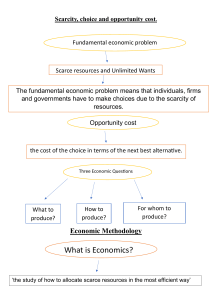
UNIT I FUNDAMENTALS OF ECONOMICS WARM-UP 1. Why have you decided to become an economist? 2. What are the advantages of being an economist in your country? 3. What job positions can you take after you have graduated from your university? TERMS EXERCISES TASK 1. Match the terms below with their definitions. 1.economics a) to try to save money by reducing the amount that you are spending 2. economy b) not using a lot of money, energy, etc. 3. to economize c) the scientific study of the system by which a country’s wealth is made and used 4. an economist d) relating to trade, industry, and money 5. economic e) a person who studies or has a special knowledge of economics 6. economical f) the system of trade and industry by which the wealth of a country is made and used TASK 2. Fill in the gaps with some of the words presented in TASK 1 in the appropriate grammatical form. 1. She's a professor of ----- at Armenian State University of Economics. 2. Tourism contributes millions of pounds to the local -----. 3. You could ----- on food by not eating in restaurants all the time. 4. Some ----- think that full employment in Europe is an unattainable goal. 5. With rents so high, it wasn’t -----to continue to live in the city. 6. The country has been in a very poor ----- state ever since the decline of its two major industries. 5 TASK 3. Read the text below and decide whether the following statements are true or false according to it. 1. Our needs and wants are limited and the resources for their satisfaction are unlimited. 2. Economics deals with the issues of studying how the economy allocates the limited resources to produce all the necessities for the societies. 3. Macroeconomics studies households and businesses while microeconomics studies the big picture. 4. Microeconomics studies the budget of a country as well as money supplies. 5. We can analyze almost all economic subjects by looking at their incentives, trade-offs, opportunity costs, marginal thinking and the principle that trade creates value. Economists study how decisions are made. Examples of economic decisions include whether you should buy or lease a car, sublet your apartment, or buy that Iphone latest model you’ve been eyeing. And just as individuals must choose what to buy within the limits of their income, society as a whole must determine what to produce from its limited set of resources. Of course, life would be a lot easier if we could have whatever we wanted, whenever we wanted it. Unfortunately, life does not work that way. Our wants and needs are nearly unlimited, but the resources available to satisfy these wants and needs are always limited. The term used to describe the limited nature of society’s resources is scarcity. Even the most abundant resources, like the water we drink and the air we breathe, are not always abundant enough everywhere to meet the wants and needs of every person. So how do individuals and societies make decisions about scarce resources? This is the basic question economists seek to answer. Economics is the study of how individuals and societies allocate their limited resources to satisfy their nearly unlimited wants. The study of economics is divided into two subfields: microeconomics and macroeconomics. Microeconomics is the 6 study of the individual units that make up the economy, such as households and businesses. Macroeconomics is the study of the overall aspects and workings of an economy, such as inflation (an overall increase in prices), economic growth, employment, interest rates, and the productivity of the economy as a whole. To understand the difference, consider a worker who gets laid off and becomes unemployed. Is this an issue that would be addressed in microeconomics or macroeconomics? The question seems to fit parts of both definitions. The worker is an individual, which is micro, but employment is one of the broad areas of concern for the economy as a whole, which is macro. However, because only one worker is laid off, this is a micro issue. If many workers were laid off and the result was a higher unemployment rate across the entire economy, the issue would be broad enough to be studied by macroeconomists. However, macroeconomics is more than just an aggregation of microeconomics. Macroeconomists examine government policies regarding the state budget and money supply, the reasons for inflation and unemployment, economic growth, international trade, and government borrowing—topics that are too complex to be understood using only microeconomic analysis. The study of economics can be complicated, but we can make it very accessible by breaking it down into a set of component parts. Almost every economic subject can be analyzed through the prism of one of these foundations: Incentives Trade-offs Opportunity cost Marginal thinking The principle that trade creates value VOCABULARY NOTES lease (v) sublet (v) eye (v) վարձակալել ենթավարձել, վարձով տալ /li s/ / sʌb let/ /aɪ/ ուշադրության