodology ● Access control policy ● Inventory of assets ● Operating procedures for IT management ● Statement of Applicability ● Secure system engineering principles ● Risk treatment plan ● Supplier security policy ● Risk assessment report ● Incident management procedure ● Business continuity procedure ● Statutory, regulatory, and contractual requirements List of Mandatory Records ● Records of training, skills, experience and qualifications (clause 7.2) ● Monitoring and measurement results (clause 9.1) ● Internal audit program (clause 9.2) ● Results of internal audits (clause 9.2) ● Results of the management review (clause 9.3) ● Results of corrective actions (clause 10.1) ● Logs of user activities, exceptions, and security events (clauses A.12.4.1 and A.12.4.3) Information Security Roles and Responsibilities The responsibilities for information security have to be defined and allocated. Example : ● Top Management : define strategy, goals and scope of the ISMS, leadership, assign responsibilities, provide resources, management review ● Chief Information Security Officer : define the ISMS, communication, contact of authorities, coordinate risk management ● IT Administrator : define, implement and maintain devices, supervise access rights, respond to threats, raise awareness ● Internal Auditor : Participate in the Audit Management Process, Prepare and distribute the Audit Report, Assess Organization’s compliance with approved security measures in Statement of Applicability, Prepare audit criteria to increase its quality Acceptable use of Assets Policy ● Define and Document the rules of acceptable use of assets ● Implement appropriate controls and communicate security requirements ● Rules for Mail and internet usages ● Guidelines for use of mobile devices ● And other specific specific rules or guidance Example of Acceptable Use Policy Purpose : outline acceptable use of computer equipment Scope : Use of information, computing devices and network resources Policy ● ● ● ● ● ● Information is the property of the company Responsibility to report theft of information Access information to fulfill duties Reasonableness of personal use of internet Authorized monitoring network traffic Right to audit networks to ensure compliance Access Control Policy ● ● ● ● Establish, document and regularly review an access control Policy Assets owners should determine appropriate access controls rules and rights Access controls are logical and physical Policy should take account of ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ Security requirements of business applications Consistency with information classification Policy relevant legislation and any contractual obligations segregation of access control roles, e.g. access request, access authorization, access administration requirements for formal authorization of access requests. requirements for periodic review of access rights Removal of access rights Arching of records of events of use of user identities Example of Access Control Policy Purpose : Provide authorized access and preserve confidentiality, integrity and availability of data Scope : All networks, IT system, data and authorized users Out of scope : External website and other information classified as ‘Public’. Policy ● ● ● ● ● ● Generic identities are not permitted The allocation of privilege rights shall be restricted upon request from a senior manager Least privilege and need to know principles Unique user account and complex password Use of access cards for physical access Regular review of this policy Secure System Engineering Principles Secure system engineering principles must be established and documented, selected and applied during development ● Secure system engineering procedures ● Security should be designed into all architecture layers ● Security engineering principles should be regularly reviewed ● Security engineering principles should be applied to outsourced systems ● Security engineering principles should be applied in development Examples of Secure System Engineering Principles 1. Treat security as an integral part of the overall system design. 2. Ensure that developers are trained in how to develop secure software 3. Assume that external systems are insecure 4. Protect information while being processed, in transit, and in storage 5. Where possible, base security on open standards for portability and interoperability 6. Implement layered security 7. Isolate public access systems from mission critical resources 8. Implement least privilege 9. Ensure proper security in the shutdown or disposal of a system. Information Security Policy for Supplier Relationship A policy to mitigate the risks on information assets accessible by suppliers. ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Identifying and documenting the types of suppliers A standardized process and lifecycle for managing supplier relationships Defining the types of access that different types of suppliers will be allowed Minimum security requirements for each type of information and type of access Processes and procedures for monitoring adherence to security requirements Accuracy and completeness controls to ensure the integrity of the information Obligations applicable to suppliers to protect the organization’s information Handling incidents and contingencies associated with supplier access Information Security Policy for Supplier Relationship (2) ● Resilience, recovery to ensure the availability of the information ● Awareness training for the organization’s personnel ○ Involved in acquisitions regarding applicable policies … ○ Interacting with supplier personnel regarding appropriate rules of engagement ● Conditions of information security requirements and controls in agreement ● Managing the necessary transitions of information and information processing facilities Example of Supplier Information Security Policy Purpose : put in place procedures so that contracts and dealings between the Council and third party suppliers have acceptable levels of data protection. Scope : Applies to contracts, service arrangements that involve IT solutions which require access to, or the processing of, personal data. Policy Statement ● ● ● ● ● Use of risk based approach on how protect data Returns of assets, Removal of access Monitor and review of supplier services at least once a year Validity : 1 year or when needed Owner : Contract manager Incident Management Procedure ● Reporting Information Security Events, Weakness and incidents ● Assessment of and Decision on Information Security Events ● Response to Information Security Incidents ● Learning from Information Security Incidents ● Collection of Evidence Example of Incident Management Procedure Purpose : Quick and consistent detection of security events and weaknesses, and quick response to security incidents. Scope : all assets and employees within the ISMS scope, suppliers Procedure Reporting incidents : all users and contractors must report incidents, weaknesses and security events to the system administrator by phone or in person. Assessment : CISO must analyse the information and suggest remediation or preventive action Response to minor incidents : Containment of the incident, investigate what occurred and how, corrective actions. Response to major incidents : Use Business Continuity Procedure if the business is interrupted. Example of Incident Management Procedure (2) Learning from security incidents : CISO must review the incident and improve the ISMS processes if required, identify recurring incidents and take corrective actions Collection of evidence : the CISO responsible of the ● Collection of evidence ● Chain of custody ● Safety of evidence ● Safety of personnel Business Continuity Procedures Planning Information Security Continuity : a disaster recovery process or business continuity plan should be put in place. Implementing Information Security Continuity : Implement required policies, procedures and physical or technical controls Verify, Review & Evaluate Information Security Continuity : At regular interval to ensure the plan is still valid and maintained against changes Availability of Information Processing Facilities : implement redundancy to ensure that fail-over will be achieved in a reasonable time-frame Disaster Recovery Plan ● Purpose: Inventory IT infrastructure & steps ● Scope: Applies to all IT infrastructure ● Team: IT manager, network admin, staff ● Risk assessment: Identify disasters & impact ● Recovery strategy: Recover IT, restore data, ensure continuity ● Procedures: Backup, store offsite, restore data ● Testing & updating: Regularly tested & staff trained ● Documentation & review: Regularly reviewed for relevance Backup Procedure ● Purpose: Safeguard data availability, integrity ● Scope: Define covered systems, data ● Roles: Assign responsibilities, involved individuals ● Schedule: Frequency, timing, backup types ● Verification: Test backups, disaster recovery ● Documentation: Logs, procedures, training Statutory, Regulatory and Contractual Requirements ● Statutory, regulatory, and contractual requirements must be considered ● Statutory requirements are mandatory laws and regulations. ● Regulatory requirements are specific to industries or sectors. ● Contractual requirements are obligations in contractual agreements. ● Compliance with requirements is mandatory and failure can lead to legal action. ● ISMS must align with requirements to ensure compliance and mitigate risk. Example ● Statutory requirements: EU GDPR (applies to all orgs processing personal data of EU residents). ● Regulatory requirements: HIPAA (applies to healthcare industry