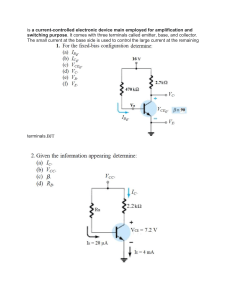
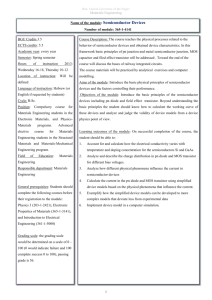
SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE FUNDAMENTALS Robert F. Pierret School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue University Addison Wesley Longman Reading, Massachusetts • Menlo Park, California • New York Don Mills, Ontario • Wokingham, England • Amsterdam • Bonn Sydney • Singapore • Tokyo • Madrid • San Juan • Milan • Paris CONTENTS General Introduction Part I Semiconductor Fundamentals Chapter 1 Semiconductors: A General Introduction 1.1 General Material Properties 1.1.1 Composition 1.1.2 Purity 1.1.3 Structure 1.2 Crystal Structure 1.2.1 The Unit Cell Concept 1.2.2 Simple 3-D Unit Cells 1.2.3 Semiconductor Lattices 1.2.4 Miller Indices 1.3 Crystal Growth 1.3.1 Obtaining Ultrapure Si 1.3.2 Single-Crystal Formation xxi 1 3 3 3 5 6 6 7 8 9 12 16 16 17 1.4 Summary 19 Problems 19 Chapter 2 Carrier Modeling 23 2.1 The Quantization Concept Y 2.2 Semiconductor Models 2.2.1 Bonding Model 2.2.2 Energy Band Model 2.2.3 Carriers ' 2.2.4 Band Gap and Material Classification Xj 2.3 Carrier Properties 2.3.1 Charge . 2.3.2 Effective Mass 2.3.3 Carrier Numbers in Intrinsic Material 23 25 26 26 29 ~ 31 32 32 32 34 ix SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE FUNDAMENTALS 2.3 A Manipulation of Carrier Numbers—Doping 2.3.5 Carrier-Related Terminology 2.4 State and Carrier Distributions 2.4.1 Density of States 2.4.2 The Fermi Function 2.4.3 Equilibrium Distribution of Carriers H 2.5 Equilibrium Carrier Concentrations 2.5.1 2.5.2 2.5.3 2.5.4 2.5.5 2.5.6 2.5.7 •+ Chapter 3 y 40 41 42 46 49 49 52 53 57 59 61 65 2.6 Summary and Concluding Comments 67 Problems 69 Carrier Action 75 V" 3.1 Drift 3.1.1 A 3.1.2 3.1.3 3.1.4 3.1.5 y- Formulas for n and p Alternative Expressions for n and p n( and the np Product Charge Neutrality Relationship Carrier Concentration Calculations Determination of EF Carrier Concentration Temperature Dependence 35 40 Definition-Visualization Drift Current Mobility Resistivity Band Bending 3.2 Diffusion 3.2.1 Definition-Visualization 3.2.2 Hot-Point Probe Measurement 3.2.3 Diffusion and Total Currents Diffusion Currents Total Currents 3.2.4 Relating Diffusion Coefficients/Mobilities Constancy of the Fermi Level Current Flow Under Equilibrium Conditions Einstein Relationship 3.3 ^Recombination-Generation 3.3.1 Definition-Visualization Band-to-Band Recombination 75 75 76 79 85 89 94 94 97 98 98 99 99 .. 99 101 101 105 105 105 CONTENTS R-G Center Recombination Auger Recombination Generation Processes 3.3.2 Momentum Considerations 3.3.3 R-G Statistics Photogeneration Indirect Thermal Recombination-Generation 3.3.4 Minority Carrier Lifetimes General Information A Lifetime Measurement 3.4 Equations of State 3.4.1 Continuity Equations 3.4.2 Minority Carrier Diffusion Equations 3.4.3 Simplifications and Solutions 3.4.4 Problem Solving Sample Problem No. 1 Sample Problem No. 2 120 121 122 124 124 124 128 3.5 Supplemental Concepts 3.5.1 Diffusion Lengths 131 131 3.5.2 Quasi-Fermi Levels .' 132 3.6 Summary and Concluding Comments 136 Problems 138 Chapter 4 Basics of Device Fabrication / / 105 107 107 107 110 110 112 116 116 116 149 4.1 Fabrication Processes 4.1.1 Oxidation 4.1.2 Diffusion 4.1.3 Ion Implantation 4.1.4 Lithography 4.1.5 Thin-Film Deposition Evaporation Sputtering Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) . 