տակ պահել, զննել 7 set (n) scarcity (n) abundant (adj) scarce (adj) unit (n) / skeə(r)səti/ /əˈbʌndənt/ առատ, հարուստ սակավ /skeə(r)s/ / ju nɪt/ interest rate (n) /ɪn fleɪʃ(ə)n/ /ˈɪntrəstreɪt/ productivity (n) / prɒdʌk tɪvəti/ lay off (v) /leɪɒf/ issue (n) address (v) /ˈɪʃu /, /ˈɪsju / /əˈdres/ fit (v) /fɪt/ employment (n) broad (adj) /ɪm plɔɪmənt/ /brɔːd/ concern (n) /kən sɜː(r)n/ inflation (n) հավաքածու, խումբ, բազմություն սակավություն /set/ միավոր գնաճ տոկոսադրույք արտադրողականություն,արդյու նավետություն աշխատանքից հարկադրված ազատել, կրճատել հիմնահարց, թողարկում հասցեագրել, անդրադառնալ համապատասխանեցնել, համապատասխանել զբաղվածություն լայն, ընդարձակ մտահոգություն, շահագրգռություն, կարևորություն գործազրկություն unemployment (n) /ʌnɪm plɔɪmənt/ aggregation (n) / æɡrɪˈɡeɪʃn/ state budget (n) /steɪt bʌdʒɪt/ supply (n) /səˈplaɪ/ topic (n) complex (adj) complicated (adj) prism (n) incentive (n) trade-off/tradeoff (n) opportunity cost marginal thinking (n) համախմբում, ամբողջություն պետական բյուջե առաջարկ, ապահովում թեմա / tɒpɪk/ /kəm pleks/ բարդ, խրթին / kɒm.plɪ.keɪ.tɪd/ / prɪz.əm/ բարդ, խճճված հատվածակողմ, պրիզմա /ɪn sentɪv/ /treɪd ɒf/ խթան, մղում, դրդապատճառ /ˌɒp.əˈtʃu .nə.tikɒst/ / mɑː(r)dʒɪn(ə)l θɪŋkɪŋ/ այլընտրանքային արժեք փոխզիջում 8 սահմանային մտածողություն redundancy (n) /rɪˈdʌn.dən.si/ gaze at (v) stunt (n) /ɡeɪz/ /stʌnt/ diminish (v) /dɪˈmɪn.ɪʃ/ գործազրկություն, ավելորդություն ակնապիշ նայել հնարք պակասել, նվազել TASK 4. Answer the following questions choosing the right option based on the article 1. The phenomenon of scarcity stems from the fact that a. Most economies’ production methods are not very good. b. In most economies, wealthy people consume disproportionate quantities of goods and services. c. Governments restrict production of too many goods and services. d. Resources are limited. e. People are greedy. 2. Can companies produce unlimited amounts of goods and services? a. Yes, as the resources are abundant. b. No, as the resources are limited and scarce. c. None of the above-mentioned. 3. What is the subject matter of macroeconomics? a. It studies households and businesses, how they perform in the economy. b. It studies the overall functioning of the economy, i.e. the big picture. c. Both the above-mentioned. 4. What is the subject matter of microeconomics? a. It studies individuals, households and businesses within the economy. b. It studies state budgets and business budgets. c. Both above-mentioned are true. 5. Is the state budget included in macroeconomic studies? a. It is separate from micro- and macro- studies. b. No c. Yes 9 6. Why should we try to save the resources while producing goods and services? a. There are unlimited resources in the world. b. Resources are concentrated in one part of the world. c. Resources are scarce and limited. 7. Which word from the text is closest in the meaning to ‘effectiveness’? a. Sublet b. Productivity c. Growth d. Supply 8. Which word from the text is closest in the meaning to ‘complicated’? a. Scarce b. Abundant c. Interest d. Complex 9. Which word from the text is closest in the meaning to ‘redundancy’? a. Unemployment b. Rates c. Lease d. Eyeing 10. Which word from the text is closest in the meaning to ‘gazing at’? a. Fitting b. Eyeing c. Issuing d. Leasing TASK 5. Find the odd word in each group of words. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. value cost downturn income diminish expand international valid monetary recession encourage define expend global merit financial slowdown motivate decrease enlarge multinational 10 advantage fiscal stunt incentivize decline stretch multiply 8. 9. lay-off goods employment productivity redundancy efficiency 11 dismissal effectiveness TASK 6. Complete the text with the words from the box. consumption, blocks, rational, efficient, resources, employ, allocate, activities, labor, governments, mining Economics is a social science concerned with the production, distribution, and 1. --- of goods and services. It studies how individuals, businesses, 2. ---, and nations make choices about how to 3. --- resources. Economics focuses on the actions of human beings, based on assumptions, that humans act with 4. --- behavior, seeking the most optimal level of benefit or utility. The building 5. --- of economics are the studies of labor and trade. Since there are many possible applications of human labor and many different ways to acquire 6. ---, it is the task of economics to determine which methods yield the best results. Economists 7. --- many different methods of research from logical deduction to pure data 8. ---. Economic theory often progresses through deductive processes, including mathematical logic, where the implications of specific human 9. -- are considered in a "means-ends" framework. This type of economics deduces, for example, that it is more 10. --- for individuals or companies to specialize in specific types of 11. --and then trade for their other needs or wants, rather than trying to produce everything they need or want on their own. TASK 7. Complete each sentence with a word formed from the verb in brackets. 