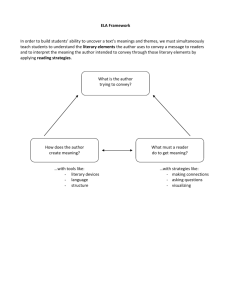
EXPLORING THE WORLD OF LITERATURE An Overview of Literary Genres, Themes, and Analysis Literature ◦ Literature consists of forms of expression including written, spoken or sung works that convey ideas, emotions and narratives. It encompasses an array of intellectual compositions. ◦ Literature plays a crucial role in shaping culture and society. It provides a mirror to reflect human experiences, fosters empathy, and allows us to explore diverse perspectives. Through literature, we gain insights into different eras, cultures, and the human condition. LITERARY GENRES Fiction ◦ Fiction: Imaginary and narrative works created from the author’s imagination, including novels and short stories. ◦ Creative storytelling, exploring characters and plot developments. Non-fiction ◦ Non-Fiction: Factual and informational writing, such as essays, biographies, and historical accounts. ◦ Non-Fiction: Presents factual information, real events, and analysis of the world. Poetry ◦ Poetry: Expressive and rhythmic language often characterized by structured verses and emotional depth. ◦ Poetry: Emphasizes emotions, imagery, and various literary devices to convey meaning. Drama ◦ Drama: Written to be performed, typically in the form of plays, exploring conflicts through dialogue and action. ◦ Drama: Depicts conflicts and relationships through dialogue and theatrical elements. COMMON LITERARY THEMES Love A recurring theme exploring the complexities of human connection and emotions. Power Examining dynamics of authority, control, and the impact on individuals and societies. Identity Delving into questions of selfdiscovery, individuality, and belonging. Conflict Addressing internal and external struggles that characters face in narratives. ELEMENTS OF STORY Key Components ◦ Plot: The sequence of events that make up a story, including exposition, rising action, climax, falling action, and resolution. ◦ Characters: Individuals or entities that drive the narrative, each with unique traits and motivations. ◦ Setting: The time and place in which the story unfolds, influencing the mood and context. ◦ Conflict: The central tension or problem that characters face, driving the narrative forward. ◦ Resolution: The conclusion of the story, where conflicts are resolved, and themes may be reinforced. Contribution to the Narrative ◦ Plot Development: Shapes the overall structure and progression of the story. ◦ Character Dynamics: Influences relationships, growth, and the reader’s connection to the narrative. ◦ Setting’s Impact: Enhances the atmosphere and provides context for the events. ◦ Conflict’s Role: Drives tension, suspense, and the overall thematic exploration. ◦ Resolution’s Significance: Offers closure and reflects on the story’s broader messages. LITERARY ANALYSIS TECHNIQUES Introduction to analyzing literature ◦ Literary analysis involves examining the components of a literary work to uncover its meaning and significance. ◦ It goes beyond the surface to explore how elements like language, structure, and themes contribute to the overall message. Literary Devices ◦ Symbolism: The use of symbols to represent ideas or qualities beyond their literal meaning. ◦ Foreshadowing: Hinting at future events in a narrative, creating anticipation and suspense. ◦ Imagery: Descriptive language that appeals to the senses, creating vivid mental pictures. ◦ Irony: A contrast between expectation and reality, often with a humorous or dramatic effect. ◦ Purpose of Literary Devices: ◦ Enhance the depth and complexity of a literary work. ◦ Convey abstract concepts in a more tangible and engaging manner. ◦ Invite readers to interpret and uncover layers of meaning. LITERATURE AND SOCIETY Reflection of Society in Literature: Literature serves as a mirror reflecting societal values, beliefs, and challenges. Explore how authors use storytelling to comment on social issues and human experiences. Influence of Literature on Society: Discuss how literature can shape perspectives, provoke thought, and contribute to cultural conversations. Examples of works that sparked social change or challenged prevailing norms. The Reciprocal Relationship: Society impacts literature, and literature, in turn, can influence societal attitudes and awareness.