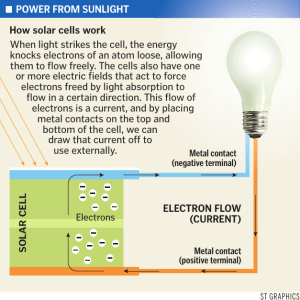
TOPIC: Electrical quantities SUB-TOPIC: Electric current Date: Wednesday, 10h January, 2024 Objectives: • Know that electric current is related to the flow of charge • Describe the use of ammeters (analogue and digital) with different ranges • Describe electrical conduction in metals in terms of the movement of free electrons • Know the difference between direct current (d.c.) and alternating current (a.c.) Charge The wires in an electric circuit are made of metal, because metal is a good conductor of electric current.. In the wires, the current is a flow of negatively charged electrons Keywords- Electrons, electric charge, conductors, electric current, Referencehttps://www.savemyexams.co.uk/igcse/physics/edexcel/19/revisi on-notes/2-electricity/2-1-current-potential-difference-resistance/2-1-1-charge--current/ Where: • • • Q = charge measured in Coulombs (C) I = current measure in amps (A) t = time measured in seconds (s) Example When will 8 mA of current pass through an electrical circuit? A When 1 J of energy is used by 1 C of charge B When a charge of 4 C passes in 500 s C When a charge of 8 C passes in 100 s D When a charge of 1 C passes in 8 s ANSWER: B Current Step 1: Write out the equation relating current, In metal wires, the current is a flow of negatively charged charge and time Electric current is defined as the rate of flow charge electrons. This image shows the electrons flowing through a • In other words, the size of an electric current is the Q = It lattice of metal ions amount of charge passing through a component per • This can be rearranged to make second current I the subject of the equation: Current flows from the positive terminal to the negative terminal Calculating Electric Charge of a cell The charge, current and time are related by the Step 2: Rule out any obviously incorrect equation: options • Option A does not mention time, so can be ruled out Charge flows from the positive terminal to the negative terminal Step 3: Try the rest of the options by applying the equation to determine the correct answer • Consider option B: I = 4 / 500 = 8 × 10–3 = 8 mA • Consider option C: I = 8 / 100 = 80 × 10–3 = 80 mA • Consider option D: I = 1 / 8 = 125 × 10–3 = 125 mA • Therefore, the correct answer is B