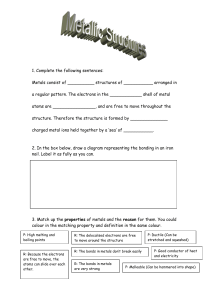
The Periodic Table
The periodic table is the study of elements. Elements are arranged in order of
increasing atomic number (proton number) and placing them in rows so that similar
elements fall into vertical columns. The horizontal rows are called periods and the
vertical columns are called groups.
There are 7 horizontal rows (periods)= represent number ofenergy levels( shells).
There are 8 vertical columns called groups = represent the number of valency
electrons.
Properties of element can be predicted from its position in the periodic table.
Periodic Table of the Elements
18
A
VIA
1H A
2 Li
IA
IV
IvB
K
Ca
sc
TI
Cs
Fr
VIA
VIA
VB
10
VIB ViIB
Fe
Co
Tc
Ru
Rh
w
Re
Os
Db
Sg
Bh
Hs
La CePr
Nd
Y
Cr
VII
Mn
Sr
Nb Mo
Ba
Ra
RE
00
3
He
Ne
Mg
6
VA
Be
Na
5Rb
IVA
Ac
Th P a
Alkali Metals
Pm
uNp
Ni
Pu
Cu
CdIn
Pt Au
Hg
Mt D s R g
Cn
Am
T b | Dy
Cm7 Bk
Transition
Halogens
IB
Pd Ag
2Sm 63Eu 4 G d
Alkal Earth Metals
O h e r Non Metals
T8
Cf
Metals
Noble Gases
Sn
TI
Pb
UutFI
Ho
6 Er
At
3
Uup
Lv
Tm
Yb
Rn
Uus Uuo
Lu
6
90100010203
E
Fm Md No
Lr7
Other Metas
Metaloids
Lanthanides& Actinides
The heavy zigzag line separates metals from non-metals.
(Majority) left zigzag = metals (except for hydrogen it is nonmetal)
Right of zigzag = non metals
Border line= metalloids or semi-metals (arsenic, germanium, silicon)
Arsenic As looks like metals shiny but doesn't behave as metals
Germanium looks like metals shiny but from covalent compounds react with Oz
forming Germanium dioxide (GeO,) as silicon dioxide (SiO).
Metalloids are semi-conductors conduct electricity under certain condition. eg Silicon used
in computer chips.
1
Groups with Special Names:
Group
l:Alkali metals.
Groups ll: alkaline earth metals.
Group VII : halogens.
Group VIll: Noble gases / inert gases.
Periods
Group
The number of electron shells in the
Group number is same as the outer
shell valency electrons.
I t indicates how the element will
atom.
react/ behave.
All elements of the same group have
similar properties (same valency
electrons).
Group VIll (8) stable arrangement
(unreactive).
Hygdrogen (non-metal): has one electron in outer ( it forms positive ion H like group
metal)s it is a gas and usually reacts as nonmetals.
Actinides elements (lowest block ): These elements are radioactive and their atoms are
broken down very quickly.
Non metals
Noble
gases
metals
metalloid
Metallic character increases
Non- metallic character increases
2
If you know where
element exists in the periodic table you
and trends to predict how it will behave.
an
can use
the patterns
Valency increases with the group number till group 4 then decreases.
Valency is not the same as the number of valency electrons.
Group
Valency
electrons
Valency
3
Lose/ gain/
Lose 1e Lose
share
2e
Charge on ions/ +1
oxide ion state
+2
Lose
Share
share
3e
3e
+3
2
Gain
Gain/share Gain/
2e
NA
share
e
+4/-4
NA
Elements in the same group have similar chemical properties because they have the
same number of electrons in the outer most energy level ( valency electrons).
Isotopes of same elements have same chemical properties since they have the
same electronic configuration (same outer shell).
Metals reacts with non metals forming ionic compounds.
N o n metals react with
non
metals forming covalent compounds.
Metal oxides are basic while non metal oxides are acidic .
Reactivity of metals increase down ( group 1).
