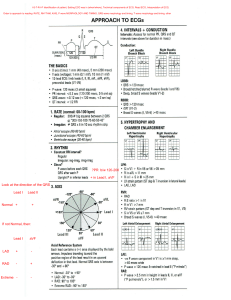
ECG Basics Clinical Part Adult One Course Prepared by: MS.RN. Reem Ahmad Jarrad Clinical Nursing Department The Nursing School The University of Jordan 2020 2 Objectives By the end of studying this ECG section the student is expected to: 1- Recognize ECG different waves and segments. 2Analyze an ECG strip reporting: heart rate, rhythm, intervals, segments, and waves. 3Recognize significant ischemic myocardial changes as reflected on the ECG. 4- Recall the 12 ECG leads and the myocardial views which each group reflects. 5- Define the characteristics of: normal sinus rhythm, sinus bradycardia, and sinus tachycardia. Definition of Electrocardiogram ( ECG ) ECG : is a visual representation of the sequence of cardiac electrical depolarization and repolarization. Definition of Heart Rhythm Rhythm : refers to the part of the heart controlling the activation sequence, which is normally the sinoatrial ( SA ) node. Definition of Cardiac Axis Axis: refers to the average direction of spread of depolarization wave through the ventricles as seen from the front. Normally, the depolarization wave spreads through the ventricles from 11 o clock to 5 o clock, so the deflections in aVR are mainly downward ( negative ) and in lead II are upward ( positive ). 3 Review of Normal Conduction System ECG Paper ECG paper is traditionally divided into 1mm squares. Vertically, ten blocks usually correspond to 1 mV, and on the horizontal axis, the paper speed is usually 25mm/s, so one block is 0.04s (or 40ms). Always check the calibration voltage on the right of the ECG, and paper speed. The following image shows the normal 1mV calibration spike: Each large square consists of five small squares. Each large square equals 0.2 second. Each small square equals 0.04 second. 4 ECG Waves - P wave: represents atrial depolarization . P duration < 0.12 seconds . P amplitude < 2.5 mm. It is upright in lead II. -PR interval: represents the duration of time required for an electrical impulse to spread from the SA node, through the atrial muscle and the AV node into the ventricular muscle. Normal value: 3-5 small squares ( = 0.12- 0.2 second ) - QRS complex: represents ventricular depolarization. Width less than 3 small squares (<0.12 second ). - T wave: represents ventricular repolarization -ST segment: segment extending from the end of the QRS complex to the beginning of the T wave. Normally, on the isoelectric line - Isoelectric line: is a reference line extending horizontally between the bases of the P and T-waves. - QT interval: is counted from the beginning of the R wave to the end of the T wave. It is longer in females than in males for the same heart rate. QT relates conversely with heart rate which means faster heart rate leads to shorter QTs. For example: HR = 75 beat/ minute, QT interval upper limit would be: 0.36 sec in men, and 0.39 in women. While for HR = 150 b/m, QT max = 0.25 sec in men, and 0.28 sec in women. 5 Characteristics of Normal Sinus Rhythm 1- P: QRS = 1: 1; this means that every p wave is followed by R wave. 2- Every beat is constituted from P-QRS-T sequence. 3- PR interval ( 0.12-0.2 ) second which is constant beat to beat. 4- Regular R-R intervals ( equal distance between the R-R ). 5- P wave is present and has normal characteristics ( width, height, shape). 6- HR range ( 60 – 100 ) beat/ minute. Characteristics of Sinus Bradycardia They are similar to those of normal sinus rhythm except that HR is less than 60 beat/minute. Characteristics of Sinus Tachycardia They are similar to those of normal sinus rhythm except that HR is more than 100 beat/minute. Heart Rate Calculation 1- Regular ECG HR = 300/ number of large squares among R-R or: HR = 1500/ number of small squares among R-R ( more precise ) HR = 1500/30 = 50 b/m ; HR = 300/6 = 50 b/m ( note R-R intervals are equal) 6 2- Irregular ECG - Take a rhythm strip for 6 seconds which corresponds to 30 large squares. - Count the number of R waves in the 6 second strip - Multiply the R wave's number by 10 HR = 8*10 = 80 beat/minute ( for the above rhythm strip). ECG description and interpretation ECG interpretation: indicates whether the record is normal or abnormal. If abnormal the underlying pathology needs to be identified. The ECG descriptive report should include: 1.Rhythm 2.Heart rate 3.Regularity 4.Conduction intervals: PR, QT. 5.Cardiac Axis 6.Description of the shape of the QRS ( narrow, wide, M shaped, peaked ,etc). 7.Description of the ST segment ( elevated; depressed or flat ). 8.Description of the T wave ( tented; flat; peaked, etc ). 9.Relationship between p waves and QRS complexes ( e.g., 1:1 ratio, sequence, etc ). 10. P wave presence and characteristics. ECG leads and their depolarization spread angles Twelve Leads ECG - Lead : is an electrical picture of the heart. - Six leads are chest leads from V1 to V6 extending across the precordium. - Three augmented voltage unipolar limb leads which are: aVR, aVL, aVF - Three standard bipolar limb leads which are : I, II, III . 7 8 10 bodily Electrodes placement Chest Leads Placement ECG ischemic Changes * ST segment depression * T inversion * ST elevation - Cardiac Ischemia: decreased coronary blood flow to the myocardium which could lead to tissue injury and necrosis ( tissue death ). ECG leads and Anatomic Groups 9 ECG Rhythm Strips for ischemic change analysis Question: determine what ischemic abnormalities are present in the upper rhythm strips?