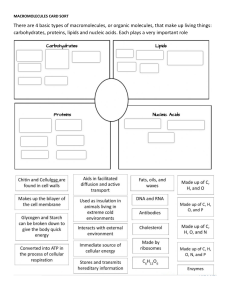
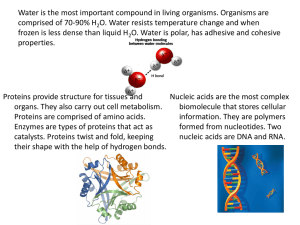
ISNHS-SHS-STEM /STEM-General Chemistry MELC: Describe the structure of proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, and carbohydrates, and relate them to their function. STEM_GC11OCIIg-j-95 Objectives: üIdentify the monomers involved in the formation of the biopolymers of carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids. üDistinguish the biomolecules of proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and lipids. üDiscuss the function of proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and lipids. üValue the importance of foods that are sources of biological macromolecules. ISNHS-SHS-STEM /STEM-General Chemistry ISNHS-SHS-STEM /STEM-General Chemistry Guide Questions 1. What can you say about the formula of glucose, fructose, and galactose? 2. What do you call compounds with the same formula but different structures? 3. What is the difference between the structure of glucose and the structure of fructose? 4. How many carbon atoms do glucose, fructose, and galactose have? 5. What functional groups are present in glucose, fructose, and galactose? ISNHS-SHS-STEM /STEM-General Chemistry Biomolecules or biological molecules are molecules present in organisms that are essential to one or more biological processes. Biomolecules include large molecules necessary for life that are built from smaller organic molecules which are called biological macromolecules. There are four major classes of biological macromolecules and each is an important component of the cell and performs a wide array of functions. These molecules when combined make up most of a cell’s mass. ISNHS-SHS-STEM /STEM-General Chemistry Carbohydrates Carbohydrates are compounds made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. They are also known as saccharides. They have the general formula Cx(H2O)y. Carbohydrates function as the energy source of the body. A simple general classification of carbohydrates is according to the number of sugar units (saccharides) present in the molecule: monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides. ISNHS-SHS-STEM /STEM-General Chemistry ISNHS-SHS-STEM /STEM-General Chemistry ISNHS-SHS-STEM /STEM-General Chemistry ISNHS-SHS-STEM /STEM-General Chemistry ISNHS-SHS-STEM /STEM-General Chemistry Carbohydrates Monosaccharides - One sugar unit per molecule. - Ex: glucose, fructose, galactose ISNHS-SHS-STEM Disaccharides - Two sugar units per molecule. - Ex: sucrose, maltose, lactose /STEM-General Chemistry Polysaccharides - Many sugar units per molecule. - Ex: cellulose, starch, glycogen Proteins Proteins are very large molecules critical for the human body’s functions. They are made from the linkage of monomers called amino acids. ISNHS-SHS-STEM /STEM-General Chemistry Proteins There are 20 kinds of amino acids depending on the —R group. An amino acid is a compound that contains at least one amino group and at least one carboxyl group. Twenty different amino acids are the building blocks of all the proteins in the human body. The simplest amino acid is glycine where R is a hydrogen atom. The body cannot make all the amino acids required by the body and is dependent on protein taken through food. ISNHS-SHS-STEM /STEM-General Chemistry ISNHS-SHS-STEM /STEM-General Chemistry ISNHS-SHS-STEM /STEM-General Chemistry Protein Functions ü Antibodies - proteins involved in defending the body against antigens. They are the molecules of the immune system. ü Contractile proteins – responsible for body movement such as muscle contraction ü Enzymes – proteins that catalyze (speed up) or facilitate biochemical reactions. ü Hormonal proteins – serve as messenger proteins to help coordinate some body functions. An example is insulin (which controls blood sugar concentration). ü Structural proteins – are fibrous and provide support. An example is collagen which provides support to connective tissues. ü Storage proteins – store amino acids like casein in milk. ü Transport proteins – are carrier proteins that move molecules from one place to another in the body. An example is hemoglobin which