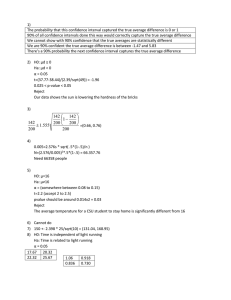
• • • • Dependent or response variable (L) -> endogenous Independent or explanatory variable (R) -> exogenous Reject and accept Ho: o P-VALUE ▪ P-value ≤ α = REJECT ▪ P-value ≥ α = FAIL TO REJECT o F-STATISTIC ▪ F-stat ≤ α = FAIL TO REJECT ▪ F-stat ≥ α = REJECT o T-STATISTIC ▪ |T-stat| ≤ α = FAIL TO REJECT ▪ |T-stat| ≥ α = REJECT o “REJECT” -> “It is statistically significant at _%.” o “FAIL” -> “It is statistically insignificant at _%.” Functional Form Misspecification: model doesn’t account for relationship bet. DV & IV. ▪ ▪ • • • P-value ≤ α = REJECT (There is enough evidence for FFM.) P-value ≥ α = FAIL TO REJECT (There is not enough evidence for FFM.) ▪ Ha: There is FFM; Ho: There is no FFM Non-random Samples: o Exogenous: sample is chosen on an X variable (unbiased). o Endogenous: sample is chosen on a Y variable (biased). Proxy Variable: mitigate omitted variable bias. o Must be related to the unobserved variable but not w/ other variables. o A bigger concern is the measurement error in X (IV) than Y. Difference-In-Differences: 𝑌𝑖𝑡 = 𝛽0 + 𝛽1 𝑡𝑟𝑒𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑡 + 𝛽2 𝑎𝑓𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑖𝑡 + 𝛽3 𝑡𝑟𝑒𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑡 ∙ 𝑎𝑓𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑖𝑡 + 𝑢𝑖𝑡 o i = index; t = time; 𝛽3= captures the effect of law/policy or measures the change of the law/policy o Diff. across groups and across time. o Change will still be there even if there is no policy. We use DID to capture that effect. • Fixed Effect Estimations: common method to get rid of bias. 𝑌𝑖𝑡 = 𝛽0 o o o • + 𝛽1 𝑋𝑖𝑡 + 𝛼𝑖 + ℷ𝑡 + 𝑢𝑖𝑡 𝛼𝑖 or 𝛼𝑛 = N – 1 (SFE) 𝜆𝑡 or 𝜆𝑛 = N – 1 (TFE) Include both SFE & TFE if some omitted variables are fixed across time periods but vary across entities (SFE) and constant across entities but vary across time periods (TFE). o Clustered standard errors: can be a defined group (ex. state, household, school, individuals, etc.) The Probit Model: non-linear model. 𝑃𝑀 = Φ(𝛽0 + 𝑥𝛽) • • • AR (P) Model: 𝑌𝑡 = 𝛽𝑜 + 𝛽1 𝑌𝑡−1 + 𝛽2 𝑌𝑡−2 + ⋯ + 𝛽𝑝 𝑌𝑡−𝑝 + 𝑢𝑡 Augmented Dickey-Fuller Test in AR (P): used to detect stochastic trends. Performed by adding and subtracting 𝑌𝑡−1 from both sides and estimating. Δ𝑌𝑡 = 𝛽0 + 𝛼𝑡 + 𝛿𝑌𝑡−1 + 𝛾1 Δ𝑌𝑡−1 + 𝛾2 Δ𝑌𝑡−2 + ⋯ + 𝛾𝑝 Δ𝑌𝑡−𝑝 + 𝑢𝑡 o 𝛿𝑌𝑡−1 ▪ The coefficient attached to the lag of y. ▪ We use this to calculate or test the stochastic trend. (See back page for example). o 𝐻0 : 𝑌𝑡 has a stochastic trend. (𝐻0 : 𝛿 = 0) o 𝐻1: 𝑌𝑡 is stationary; doesn’t have a trend. (𝐻1 : 𝛿 < 0) Instrumental Variables: used when model has endogenous x’s. o Requirements for IV validity: ▪ Exogeneity • Cov (z,u) = 0 • Instrument (z) must be uncorrelated with unobservables or error term (u). • If not, IV estimator will be inconsistent. ▪ Relevant • Cov (z,x) ≠ 0 • Instrument (z) must be correlated with explanatory variable (x). • If weak or small, it is better to do OLS than IV. 𝐶𝑜𝑟𝑟 (𝑧,𝑢) o Prefer IV if: < 𝐶𝑜𝑟𝑟 (𝑥, 𝑢) 𝐶𝑜𝑟𝑟 (𝑧,𝑥) o Good or strong IV if: ▪ With 1 instrument: |t| > 3.2 ▪ With more than 1 instrument: F > 9 Since the p-value associated with f-statistic = 0.2659 > 0.05, we fail to reject the null hypothesis. There is not enough evidence for a functional form misspecification. 𝑎𝑟𝑟𝑒𝑠𝑡 = 𝛽0 + 𝛽1 𝑑𝑢𝑚𝑓𝑙𝑜𝑟𝑖𝑑𝑎 + 𝛽2 𝑑𝑢𝑚1990 + 𝛽3 𝑑𝑢𝑚𝑓𝑙𝑜𝑟𝑖𝑑𝑎 𝑥 𝛽2 𝑑𝑢𝑚1990 + 𝑢𝑖𝑡 The coefficient 𝛽3 measures the effect of the law. It captures the change in the probability of getting arrested for drunk driving. The coefficient 𝛽2 allows for aggregate trends. The coefficient 𝛽1 allow differences between Florida and Georgia. Estimated probability of loan approval for WHITE: 1st term of eq. Estimated probability of loan approval for NONWHITES: 2nd term of eq. Expected effect of being white on probability of loan approval: Substitute the answers above in the equation in the previous sub-item. For testing stochastic trend in ln(IPt), use the augmented dickey-fuller test. Use the term with the coefficient attached to the lag of Y. One year increase of schooling will increase hourly wages by 7.3% (100% x 0.073 = 7.3%). Since |0.073/0.004| = 18.25 > 1.96, at 5% level, the estimated coefficient or educ is statistically significant. Ha: Educ is endogenous; Ho: Educ is exogenous. Since the magnitude of the t-statistic for vhat = |-1.08| < 1.96, we fail to reject the null hypothesis that claims that educ is exogenous (or we don’t have evidence to conclude that educ is endogenous). Thus, it is statistically insignificant at 5% level.