Fr> Cs> Rb K>Na>li
Reactivity of non metals decrease down( group 7/ halogens)
FCbBi>At
A) Group 1Alkalimetals (very reactive)
"Alkali metals" because they react with cold water to form alkaline solution
(producing metal hydroxides soluble in water) ( pH greater than 7)
Metal
Lithium(lightest)
Sodium
Symbol
Li
Na
Melting point('C)Density g/cm
181
0.53
98
0.97
63
Potassium
Rubidium
Rb
0.86
1.53
Caesium
CS
|1.88
float
Melting
decrease
denisty,
softness
increase
down
group
3
Phvsical properties of Group1
1) Good conductor of heat & electricity.
2) Light silvery grey surface.
3) Softer than most metals, cut with a knife.
4) Lighter than most other metals( low density).
(Li,Na,K) float on water surface ( density <1)
5) Low melting and boiling points compared with most metals not typical
metals
Chemical properties of Group 1:
Very reactive metals and reactivity increase as you go down group.
Fr>Cs>Rb>K>Na>Li (cannot be found in nature as elements only exist in compounds)
All Salts of group 1 are soluble in water
Group 1,2,3 produce white salts/solids when dissolved in water produce colorless
solutions
1-Reaction with Air (OxVgen l:
Burn easily inair to form metal oxides,
4Na(s)+O:le)
2Na20(s)
Potassium+ oxygen .
4K +02
potassium oxide
2K20
That's why they are stored under oil because they react with air and
water vapour.
.Metals of group 1 are shiny when freshly cut, they quickly tarnish as they
react with air.
2- Reaction with water:
React with cold water to form alkaline solutions. The heat from the reaction
melts the metal ( reaction is exothermic ) (Displacement. )And bubbiles of
hydrogen are seen.
Group 1 metal +water
trough
o
na
indicator
Bubbles due
hydroxide +hydrogen
sodium hydroxide + hydrogen
2Na (s)+2H:0 ( ) -
2NaOH (aq)+ Halg)
hetal
water
metal
Sodium +water
lithium tloats and fizzes
.sodium shoots across the water
increasing
vty
.potassium melts with the heat
of the reaction, and the hydrogen
catches fire
to Ha gas
4
3-Reaction with Chlorine(Cll:
Metals react easilyto form chlorides ( ionic compounds)
2 Li (s)+ Clals)
Lithium+chlorine
2Na(s)+Clle)-
Sodium +chlorine-
> 2LiCI (s)
lithium chloride
2NaCl (s)
sodium chloride
Remember reactivity increases down the group.
The alkali metals form white ionic solids, metal ion charge is (+1). Salts of
group 1 (white ionic ) soluble in water giving colourless solutions
WHY?
Reactivity increases down the group?
Metals of group 1
Most reactiveof all metals
2,1
2,8,1
2,8,8,1
Search for it??2
B)Transition elements (Cu.Zn.Fe.Ag
Transition metals starts from period 4 with no specific group, it starts
with Scandium.
Have complex electronic configuration and more than one valency.
General propertiesof/Tvpical Metalslphysical):
1- Hard, tough, and strong ( not like group 1)
2- High melting point and boiling point except Hg
3- Malleable and ductile.
4- Good conductor of heat and electricity, silver is the best then copper.
5- High density.
5
Chemical eroperties ofTransition Metals
1
They are much less reactive than group 1 metals, e.g Copper and Nickel
don't react with water or catch fire in air as Sodium, so transition metals
don't rust easily except (iron).
2- Most transition elements form coloured (salts)compounds when dissolved
in water gives colored solutions in contrast to group 1 form white
compounds, eg Cu ions (aq) blue , Fe* (aq) green, Fe" (aq) reddish
brown.
3- Have more than one valency/ oxidation state, they form ions with
different charge.
eg IronFe Iron (1) react O, Feo
Fe" Iron (I) react O2 Fe203
Copper Cu" Copper ()react O2
Cu20
-Cu Copper (1) react Oz_Cuo
4- Most transition metals and its compounds act as catalysts (speed up the
reaction while remaining unchanged).
e.g. iron used in manufacture of Ammonia (NH3) Haber process.
Vanadium (v) oxide V;05 in Sulphuric acid manufacture contact
process.