4.1.6 Epitaxy 149 149 152 155 159 162 162 162 164 164 4.2 Device Fabrication Examples 4.2.1 pn Junction Diode Fabrication 4.2.2 Computer CPU Process Flow 165 166 166 4.3 Summary 174 • Xi Xii SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE FUNDAMENTALS Rl Part I Supplement and Review 175 Alternative/Supplemental Reading List 175 Figure Sources/Cited References 177 Review List of Terms 178 Part I—Review Problem Sets and Answers 179 Part MA pn J u n c t i o n Diodes 193 Chapter 5 pn Junction Electrostatics 195 5.1 Preliminaries 195 5.1.1 5.1.2 5.1.3 5.1.4 5.1.5 Junction Terminology/Idealized Profiles Poisson's Equation Qualitative Solution The Built-in Potential (Vbi) The Depletion Approximation 195 197 198 203 206 5.2 Quantitative Electrostatic Relationships 5.2.1 Assumptions/Definitions 5.2.2 Step Junction with VA = 0 Solution for p Solution for % Solution for V Solution for xn and xp 5.2.3 Step Junction with VA * 0 5.2.4 Examination/Extrapolation of Results 5.2.5 Linearly Graded Junctions 209 209 210 210 210 212 213 215 219 223 5.3 Summary 226 Problems 227 Chapter 6 pn Junction Diode: I-V Characteristics 6.1 The Ideal Diode Equation 6.1.1 Qualitative Derivation 6.1.2 Quantitative Solution Strategy General Considerations Quasineutral Region Considerations Depletion Region Considerations Boundary Conditions 235 235 235 "241 241 242 243 244 CONTENTS "Game Plan" Summary 6.1.3 Derivation Proper 6.1.4 Examination of Results Ideal I-V The Saturation Current Carrier Currents Carrier Concentrations 246 247 249 249 250 254 255 6.2 Deviations from the Ideal 6.2.1 Ideal Theory Versus Experiment 6.2.2 Reverse-Bias Breakdown Avalanching Zener Process 6.2.3 The R-G Current 6.2.4 VA -» Vbi High-Current Phenomena Series Resistance High-Level Injection 260 260 263 264 268 270 277 278 279 6.3 Special Considerations 6.3.1 Charge Control Approach 6.3.2 Narrow-Base Diode Current Derivation Limiting Cases/Punch-Through 281 282 284 284 286 6.4 Summary and Concluding Comments 288 Problems 289 Chapter 7 pn Junction Diode: Small-Signal Admittance 301 7.1 Introduction 301 7.2 Reverse-Bias Junction Capacitance 7.2.1 General Information 7.2.2 C-V Relationships 7.2.3 Parameter Extraction/Profiling 7.2.4 Reverse-Bias Conductance 301 301 305 309 313 7.3 Forward-Bias Diffusion Admittance 7.3.1 General Information 7.3.2 Admittance Relationships 315 315 318 7.4 Summary 323 -—"Problems 324 Xiii XiV SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE FUNDAMENTALS Chapter 8 pn Junction Diode: Transient Response 8.1 Turn-Off Transient 8.1.1 Introduction 8.1.2 Qualitative Analysis 8.1.3 The Storage Delay Time Quantitative Analysis Measurement 8.1.4 General Information 327 327 329 333 333 334 338 8.2 Turn-On Transient 338 8.3 Summary 343 Problems 344 Chapter 9 Optoelectronic Diodes 347 9.1 Introduction 347 9.2 Photodiodes 9.2.1 pn Junction Photodiodes 9.2.2 p-i-n and Avalanche Photodiodes p-i-n Photodiodes Avalanche Photodiodes 349 349 352 352 355 9.3 Solar Cells 356 9.3.1 Solar Cell Basics 9.3.2 Efficiency Considerations 9.3.3 Solar Cell Technology 9.4 LEDs 9.4.1 General Overview 9.4.2 Commercial LEDs 9.4.3 LED Packaging and Photon Extraction Part IIB BJTs a n d Other J u n c t i o n Devices Chapter 10 BJT Fundamentals s' 327 356 357 360 361 