transports oxygen. ISNHS-SHS-STEM /STEM-General Chemistry Protein Denaturation Denaturation is a process in which a protein loses its secondary, tertiary, or quaternary structures. This may be caused by physical or chemical agents like strong acid, base, inorganic salt, heat, or solvent which disrupt the bonds that hold the protein structures together. Denaturation does not cause the cleavage of the peptide bond (the primary structure). Note that a protein will lose its biological activity if it loses its 3dimensional shape. ISNHS-SHS-STEM /STEM-General Chemistry Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids play an essential role in protein synthesis. The two main types of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). DNA and RNA are polymers made up of monomers in the form of nucleotides. When these nucleotides combine, they form polynucleotides. Each nucleotide is made up of three parts: a nitrogen base; a five-carbon sugar; and a phosphate. ISNHS-SHS-STEM /STEM-General Chemistry ISNHS-SHS-STEM /STEM-General Chemistry Lipids Lipids are molecules that contain hydrocarbons and make up the building blocks of the structure and function of living cells. Examples of lipids include triglycerides (fats), oils, axes, certain vitamins (such as A, D, E, and K), hormones, and most of the cell membrane that is not made up of protein. Fatty Acids are the simplest form of lipids and are the building blocks of the fat in our body and in the food we eat. During digestion, the body breaks down fats into fatty acids, which can then be absorbed into the blood. Fatty acids consist of a long hydrocarbon chain (typically about 12 – 18 carbons) attached to a carboxyl group. ISNHS-SHS-STEM /STEM-General Chemistry Saturated fatty acid – contains only single C-C bonds because the carbon atoms are saturated or filled up with hydrogens. Because their structure is straight, they can pack well and are solid at room temperature (e.g. fat in butter). ISNHS-SHS-STEM /STEM-General Chemistry Unsaturated fatty acids – contain carbon-carbon double bonds. When there is only one C-C double bond, it is called monounsaturated; if there are several C-C double bonds, they are called polyunsaturated. Remember that when there are double bonds, there will be geometric isomers (cis and trans). Because of the double bonds, they do not pack as tightly as saturated fatty acids. They are usually liquids at room temperature. An example of an unsaturated fatty acid is olive oil. ISNHS-SHS-STEM /STEM-General Chemistry Triglycerides can be broken down by treatment with aqueous sodium hydroxide. The products are glycerol and the fatty acid salts; the latter are known as soaps. This process is called saponification. ISNHS-SHS-STEM /STEM-General Chemistry ISNHS-SHS-STEM /STEM-General Chemistry Analogy 1. 2. 3. 4. Monosaccharide: One sugar unit; Disaccharide: ______________ Glucose + Fructose: Sucrose; __________________: Lactose Carbohydrates: saccharides; Proteins: __________________ ________________: Glycosidic bond; Amino acids: Peptide bond 5. Lactose: _______________; Fructose: C6H12O6 ISNHS-SHS-STEM /STEM-General Chemistry Identification 1. This type of carbohydrate is composed of only one sugar unit. 2. The monosaccharide is found in starch. 3. It is also known as “animal starch”. 4. The elements make up carbohydrates. 5. The carbohydrate that cannot be digested by humans. 6. They are called long chains of sugars. 7. The small repeating units that makeup proteins. 8. The polymer of glucose. 9. The type of proteins that speed up biochemical reactions. 10.The molecules of the immune system. ISNHS-SHS-STEM /STEM-General Chemistry TRUE or FALSE 1.Sucrose and maltose have the same structural formula. 2.Glucose and galactose have the same chemical formula. 3.DNA contains nitrogen base thymine. 4.Unsaturated fatty acids contain double C-C bond. 5.RNA are polymers made up of monomers in the form of amino acids. ISNHS-SHS-STEM /STEM-General Chemistry Give It Some Thought What are the side effects of having too much or too little of carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids in our body? ISNHS-SHS-STEM /STEM-General Chemistry