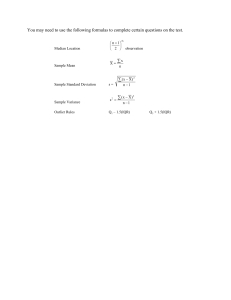
Symbols/Equations ❖ Sample mean ❖ Population mean ❖ Summation ❖ Sample Variance ❖ Population Variance ❖ S - Sample Standard Deviation ❖ ❖ Z-score ❖ Y-hat (predicted value) ❖ R (Correlation Coefficient) ❖ R^2 (Coefficient of Determination) ❖ Standard deviation of Residuals (Root Mean Square Deviation RMSD) ❖ Standard Error *Excel Functions for equations ● Mean ○ ⇒ Average() ● Standard Dev, ○ ⇒ =stdev() ● Median ○ ⇒ median() ● Interquartile Range ○ ● R - Correlation Coefficient ○ ● R^2 → Correlation of determination ○ *Logarithms Log(x) - no base ● Assumed to be Log Base 10 Unit 1 - exploring categorical data Marginal Distribution ● Marginal distributions are totals for each row OR column in a two-way table (or joint distribution table), showing the distribution of one variable Conditional Distribution ● Conditional distributions show the distribution of one variable GIVEN a condition on the other. They're usually in percentages. Classifying shapes of distributions Unit 3 - Summary Statistics Interquartile Range ● What is it : statistical measure used to find the range of the middle 50% of values in a dataset ● Why use it : Non-Parametric Data Analysis: For data that is not normally distributed or when the sample size is small, the IQR is a better measure of spread than the standard deviation, as it is not as influenced by extreme values. ● Equation : Interquartile Range (IQR) = Q3 - Q1 ○ How to find Q3 and Q1 : Q3 and Q1 are the medians of the values of each side of the median. Sample Variance ● What is it : Sample variance quantifies the dispersion or spread of data points in a sample around the mean. ● A high variance indicates that the data points are spread out over a wide range of values, ● A low variance suggests that the data points are clustered closely around the mean ● Sample Standard Deviation ● What is it : measures the dispersion of a dataset relative to its mean in the same unit as the original data ● Low S.D = low variance = minimum fluctuation in data values (could be good or bad depending on context) ● Excel() Mean, STD, IQR, Median ● Mean ⇒ Average() ● Standard Dev, ⇒ =stdev() ● Median ⇒ median() ● Interquartile Range ⇒ ○ Unit 4 -One-var quantitative data z - score ● What is it: The number of standard deviations from the mean for a specific data point ○ Z score is 0 if the value is equal to the mean ○ Z-score is positive if the value is > the mean ○ Z-score is negative if value < mean ○ Ex ) z score of -1.5 ⇒ the value is 1.5 S.D away from the mean to the left ● Why? : Tells you how usual / unusual a data value is in your dataset b/c it tells you how far away from the mean it is. Density Curve / Norm Distribution ● Area under the curve is basically length x width Empirical rule ● ● the 68–95–99.7 rule 68%, 95%, and 99.7% of the values lie within one, two, and three standard deviations of the mean, respectively. Using z - score Tables ● Why/ when to use one : when you have a data point that you want to compare against the normal distribution ● ● ● Steps 1 ⇒ Find the z score of that data point Step 2 ⇒ open the z-score table and find the value corresponding to z-score Step 3 ⇒ This value is the percentile of the normally distributed dataset. ○ In example above , Darnell is taller than 71.57% of all students. Find z-score for a percentile Unit 5 - Two-var quantitative data R - Correlation Coefficient ● What is it : statistical measure of the strength of a linear relationship between 2 variables ○ Value ranges from -1 to 1 ○ -1 = negative linear correlation ○ 0 = no linear correlation ○ 1 = positive linear correlation ● ○ ○ Formula is basically saying add up each x,y coord’s multiplied z-score. Nobody does this by hand, use software / excel Residuals & Least-Squares regression Residual ● ● What is it : the difference between actual - estimate Equation : Residual = y data point - (the linear regression equation) ○ Residual = actual - expected Least-Squares Regression ● Basically just choosing the best linear regression model Equation of Regression line R^2 (Also known as Coefficient of Determination) ● ● ● ● What is it : It shows how correlated one dependent variable is with one independent variable Range: a number between 0 and 1. ○ The closer the value is to 0, the less correlated the dependent value is. ○ The closer the value is to 1, the more correlated the value is. Watch out for : high correlation does not assure significance. ○ Correlation does not imply causation typea shit Example : ○ ○ 60.032% of the variation in study time can be explained by the regression on caffeine intake Standard deviation of Residuals (Root Mean Square Deviation RMSD ● What is it : the average difference between a set of observed and predicted values from the regression line. Unit 7: Probability Conditional Probability Atleast 1 condition https://www.khanacademy.org/math/ap-statistics/probability-ap/probability-multiplication-rule/a/pr obabilities-involving-at-least-one-success Unit 10: Confidence Intervals, Significance tests. Margin of error Standard Error ● What is it : The standard deviation of a SAMPLE distribution. ○ Measures the amount of discrepancy between a sample estimate and the true value in the population ○ Smaller S.E ⇒ better ○ S.E = 0 ⇒ estimated value is exactly the true value ○