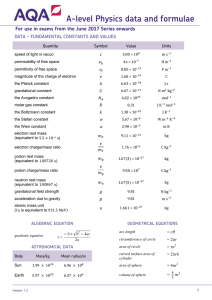
A-level Physics data and formulae For use in exams from the June 2017 Series onwards DATA - FUNDAMENTAL CONSTANTS AND VALUES Quantity Symbol Value Units speed of light in vacuo 3.00 10 m s– permeability of free space 4 10– H m– permittivity of free space 8.85 10– F m– magnitude of the charge of electron 1.60 10– C the Planck constant 6.63 10– Js gravitational constant 6.67 10– N m kg – the Avogadro constant 6.02 10 mol– 8.31 molar gas constant J K – mol– the Boltzmann constant 1.38 10– J K– the Stefan constant 5.67 10– W m– K – the Wien constant 2.90 10– mK electron rest mass (equivalent to 5.5 × 10–4 u) 9.11 10– kg electron charge/mass ratio 1.76 10 C kg – proton rest mass (equivalent to 1.00728 u) 1.67(3) 10– kg proton charge/mass ratio 9.58 10 C kg – neutron rest mass (equivalent to 1.00867 u) 1.67(5) 10– kg gravitational field strength 9.81 N kg – acceleration due to gravity 9.81 m s– atomic mass unit (1u is equivalent to 931.5 MeV) u ALGEBRAIC EQUATION quadratic equation x b Mass/kg kg GEOMETRICAL EQUATIONS b2 2a 4 ac ASTRONOMICAL DATA Body 1.661 10– Mean radius/m arc length =r circumference of circle =2 r area of circle = r2 curved surface area of cylinder = 2 rh Sun 1.99 × 10 6.96 × 10 area of sphere = 4 r2 Earth 5.97 × 10 6.37 × 10 volume of sphere = Version 1.5 4 3 r3 1 Particle Physics Waves Class Name Symbol photon photon lepton neutrino Rest energy/MeV first harmonic 0 e 0.510999 fringe spacing 105.659 refractive index of a substance s, 139.576 K meson K 0 law of refraction 493.821 critical angle sin proton p 938.257 Mechanics neutron n 939.551 moments Properties of quarks antiquarks have opposite signs Baryon number + d s + 1 3 1 e 3 + 1 3 1 e 3 + e = 134.972 497.762 Charge = = = for two different substances of refractive indices n1 and n2, K u sin v 0 2 3 diffraction grating 1 2 0 meson Type = ve muon baryons 1 period 0 electron mesons = wave speed sin = = sin for > moment = velocity and acceleration = equations of motion = = + + 2 = Strangeness = 0 0 force = force = 1 ( work, energy and power ( = = + 2 ) cos = Properties of Leptons = ) = impulse 1 3 + 2 1 2 , = = Lepton number Particles: e , ; , +1 Antiparticles: e , , , 1 = Materials density Photons and energy levels photon energy = = photoelectricity = + energy levels = – de Broglie wavelength = = 2 Hooke’s law = = tensile stress = Young modulus = ( ) tensile strain = energy stored = Version 1.5 AQA A-LEVEL PHYSICS DATA AND FORMULAE Electricity Gravitational fields = current and pd resistivity = = = resistors in series = resistors in parallel = + + + + … + + force between two masses = gravitational field strength = magnitude of gravitational field strength in a radial field = = work done gravitational potential power = = = = emf =– =– = ( + ) Electric fields and capacitors Circular motion magnitude of angular speed = = 2 centripetal acceleration = centripetal force = = Simple harmonic motion = displacement = speed = ± cos ( maximum speed = maximum acceleration = ) ( ) = 2 for a simple pendulum = field strength for a uniform field = = 2 = electric potential = field strength = capacitance = capacitor charging decay of charge energy to change temperature = energy to change state = gas law = = kinetic theory model = 1 2 4 = field strength for a radial field capacitor energy stored Thermal physics Version 1.5 force on a charge 1 1 4 1 4 = for a mass-spring system kinetic energy of gas molecule = work done = acceleration force between two point charges ( = 1 2 = = (1 = e– 1 2 e– = 1 2 ) time constant 1 3 ( ) = ) 3 2 = 3 2 3 Magnetic fields OPTIONS force on a current = force on a moving charge = Astrophysics magnetic flux = 1 astronomical unit = 1.50 × 10 = magnetic flux linkage magnitude of induced emf 1 light year = 9.46 × 10 cos cos = = sin Hubble constant, t = 2 = transformer equations m = 3.26 ly = alternating current m 1 parsec = 2.06 × 10 AU = 3.08 × 10 = emf induced in a rotating coil m = 65 km s– Mpc– = 2 telescope in normal adjustment = Rayleigh criterion efficiency = s s p p – = 5 log Stefan’s law = =– radioactive decay , = activity ½ = nuclear radius = energy-mass equation = = e 10 = 2.9 × 10 Wien’s law Nuclear physics half-life magnitude equation mK = 2GM Schwarzschild radius c2 =– Doppler shift for v << c = ln 2 / red shift = Hubble’s law = Medical physics lens equations = 1 = = threshold of hearing + = 1.0 × 10 = 10 log intensity level absorption Wm – = = ultrasound imaging = = half-lives 4 = + Version 1.5 AQA A-LEVEL PHYSICS DATA AND FORMULAE Engineering physics Turning points in physics = moment of inertia electrons in fields 1 = 2 angular kinetic energy equations of angular motion = = = + = ½ + 2 Millikan’s experiment = + ( = = 2 = = = 6 + 2 ) Maxwell’s formula 1 = = torque = = = 2 = angular momentum ( = angular impulse ) special relativity = 1 = work done power = thermodynamics = + = = = constant adiabatic change = = constant isothermal change 1 = 1 heat engines = efficiency = Electronics resonant frequency maximum theoretical efficiency = Q-factor work done per cycle = area of loop input power = calorific value × fuel flow rate indicated power = ( ) ×( ×( ) = output or brake power – friction power = heat pumps and refrigerators refrigerator: heat pump: = = = = ) = inverting amplifier ( ) = non-inverting amplifier difference amplifier 2 = operational amplifiers: open loop summing amplifier 1 =1+ = + =( ) + + = Bandwidth requirement: for AM for FM Version 1.5 =2 = 2( + ) 5 6 Version 1.5 AQA A-LEVEL PHYSICS DATA AND FORMULAE Version 1.5 7 8 Copyright © 2017 AQA and its licensors. All rights reserved. Version 1.5