361 362 366 369 371 10.1 Terminology 171 10.2 Fabrication 374 --10.3 Electrostatics 378 10.4 Introductory Operational Considerations 380 10.5 Performance Parameters Emitter Efficiency 382 382 CONTENTS Base Transport Factor Common Base d.c. Current Gain Common Emitter d.c. Current Gain 383 383 384 10.6 Summary 385 Problems 385 Chapter 11 BJT Static Characteristics 389 11.1 Ideal Transistor Analysis 11.1.1 Solution Strategy Basic Assumptions Notation Diffusion Equations/Boundary Conditions Computational Relationships 11.1.2 General Solution (W Arbitrary) Emitter/Collector Region Solutions Base Region Solution Performance Parameters/Terminal Currents 11.1.3 Simplified Relationships (W < LB) A/? B (x)intheBase Performance Parameters 11.1.4 Ebers-Moll Equations and Model 389^ 389 389 390 390 392 393 393 394 395 397 398 398 403 11.2 Deviations from the Ideal 407 11.2.1 11.2.2 11.2.3 11.2.4 Ideal Theory/Experiment Comparison Base Width Modulation Punch-Through Avalanche Multiplication and Breakdown Common Base Common Emitter Geometrical Effects Emitter Area ^ Collector Area Series Resistances Current Crowding Recombination-Generation Current Graded Base Figures of Merit 407 410 412 414 414 414 420 420 421 421 422 423 424 11.3 Modern BJT Structures 11.3.1 Poly silicon Emitter BJT 11.3.2 Heterojunction Bipolar Transistor (HBT) 426 426 429 11.2.5 11.2.6 -^11.2.7 11.2.8 XV XVi SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE FUNDAMENTALS 11.4 Summary 432 Problems 433 Chapter 12 BJT Dynamic Response Modeling 443 12.1 Small-Signal Equivalent Circuits 12.1.1 Generalized Two-Port Model 12.1.2 Hybrid-Pi Models 443 443 446 12.2 Transient (Switching) Response 12.2.1 Qualitative Observations 12.2.2 Charge Control Relationships 12.2.3 Quantitative Analysis Turn-on Transient Turn-off Transient 12.2.4 Practical Considerations 449 449 452 454 454 456 457 12.3 Summary 458 Problems 459 Chapter 13 PNPN Devices 463 13.1 Silicon Controlled Rectifier (SCR) 463 13.2 SCR Operational Theory 465 13.3 Practical Turn-on/Turn-off Considerations 13.3.1 Circuit Operation 13.3.2 Additional Triggering Mechanisms 13.3.3 Shorted-Cathode Configuration 13.3.4 di/dt and dv/dt Effects 13.3.5 Triggering Time 13.3.6 Switching Advantages/Disadvantages 470 470 471 471 472 473 473 13.4 Other PNPN Devices 474 Chapter 14 MS Contacts and Schottky Diodes 477 "fv. 14.1 Ideal MS Contacts -j 14.2 Schottky Diode 14.2.1 Electrostatics —_^ Built-in Voltage p, %, V Depletion Width 14.2.2 I-V Characteristics 14.2.3 a.c. Response 477 483 483 483 485 486 487 493 CONTENTS V 14.2.4 Transient Response 496 14.3 Practical Contact Considerations 14.3.1 Rectifying Contacts 497 497 14.3.2 Ohmic Contacts 498 14.4 Summary 500 Problems 501 R2 Part II Supplement and Review 505 Alternative/Supplemental Reading List 505 Figure Sources/Cited References 506 Review List of Terms 507 Part II—Review Problem Sets and Answers 508 Part III Field Effect Devices Chapter 15 Field Effect Introduction—The J-FET and MESFET 523 525 15.1 General Introduction 525 15.2 J-FET 15.2.1 15.2.2 15.2.3 15.2.4 530 530 531 536 547 Introduction Qualitative Theory of Operation Quantitative ID—VD Relationships a.c. Response 15.3 MESFET 15.3.1 General Information 15.3.2 Short-Channel Considerations Variable Mobility Model Saturated Velocity Model Two-Region Model 550 550 552 553 554 555 