Q) Mention 3 physical and 4 chemical differences between Potassium (group 1) and
Vanadium (transition metal).
C) Group VIlHalogen ( Non metals):
Halogen
Symbol
Molecule
Color of
(diatomic)
molecules
Halide ion Color of
ionsin
aqueous
solution
Fluorine
Chlorine C
F
Bromine
Br
Cl2
Br2
Yellow
Green
Reddish
|F(ide)
|Cr (ide)
3r
(ide)
Colorless
brown
lodine
Astatine
Greyish
At
Atz
black
Black
(ide)
At (ide)
6
Symbol
F
State at rtp
Mpt
BptC
-220
188
Density
g/cm
1.7
34
3.2
CI
Br
Gas
Gas
-101
Liquid
-7
Solid
114
183
At
| Solid
302
337
58
3.12
4.93
Trend:
Melting and boiling pt
Density increase
darker
down group
Down group
Why reactivity decrease down the group??
Searchfor it2
Bromine is very volatile (low boiling point 58°C) easily turn into gas.
lodine (l) dark grey solid when warmed turn to purple vapour (Sublimation)
solid-gas.
Aqueous solution of iodine is brown, starch is an indicator of iodine; forms
blue black complex.
Chemical propertiesof HaloRens
Reactivity decrease down the group, Fluorine is the most reactive.
Exist
h
diatomic molecules Fa, Clh, Brz
7 electrons in outer most shell (1 valency) either gain 1 electron to become negative
as
ion or share 1 electron to with non-metal by single covalent bond.
7
Chemical reactions:
1- Reactionwith metals
Halogens react with most metals to form salts (ionic compounds)
Sodium+ chlorine
sodium chloride
2Na(s)+Clls)> 2Naci(s)
2- Displacementreaction: (when halogens react with halides)/reaction exothermic
Fluorine> Chlorine> Bromine> Iodine
(Most reactive)
(least reactive)
The most reactive halogen displace the least reactive halide from its salt solution
e8:Cllg)+2Kl{ag)> 2KCl(aq) + llaq)
brown
colorless
Clalg)+2Na Br(aq)
colorless
2Nacllaq)+Bra()
colorless
reddish brown
The change in color indicates that the more reactive halogen displaced the less reactive
halide in its salt.
If solution contains
Chloride ions (CI)
Bromide ions (Br)
lodide ions()
When you add Clh
Br2
2
No change
Bromine displaced
lodine displaced | lodine displaced
No change
No change
Chlorine: (Cl,J/toxic
1
Pale green diatomic gas denser than air and soluble in water.
2-
Test for chlorine presence
by using damp litmus
paper
Result: bleach damp litmus (remove color and make it white)
3- Uses: a) make bleach
b) Water purification (kill bacteria/ microorganisms)
c) make PVC (polyvinyl chloride) insulation of electric wires
4- Make hydrochloric acid
Fluorine (E>) tooth paste
lodine (L) disinfectant
8
D)Noblegases(group O
Helium,
Neon, Argon,Krvptonand Xenon
Colorless monoatomic gases naturally occurring in air
Unreactive (inert) they have complete stable outer shell of electrons
Obtained from air by fractional distillation of liquid air
Use
Noble gasS
Very light and does
Helium (He)
not burn
(will
not catch
fire) used in filling balloons and aircrafts
Advertising signs: emit bright light when
Ne n (Ne)
electric
current passesthroughit
inert atmosphere to fill light bulbs. This
Argon (Ar)
prevent metal filament (tungsten) from
burning. Filament lasts longer
Laser
(eye surgery)
Used in light house lamps, lights for
Krypton (Kr)
Xenon (Xe)
N.B:as we
go down the group, the gases
hospitals operating rooms
get heavier and denser because the
mass
of the
atom increases.
TUNGSTEN
FILAMEN
GAS-FILLED
ASS.
