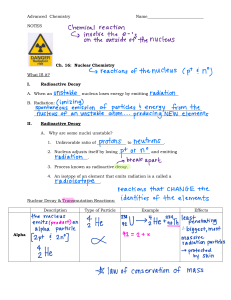
Radioactivity 1. The diagram shows emissions from a source passing into the electric field between two charged plates. What is emitted by this source? A neutrons and γ-rays only B α-particles and β-particles only C α-particles and γ-rays only D β-particles and γ-rays only 2. Which row in the table describes the process of nuclear fusion and identifies the change in total mass of the particles involved? 3. A scientist was asked to separate the following equations into two categories: nuclear fission and nuclear fusion. Which equations show nuclear fission? A 1 and 2 B 1 and 3 C 1 and 4 D 2 and 4 1 © 2023 NS GR10 PHYSICS 4. How do the sizes of the two nuclei produced in a nuclear fission reaction compare to the size of the original nucleus? A both larger than the original nucleus B one larger and one smaller than the original nucleus C both smaller than the original nucleus D one smaller and one the same size as the original nucleus 5. Which statement about the radioactive decay of a substance is correct? A It cannot be predicted when a particular nucleus will decay. B Placing a radioactive substance inside a lead-lined box prevents it from decaying. C The decay always produces poisonous gases. D The rate of decay increases if the substance is dissolved in water. 6. Carbon-14 has a proton number (Z) of 6 and a nucleon number (A) of 14. Nitrogen-14 has a proton number of 7 and a nucleon number of 14. Carbon-14 emits β-particles to form nitrogen-14. Which nuclide equation describes this process? 7. 8. Some radioactive nuclei decay to give new nuclei which are also radioactive. Part of a series of decays is shown. How many decays involve the emission of a A1 B2 C3 -particle? D5 2 © 2023 NS GR10 PHYSICS 9. The graph shows the activity of a radioactive source over a period of time. What is the half-life of the source? A 1.0 minute B 2.0 minutes C 2.5 minutes D 4.0 minutes 10. A scientist uses a counter to measure the radioactivity of a sample of nitrogen-13. The counter and sample of nitrogen-13 are on a table in a laboratory. The reading on the counter is recorded for a period of 80 min and a graph is drawn using the measurements. What is the best estimate for the half-life of the sample of nitrogen-13? A 10 min B 12 min C 14 min D 40 min 3 © 2023 NS GR10 PHYSICS 11. A radioactive source has a half-life of 0.5 hours. A detector near the source shows a reading of 6000 counts per second. Background radiation can be ignored. What is the reading on the detector 1.5 hours later? A 750 counts per second B 1500 counts per second C 2000 counts per second D 3000 counts per second 12. A radioactive material has a half-life of 20 days. A sample of the material contains 8.0 × 1010 atoms. How many atomic nuclei have decayed after 60 days? A 1.0 × 1010 B 4.0 × 1010 C 6.0 × 1010 D 7.0 × 1010 13. A thin sheet of paper is placed between a radioactive source and a radiation detector. The count rate falls to a very low reading. From this result, which type of radiation is the source emitting? A α-particles B β-particles C γ-rays D X-rays 14. Uranium-235 can undergo nuclear fission in many ways. Which equation correctly shows a possible fission reaction for uranium-235? 4 © 2023 NS GR10 PHYSICS 15. The diagram shows a piece of apparatus used to determine the nature of the emissions from a radioactive source. The absorbers can be raised out of or lowered into the path of the radiation from the source to the detector. The apparatus is evacuated. The table gives a set of results for a particular radioactive source. Which types of radiation are being emitted by the radioactive source? A α-particles and β-particles B α-particles only C β-particles and γ-rays D β-particles only 5 © 2023 NS GR10 PHYSICS 1 (a) (i) An americium (Am) nucleus decays by the emission of an α-particle into a neptunium (Np) nucleus. Complete the nuclear equation for this decay. 241 Am 95 (ii) → [2] Americium is used in smoke detectors. Explain why beta (β) emitters or gamma (γ) emitters are not used in smoke detectors. ........................