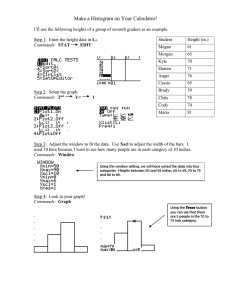
Command Line Interface (CLI): The Command Line Interface (CLI) is an alternative configuration tool to the web-based manager. While the configuration of the web-based manager uses a point-and-click method, the CLI requires typing commands or uploading batches of commands from a text file. Most features are available on both the GUI and CLI, but there are a few exceptions. Reports cannot be viewed on the CLI. On the other side advanced settings and diagnostic commands for super users are usually not available on the GUI. Default Setting: Port1, the management interface, has a default IP address and netmask: 192.168.1.99/24. The default credentials are user name admin and a blank password. PING, HTTP, HTTPS, and SSH protocols are enabled for management access. The initial configuration of FortiManager is very similar to FortiGate. In order to configure FortiManager for your network, you must set the IP address and netmask, select supported administrative access protocols, and specify a default gateway for routing packets. Port1, the management interface, if your management subnet uses a different subnet, change these settings. Commands: When entering a command, the Command Line Interface (CLI) requires that you use valid syntax and conform to expected input constraints. It will reject invalid commands. 1 | P a g e Created by Ahmad Ali E-Mail: ahmadalimsc@gmail.com , Mobile: 00966564303717 Commands for Tables clone <table> Clone (or make a copy of) a table from the current object. Clone may not be available for all tables. delete <table> Remove a table from the current object. Delete is only available within objects containing tables. edit <table> Create or edit a table in the current object. Edit is an interactive subcommand: further sub-commands are available from within edit. Edit changes the prompt to reflect the table you are currently editing. Edit is only available within objects containing tables. end Save the changes to the current object and exit the config command. This returns you to the top-level command prompt. get List the configuration of the current object or table. purge Remove all tables in the current object. rename Rename a table. Rename is only available within objects containing tables. show Display changes to the default configuration. Changes are listed in the form of configuration commands. Commands for Fields abort Exit both the edit and/or config commands without saving the fields. append Add an option to an existing list. end Save the changes made to the current table or object fields and exit the config command. (To exit without saving, use abort instead.) get List the configuration of the current object or table. move Move an object within a list, when list order is important. next Save the changes you have made in the current table’s fields and exit the edit command to the object prompt. select Clear all options except for those specified. set <field> Set a field’s value. <value> show Display changes to the default configuration. Changes are listed in the form of configuration commands. unselect Remove an option from an existing list. unset <field> Reset the table or object’s fields to default values. 2 | P a g e Created by Ahmad Ali E-Mail: ahmadalimsc@gmail.com , Mobile: 00966564303717 CLI Command Branches: Config: The config commands configure objects of FortiManager functionality. Top-level objects are not configurable; they are containers for more specific lower level objects. Get: Use get to display settings. You can use get within a config shell to display the settings for that shell, or you can use get with a full path to display the settings for the specified shell. Show: Use show to display the FortiManager unit configuration. Only changes to the default configuration are displayed. You can use show within a config shell to display the configuration of that shell, or you can use show with a full path to display the configuration of the specified shell. Execute: Use execute to run static commands, to reset the FortiManager unit to factory defaults, or to back up or restore the FortiManager configuration. The execute commands are available only from the root prompt. Diagnose: Commands in the diagnose branch are used for debugging the operation of the FortiManager unit and to set parameters for displaying different levels of diagnostic information. Shortcuts Key: Action List valid word completions or subsequent words. If multiple words could complete your entry, display all possible completions with helpful descriptions of each. Complete the word with the next available match. Press the key multiple times to cycle through available matches. Recall the previous command. Limited to the current session. Recall the next command. Move the cursor left or right within the command line. Move the cursor to the beginning of the command line. Move the cursor to the end of the command line. Move the cursor backwards one word. Move the cursor forwards one word. Delete the current character. Abort current interactive commands, such as when entering multiple lines. If you are not currently within an interactive command such as config or edit, this closes the CLI connection. Keys ? Tab Up arrow, or Ctrl + P Down arrow, or Ctrl + N Left or Right arrow Ctrl + A Ctrl + E Ctrl + B Ctrl + F Ctrl + D Ctrl + C 3 | P a g e Created by Ahmad Ali E-Mail: ahmadalimsc@gmail.com , Mobile: 00966564303717 TAB Key & Question Mark: In addition to TAB to complete commands, you can use the? mark to see available commands. Using after an edit such as in "config sys int" or "config firewall rule" will list the names of existing interfaces, rules, objects, etc. It's a great way to see what is configured or possible to configure. Get Command: When editing a specific object (interface, vpn tunnel, rule) you can use the get command. Show only displays the configured object, which is typically what you'll use. Get displays all settings though, including default values. It's another great command to see what is configurable and find default values you might not realize. 4 | P a g e Created by Ahmad Ali E-Mail: ahmadalimsc@gmail.com , Mobile: 00966564303717 Diagnose & Debug CLI Option: What I typically recommend is to watch the CLI commands that are being used when you are using the FortiGate WebGUI. You can do this by doing open up putty (SSH) use the following commands: Turn On Debug Session HQ-FW # diagnose debug cli 8 HQ-FW # diagnose debug enable Turn Off Debug Session HQ-FW # diagnose debug reset HQ-FW # diagnose debug disable Fortinet CLI Reference: https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortimanager/7.2.0/cli-reference/23811/introduction 5 | P a g e Created by Ahmad Ali E-Mail: ahmadalimsc@gmail.com , Mobile: 00966564303717 # get system status # show system interface # show system dns 6 | P a g e Created by Ahmad Ali E-Mail: ahmadalimsc@gmail.com , Mobile: 00966564303717 # show system ntp # get system ntp # show system route # execute ping 7 | P a g e Created by Ahmad Ali E-Mail: ahmadalimsc@gmail.com , Mobile: 00966564303717