BULB
LEAD-IIN
WIRES
Group
Test for Gases:
Gas
Hydrogen
Oxygen
Carbon dioxide
Chlorine
Ammonia
Sulphur dioxide
Hydrogen chloride
(gas)
Formula
Result
Test
Lightedsplint
Glowing Splint
CO2
Pass through lime
water
Damp litmus paper
NH3 (pungent smell) | Damp red litmus
Cl (green)
SO
HCI
paper
Add acidified
Burn with popsound
Red light/glow more
Turn milky
Bleached turn white)_
Turn blue
Color change from
Potassium
pink/purple to
manganate (VII)
colorless
Damp blue
Turn red
litmus paper
Bring with
NH3 gas
White smoke
NHACI
9
Collection of gases:
Downward delivery
Over water
Upward delivery
8as jar
gas
gas
water
gas
For gases which are
soluble in water and
For gases insoluble in water
H2, O2& N2
-Forgases
less dense
than air and soluble in
water (NHs)
CO, Cl & SO2
Also Ha but it is
insoluble in water
Also any gas can be collected using gas syringe giving accurate measurement of gas
denser than air
volumes
Drying ofgases (removemoisture)
Gases that do not react with acids such as (CO &So,) gases can be dried by passing
through concentrated sulphuric acid (drying agent).
Dry
sulfuric
acld
2- Gases that react with acids such as NH3 8as can be dried by passing it through
calcium oxide (drying agent)
Concentrated sulphuric acid cannot be used because it reacts with ammonia to form
ammonium sulphate.
2NH+HS0
(NH&),5O
*Silica gel/granules used as drying agent
10
Oxidation andreduction(redoxreaction)
A)Redoxin terms ofoxVRen/ hydrogen gain orloss
Oxidation
Gaining of oxygen
Reduction
Removal of oxygen
Removal of hydrogen
Substance is said to be oxidized
Gaining of hydrogen
Substance is said to be reduced
when it gains oxygen/ loses
when it loses oxygen/ gain
hydrogen during reaction
Substance which is oxidized is
called reducing agent (reductant)
hydrogen during reaction
Substance which is reduced is
called oxidizing agent (oxidant)
eg:Oxidation(oxvgengained)
Magnesium burns in air to form white ash of magnesium oxide
2Mgls)+O2(s)- >2Mgo(s)
Magnesium is oxidized as it gained oxygen
Reduction (oxvgenislost
When hydrogen is passed over black copper (1) oxide in the apparatus below, the
black powder turn into pink brown (copper)
hydrogen<
CuO
Copper (1) oxide + hydrogen-
Copper +water
reduction
CuolsHal@
Oxidizing
Reducing
agent
agent
wls)H;o)
11
Copper () oxide (black color) is reduced as it lost oxygen to copper (reddish brown)
Hydrogen is oxidized as itgained oxygen
The reaction involve both oxidation and reduction so it is called redox reaction
The reactant with oxygen is always the oxidizing agent
Q) which substance is oxidized and which is reduced in the following reactants. Mention the
reducing and oxidizing agent.
Fe0+3CO-2Fe +3Co
Burningreactions:
Reaction between calcium and oxygen
oxidation
2Ca(s)+Ozls)_
2Ca0(s)
Lreduction
Calcium is oxidized while oxygen is reduced
Another name for burning is combustion
Combustion is redox reaction
F o r example: when element burns in oxygen, it is oxidized to its
oxide
N.B:
Rusting is considered oxidation
Iron is being oxidized to iron() oxide this is called rusting
Formula of rust is Fe0,.24;0
Oxidizing agent: substance which oxidize another substance (gives oxygen) during
a
redox
reaction and is itself reduced. Also called oxidants
e-g.: oxygen(O:), ozonelOs), hydrogen peroxide(H,0:), potassium chromate(K,CrOa),
potassium dichromate Vilk,Cr,0,) & potassium manganate VIl (KMnO,)
Reducing
agent:substance which reduce another substance (remove oxygen/ add
hydrogen) during a redox reaction and is itself oxidized. Also called reductants.
eg: carbon, carbon-monoxlde, hydrogen, reactive metals (Na, K, Ca) and potassium
iodide(KI)
12
B) Redox in terms of electron transfer:
Oxidation (oIL)
Oxidation is loss of electrons (OIL)
Reduction (RIG)
Reduction is gain of e trons (RIC)
Decrease in oxidation state
Increase in oxidation state
Fe2-
Fes
Fe
Fe2
Reducing agent lose/ give electrons
Oxidizing agent gain/ accept electrons
e-g: Magnesium+ oxygen
Magnesium oxide
2/Mgols)
2Mgls)+Oal
Write half equations to show electron transfer (ionic equations)
1- Write down each reactant with the electrons it loses/ gains:
i.