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... [1] (b) The half-life of this americium nuclide is 470 years. A sample of this nuclide contains 8.0 × 1014 atoms. After some time, 6.0 × 1014 americium atoms have decayed. Calculate the time required for this decay. time = .......................................................... [3] [Total: 6] (c) A radioactive isotope has a half-life of 6.0 years. A sample of this isotope has a mass of 12 mg. Calculate the mass of this isotope that remains in the sample after 18 years. mass remaining = .................................................... mg [3] 6 © 2023 NS GR10 PHYSICS 2 Two of the isotopes of hydrogen are hydrogen-2 ( 12H ) and hydrogen-3 ( 13H ). (a) (i) State one similarity in the composition of their nuclei. ..................................................................................................................................... [1] (ii) Describe how a nucleus of hydrogen-3 differs from a nucleus of hydrogen-2. ........................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... [2] (b) In a nuclear fusion reactor, a nucleus of hydrogen-2 fuses with a nucleus of hydrogen-3 at an extremely high temperature. This fusion reaction produces an isotope of element X and releases a neutron. (i) Explain why an extremely high temperature is needed when forcing these two nuclei together. ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... [3] (ii) Using nuclide notation, complete the equation for this reaction. 2 1H + 3 1H [2] [Total: 8] 7 © 2023 NS GR10 PHYSICS 3 (a) A student investigates a radioactive substance in a laboratory. Fig. 3.1 is a graph showing the count rate detected as the substance decays for 7.5 minutes. count rate counts / min 250 200 150 100 50 0 0 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0 7.0 8.0 time / min Fig. 3.1 The background radiation is 20 counts / min. (i) Determine the half-life of the substance. half-life = ......................................................... [3] (ii) Calculate the count rate detected at time = 9.6 minutes. count rate = .......................................counts / min [2] (b) The substance emits α-particles and γ-rays. The student suggests that it is safe to store the substance in a plastic container of thickness 2 mm. State and explain whether the student’s suggestion is correct. statement .................................................................................................................................. explanation ............................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................. [3] [Total: 8] 8 © 2023 NS GR10 PHYSICS 4 (a) A radioactive nucleus of uranium-235 decays to a nucleus of thorium and emits an α-particle. Complete the equation. 235 92 U ....... ....... Th + 4 2α [2] (b) A nucleus of uranium-235 undergoes nuclear fission in a reactor. (i) State what is meant by nuclear fission. ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................................[1] (ii) Suggest why a nuclear reactor is surrounded by thick concrete walls. ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................................[2] (iii) State one environmental advantage and one environmental disadvantage of using a fission reactor to generate electrical energy in a power station. advantage ......................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... disadvantage ..................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... [2] (c) The thorium produced by the decay in (a) is also radioactive and has a half-life of 26 hours. At a certain time, a pure sample of this isotope initially contains 4.8 × 109 atoms. Calculate the number of atoms of this sample that decay in the following 52 hours. number = ...........................................................[3] [Total: 10] 9 © 2023 NS GR10 PHYSICS 5 (a) The magnitude of the charge on a β (beta)-particle is 1.6 × 10–19 C. (i) State the proton number and nucleon number of an α (alpha)-particle. proton number ................................................................................................................... nucleon number ................................................................................................................ [2] (ii) Determine the magnitude of the charge of an α (alpha)-particle. charge ............................................................................................................................... [1] (b) A nucleus of radium-230 consists of 88 protons and 142 neutrons. Radium-230 is radioactive and decays by β (beta)-emission to an isotope of actinium. The symbol for radium is Ra and the symbol for actinium is Ac. Write down the nuclide equation for this decay. [3] (c) The half-life of radium-230 is 93 min. A sample contains 9.6 × 10–12 g of radium-230. Calculate the mass of radium in the sample after 279 min. mass = ......................................................... [2] [Total: 8] 10 © 2023 NS GR10 PHYSICS