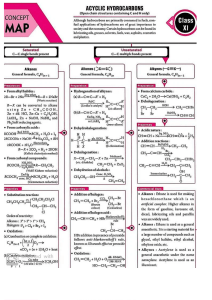
what is chemical analysis? ● the process of determining the composition of a substance by identifying its parts ● has many impt applications in our society ○ analysis of drinking water ○ analysis of food ○ in the forensic investigation of crimes ● can be divided into 2 broad categories ○ qualitative analysis: to identify elements and compounds present in an unknown substance (what is present) ○ quantitative analysis: to measure the concentration of elements and compounds present (how much is present) (not the focus) ● in QA: we are interested in 2 things: ○ determine the name of a given unknown substance ○ determine the ions (cations & anions) that are present in a given unknown substance ● QA is carried out using chemical reactions & chemical test reagents ● these reactions mostly involve observable changes including: ○ formation of a precipitate ○ evolution of a gas ○ colour change in carrying out Qualitative Analysis to determine the identity of an unknown substance, we can carry out: ● physical test/preliminary examination ○ colour ○ solubiliity ○ smell ○ pH ● chemical tests ○ tests for cations (NaOH & NH3) ○ tests for anions ○ tests for gases ■ precipitation ■ acid-base reaction ○ tests for oxidising & reducing agents ■ redox ● thermal decomposition (application for solid unknown only) thermal decomposition eg1: CuCO3 (s) [green]→ CuO (s) [black] + CO2 (g) eg2: Zn(NO3)2 (s)→ 2ZnO (s) [yellow when hot, white when cold]+ 4NO2 (g) + O2 (g) test for cations ● reagents used ○ aqeuous sodium hydorxide, NaOH ○ aqeuous ammonia, NH3 ● how to add the reagents to an unknown solution ○ add a few drops ○ add in excess ● how to observe? ○ colour of ppt how can we further differentitate Na+ and K+, since solutions containing