Magnesium Mg-2e
-Mg
i.
Oxygen
>0*
O+ 2e-
2- Check that each substance is in correct balance as main equation:
Add 2 to both equations
2Mg-4e-2Mg"
20
O +4e-
3- The number of electrons must be balanced on both sides of the equation. If not,
multiply one or both equations by a number to balance them.
2Mg-4e 2Mg
>20
O2+ 4e
Multiply electrons by 2
(each Mg will lose 2 electrons)
(each oxygen will gain 2
electrons)
OR
You
can
Mg
just write this: Mg-2e
(both are correct but not balanced
as
Mg
Or
Mg"+2e
main equation)
Here magnesium is oxidized, while oxygen is reduced.
e-g.: Magnesium + SulphurMg+
lonic equation:
-
Mg+ S
magnesium
sulphide
MgS
Mg" +S
13
Write each half:
1- Mg-2e
M g " (balanced)
.Magnesium is oxidized and
act as
>S (balanced)
2- S+2e
reducing agent as
it
gives electrons
Sulphur is reduced and act as oxidizing agent as it accepts electrons
e.g.: reaction between chlorine and potassium bromide
Calg)+2KBr (aq)
2KCI (aq)+ Bra (ag)
reddish brown
Colorless
Ch+2e
2C
2Br- 2e
Br2
(reduction)
(oxidation)
KBr acts as reducing agent
Completeionicequation: Cl +2Br
2C
+Br2
lonicequations: it shows the ions that take part in reaction
Oxidation state /oxidation number
1- Itis the number given to an element to show whether it has been oxidized or
reduced. It is the charge on the ion.
2- When an element is not combined to another element, oxidation state is zero
3- Many elements have the same oxidation state in most or all of their compounds.
eg:group 1 elements (+1) Na"
4- But transition metals have more than one oxidation state
Element
Common oxidation states in compounds
Iron
+ll +I1 Iron(||)oxide/ Iron(l) oxide
Fe
Fe" (oxidation occurred)
Increased in oxidation number
Copper
Manganese
+1/+
+1l/+IV/+VII
Manganese (IV)oxide and in potassium
Chromium
manganate (VII)7
+l1/+V1
Chromium () oxide (3) and in potassium
dichromate(VI)6
So these
elements, the oxidation state
chloride, copper(1|) oxide
is included in
the compounds
name as
iron(111)
14
Oxidation state during redox reaction:
2Na(s)+Cl:(8Oxidation state:
ZNaCU)
+1
1
So sodium is oxidized, oxidation state rise from 0to +1
Chlorine atom gained electron to form Cl ion so chlorine is reduced. Oxidation state
falls from 0 to-1
A rise in oxidation number means oxidation occurred
-IV
I
0
+
+II
+l
+IV
A fall in oxidation number means reduction occurred
Oxidizing agent
Is reduced
Reducingagent
Is oxidized
Oxygen
Electrons
gives away oxygen
Oxygen
gain electrons
Electrons>lose electrons
To test the presence of oxidizing agent
accept oxygen
To test the presence of reducing agent
Add potassium iodide (K) solution which is
1.Add acidified potassium Manganate(VIl)
reducing agent
solution which is oxidizing agent
The color change from colorless to brown
(aq
k{aq)
colorless
brown
Color change from purple tocolorless
Mn"laq)
Potassium iodide is used to test the
MnOalag)
Manganate(Vil)
presence of oxidizing agent.
ions
ions
Purple
Colorless
Manganese()
2-add acidified potassium dichromate(VI)
solution. Oxidizing agent
Color change from orange to green
so KMnO4 and KCr0, are used to test the
presence of reducing agent.
15