15.4 Summary 557 Problems 557 Chapter 16 MOS Fundamentals 563 X 16.1 Ideal Structure Definition 563 y 565 565 565 566 16.2 Electrostatics—Mostly Qualitative 16.2.1 Visualization Aids Energy Band Diagram Block Charge Diagrams XVii XVIII SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE FUNDAMENTALS 16.2.2 Effect of an Applied Bias General Observations Specific Biasing Regions \^ / 16.3 Electrostatics—Quantitative Formulation 16.3.1 Semiconductor Electrostatics Preparatory Considerations Delta-Depletion Solution 16.3.2 Gate Voltage Relationship \i 16.4 Capacitance-Voltage Characteristics 16.4.1 Theory and Analysis Qualitative Theory Delta-Depletion Analysis 16.4.2 Computations and Observations Exact Computations Practical Observations v- 571 571 571 576 580 584 584 584 590 591 591 595 16.5 Summary and Concluding Comments 599 Problems 600 Chapter 17 MOSFETs—The Essentials 7S 567 567 568 611 17.1 Qualitative Theory of Operation 611 17.2 Quantitative / D -V D Relationships 17.2.1 Preliminary Considerations Threshold Voltage Effective Mobility 17.2.2 Square-Law Theory 17.2.3 Bulk-Charge Theory 17.2.4 Charge-Sheet and Exact-Charge Theories 617 r7r3—a:c. Response 17.3.1 Small-Signal Equivalent Circuits 17.3.2 Cutoff Frequency 17.3.3 Small-Signal Characteristics 630 630 633 634 17.4 Summary Problems Chapter 18 Nonideal MOS 18.1 Metal-Semiconductor Workfunction Difference 617 617 618 620 625 628 -637 638 645 645 CONTENTS 18.2 Oxide Charges 18.2.1 18.2.2 18.2.3 18.2.4 18.2.5 General Information Mobile Ions The Fixed Charge Interfacial Traps Induced Charges Radiation Effects Negative-Bias Instability 18.2.6 A Vc Summary 18.3 MOSFET Threshold Considerations 18.3.1 18.3.2 18.3.3 18.3.4 18.3.5 VT Relationships Threshold, Terminology, and Technology Threshold Adjustment Back Biasing Threshold Summary Problems Chapter 19 Modern FET Structures \ \ \ \ 650 650 653 658 662 668 668 669 670 674 675 676 678 680 681 684 691 19.1 Small Dimension Effects 19.1.1 Introduction 19.1.2 Threshold Voltage Modification Short Channel Narrow Width 19.1.3 Parasitic BJT Action 19.1.4 Hot-Carrier Effects Oxide Charging Velocity Saturation Velocity Overshoot/Ballistic Transport 691 19.2 Select Structure Survey 702 702 702 703 704 704 705 707 19.2.1 MOSFET Structures LDD Transistors DMOS Buried-Channel MOSFET SiGe Devices SOI Structures 19.2.2 MODFET(HEMT) Problems 691 694 694 697 698 700 700 700 701 710 xix XX SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE FUNDAMENTALS R3 Part III Supplement and Review 713 Alternative/Supplemental Reading List 713 Figure Sources/Cited References 714 Review List of Terms 717 Part III—Review Problem Sets and Answers 718 Appendices 733 Appendix A Elements of Quantum Mechanics 733 A. 1 The Quantization Concept A. 1.1 Blackbody Radiation A. 1.2 The Bohr Atom A. 1.3 Wave-Particle Duality 733 733 735 737 A.2 Basic Formalism 739 A. 3 Electronic States in Atoms A.3.1 The Hydrogen Atom A.3.2 Multi-Electron Atoms 741 741 744 Appendix B MOS Semiconductor Electrostatics—Exact Solution 749 Definition of Parameters 749 Exact Solution 750 Appendix C MOS C-V Supplement 753 Appendix D MOS I-V Supplement 755 Appendix E List of Symbols 757 Appendix M 771 MATLAB Program Script Exercise 10.2 (BJT_Eband) Exercise 11.7 (BJT) and Exercise 11.10 (BJTplus) Exercise 16.5 (MOS^CV) 771 774 778 Index 781