in the US). ● Contractual requirements: compliance with ISO 27001 as a requirement from a client. Implement Training and Awareness Program Formal induction process including introduction to ● ● Security Policies Expectations Continual training should include ● ● ● ● Security requirements Legal responsibilities Business controls Correct use of facilities Example of Awareness Program Awareness raising activities ● ● ● ● Campaigns : Information security day Issuing booklets Newsletters Email alerts Can use different delivery media ● ● ● Classroom based Distance learning Self paced Operate the ISMS Day to day routine Records generated from Procedure execution Examples : ● Records of training, skills, experience and qualifications ● Results of internal audits ● Logs of user security incidents ● Logs of access requests ● Log an asset purchase Monitor the ISMS ● What needs to be monitored and measured; ● The methods for monitoring and measurement; ● When the monitoring and measurement shall be undertaken; ● Who shall undertake the monitoring and measurement results. Internal Audit ● Audits are performed at planned intervals ● Auditors should be independent ● Audit program should be documented ● Criteria and scope must be defined ● Non conformities should be reported ● Audit program and records should be retained Internal Audit Program Audit Period Scope Criteria Method Auditors Q1 2023 HR Department HR information system security Interview, documentation review, vulnerability scanning John Doe, Jane Smith Q1 2023 Finance Department Financial data protection and privacy Interview, documentation review, penetration testing John Doe, Jane Smith Steps of Internal Audit 1. Document Review 2. Create checklist 3. Write the audit plan 4. Main Audit 5. Reporting 6. Corrective actions 7. Follow-up Document Review ● ● Purpose ○ Check the documentation ○ Get familiar with the Organization What to do ○ Read all documents ○ Write what to check in main audit ○ Note nonconformities The Audit Plan Time Department Process Contact Clause 08:00 IT Access Control Operations Manager Annex A 5.15 10:00 HR Screening Awareness and Training HR Manager Annex A. 6.1, 6.3 Internal Audit Checklist Clause Requirement of the standard A.8.3 Backup policy (clause A.8.13) Backup logs A.5.9 Inventory of Assets The asset register exists and contains assets observed 6.3.1 Is Statement of Applicability created? Change control procedure 6.1.3 Does Risk treatment plan exist? Business continuity procedures Compliant (Yes/No) Evidence Tha Main Audit ● Main audit assesses organization's compliance ● Use checklist to verify compliance ● Check evidence to support compliance ● Observe how ISMS works in practice ● Interview staff to verify compliance ● Perform audit tests to validate evidence Report : Internal Audit Findings Nonconformity : Non-fulfillment of a requirement Observation : Not enough evidence for a Nonconformity Report document is mandatory Internal Audit Report : ● ● ● Header Nonconformities Observations Examples of Nonconformities The failure to comply with clause 4.1 lack of defining the scope No ISMS policy, No risk assessment, Absence of statement of applicability Failure to comply with Clause 7: Management review of the ISMS. ● Failure to comply with the Internal ISMS audit (Clause 6) ● ● ● ● ● Corrective actions In the event of nonconformity ● ● ● ● Take action to correct it Deal with the consequence Review effectiveness of corrective action Documentation Evaluate the need for action to eliminate causes by ● ● ● Review of the nonconformity Determine the cause Determine if similar non conformity exist or may occur. Example of corrective action Nonconformity : 2 of 100 PCs have no antivirus installed Corrective action : install antivirus on the 2 PCs Cause : finance department buy its own PCs directly Similar non conformities : check if any other departments are buying their PCs directly. Root cause corrective action : set up a procurement process for PCs and enforce it. Follow up ● Challenge: ensure timely corrective actions ● Schedule corrective actions by responsible persons ● Verify resolution of nonconformities ● Document resolution through corrective action form ● Conduct small audits for unresolved issues Management Review ● Importance of management reviews ● Previous actions: Review status, ensure implementation ● Nonconformities: Address, implement corrective actions ● Monitoring results: Assess system effectiveness ● Improvement opportunities: Identify, address areas ● Documented evidence: Retain, securely store records Conclusion ● Comprehensive, easy-to-understand course ● Covers management support, ISMS scope ● Risk assessment, asset identification ● Selecting controls, risk treatment plan ● Procedures, monitoring, internal audits ● Tailored support, values feedback