1. The Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is considered by many to be the broadest measure of a country's (to economize) performance. 2. Many (to invest), analysts, and traders don't actually focus on the (to finalize) annual GDP report, but rather on the two reports issued a few months before. 3. The industrial (to produce) report, released monthly by the Federal Reserve, reports on the changes in the production of factories, mines, and (to utilize) in the U.S. 4. It is (to prefer) for a country to see (to increase) values of production and capacity utilization at high levels. 12 5. Families and tribes would build their own (to dwell), grow their own crops, fashion their own clothes, bake their own bread, etc. 6. Later, as (to civilize) developed, economies based on production by social class emerged, such as feudalism and slavery. 7. Capitalism is defined as a system of production whereby business owners organize (to produce) resources including tools, workers, and raw materials to produce goods for sale in order to make a profit and not for personal consumption. 8. Economic socialism is a system of production where there is limited (to own) of the means of production and a system of prices, profits, and losses is not the sole (to determine) used to establish who is engaged in production, what to produce and how to produce it. TASK 8. Search the words on paper version. abundant analysis complex depression economic expansion incentivize marginal aggregation boom concern diminish economy government individual market allocate bubble demand downturn expand incentives inflation monetary 13 supply sublet unlimited value recession recovery resources scarcity stagnation TASK 9. Identify whether each of the following statements identifies a microeconomic issue or a macroeconomic issue. Microeconomics and Macroeconomics: The Big Picture 1. 2. 3. 4. The national savings rate is less than 2% of income. Jim was laid off from his job and is currently unemployed. Apple decides to open 100 new stores. The government passes a jobs bill designed to stabilize the economy during a recession (an economic downturn). TASK 10.1. Pre-listening. Look through the words below and learn their definitions. 14 caveat - a warning to consider something before taking any more action, or a statement that limits a more general statement bottom-up - considering the smaller or less important parts or details of a plan, organization, etc. first top-down - starting from the highest levels or from the most general ideas of an organization, system, etc. scope - the range of a subject covered by a book, programme, discussion, class, etc. to interrogate - to ask questions about something as a way of analysing it or finding out more about it variable - a number, amount, or situation that can change finite - having a limit or end TASK 10.2. Pre-listening. Fill in the gaps with some of the words presented above. 1. ----- analysis usually encompasses a vast universe of macro variables while ----- analysis is more narrowly focused. 2. I'm afraid that problem is outside the ----- of my lecture. 3. The ----- in the equation are X, Y, and Z. 4. He agreed to the interview, with the ----- that he could approve the final article. 5. The funds available for the health service are ----- and we cannot afford to waste money. 6. This all sounds perfectly sensible until we start ----- the underlying assumptions. TASK 10.3. You are going to watch a video explaining the difference between macroeconomics and microeconomics. Visit the following website: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nJbWj_kHCJQ&t=2s and answer the questions or fill in the gaps when listening to the sentences below. 1. Economics is the study of how scarce or ----- resources are allocated for production, distribution, and consumption, both ---- and collectively. 2. What kind of approach does microeconomics take? 3. The prefix “macro” indicates a large or collective -----. 4. What kind of approach does macroeconomics take? 15 5. What official bodies is macroeconomics used by and for what purposes? 6. According to the video, in the media only ----- questions are discussed. 7. Start small before going -----. 9. What is the caveat that should be borne in mind? WRAPPING UP 1. What is the most fundamental issue of economics as a discipline in the statements mentioned below? a. The allocation of resources among competing wants because there are unlimited wants but limited resources. b. How to ensure continuous economic growth in the face of uncertainty. c. How to maximize profits for companies and consumer value for citizens. 2. What I have learnt in this unit is that --3. Which terms have I learnt and memorized so far? HOMEWORK Prepare a small presentation on the topic of economics, its main issues or choose micro or macro studies with examples and justify your choice. 16