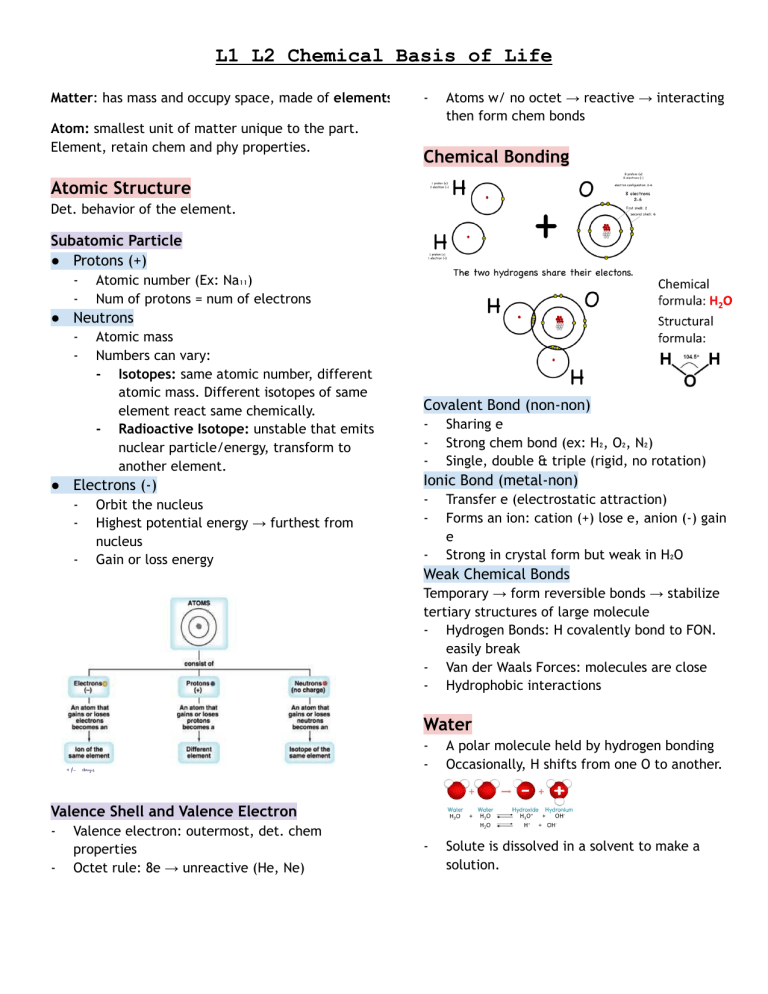
L1 L2 Chemical Basis of Life Matter: has mass and occupy space, made of elements Atom: smallest unit of matter unique to the part. Element, retain chem and phy properties. - Atoms w/ no octet → reactive → interacting then form chem bonds Chemical Bonding Atomic Structure Det. behavior of the element. Subatomic Particle ● Protons (+) - Atomic number (Ex: Na₁₁) Num of protons = num of electrons ● Neutrons - Atomic mass Numbers can vary: - Isotopes: same atomic number, different atomic mass. Different isotopes of same element react same chemically. - Radioactive Isotope: unstable that emits nuclear particle/energy, transform to another element. ● Electrons (-) - Orbit the nucleus Highest potential energy → furthest from nucleus Gain or loss energy Covalent Bond (non-non) - Sharing e Strong chem bond (ex: H₂, O₂, N₂) Single, double & triple (rigid, no rotation) Ionic Bond (metal-non) - Transfer e (electrostatic attraction) Forms an ion: cation (+) lose e, anion (-) gain e Strong in crystal form but weak in H₂O Weak Chemical Bonds Temporary → form reversible bonds → stabilize tertiary structures of large molecule - Hydrogen Bonds: H covalently bond to FON. easily break - Van der Waals Forces: molecules are close - Hydrophobic interactions Water - A polar molecule held by hydrogen bonding Occasionally, H shifts from one O to another. - Solute is dissolved in a solvent to make a solution. Valence Shell and Valence Electron - Valence electron: outermost, det. chem properties Octet rule: 8e → unreactive (He, Ne) Acids and Bases Acids: in H₂O, donates H+ to solution Bases: in H₂O, OH- combine with H+, takes out H+ Equilibrium (pure water): [H+] = [OH-] Acidic: pH < 7 Basic: pH > 7 Most biological systems 6-8 (except stomach), maintained by a buffer system Carbon - Primary cellular composition Able to form large molecules Contain C → organic molecules More versatile, 4 valence e, rings and others C-C combinations introduce complexity and variety Organic molecules with C and covalently bonded vary in length, shape, num and loc of double bond Functional Groups A num of small groups of atoms freq. bound to C - Specific chem and phy properties - Chemically reactive - Num and arrangement det. unique chem properties Types: 1. Hydroxyl group (-OH): alcohols 2. Carbonyl group (CO-): aldehyde or ketone 3. Carboxyl group (-COOH): carboxylic acids 4. Amino group (-NH₂): amines 5. Sulfhydryl group (-SH): thiols 6. Phosphate group (PO43-): cellular energy storage 7. Methyl group (-CH₃): tertiary structure of macromolecules Macromolecules (Polymers) Polymerization: the process of forming macromolecules. Condensation reaction that links 2 or more small molecules through formation of covalent bonds, removing 1 H₂O per covalent bond formed. Hydrolysis → break covalent bond by adding H₂O




