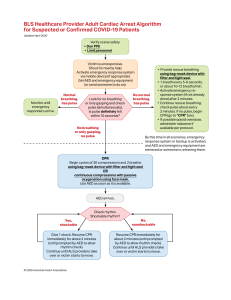
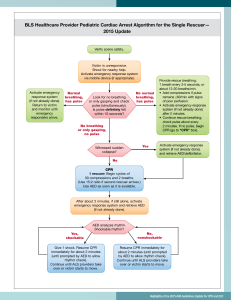
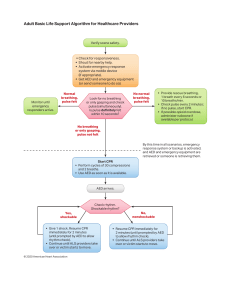
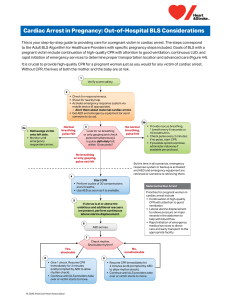
BLS Healthcare Provider Pediatric Cardiac Arrest Algorithm for the Single Rescuer for Suspected or Confirmed COVID-19 Patients Updated April 2020 Verify scene safety • Don PPE • Limit personnel Victim is unresponsive. Shout for nearby help. Activate emergency response system via mobile device (if appropriate). Activate emergency response system (if not already done). Return to victim and monitor until emergency responders arrive. Normal breathing, has pulse Look for no breathing or only gasping and check pulse (simultaneously). Is pulse definitely felt within 10 seconds? No normal breathing, has pulse No breathing or only gasping, no pulse Witnessed sudden collapse? Yes • Provide rescue breathing using bag-mask device with filter and tight seal. • 1 breath every 3-5 seconds, or about 12-20 breaths/min. • Add compressions if pulse remains ≤60/min with signs of poor perfusion. • Activate emergency response system (if not already done) after 2 minutes. • Continue rescue breathing; check pulse about every 2 minutes. If no pulse, begin CPR (go to “CPR” box). Activate emergency response system (if not already done), and retrieve AED/defibrillator. No CPR 1 rescuer: Begin cycles of 30 compressions and 2 breaths using bag-mask device with filter and tight seal. (Use 15:2 ratio if second rescuer arrives.) Use AED as soon as it is available. After about 2 minutes, if still alone, activate emergency response system and retrieve AED (if not already done). Yes, shockable AED analyzes rhythm. Shockable rhythm? Give 1 shock. Resume CPR immediately for about 2 minutes (until prompted by AED to allow rhythm check). Continue until ALS providers take over or victim starts to move. © 2020 American Heart Association No, nonshockable Resume CPR immediately for about 2 minutes (until prompted by AED to allow rhythm check). Continue until ALS providers take over or victim starts to move. BLS Healthcare Provider Adult Cardiac Arrest Algorithm for Suspected or Confirmed COVID-19 Patients Updated April 2020 Verify scene safety • Don PPE • Limit personnel Victim is unresponsive. Shout for nearby help. Activate emergency response system via mobile device (if appropriate). Get AED and emergency equipment (or send someone to do so). Monitor until emergency responders arrive. Normal breathing, has pulse Look for no breathing or only gasping and check pulse (simultaneously). Is pulse definitely felt within 10 seconds? No normal breathing, has pulse No breathing or only gasping, no pulse • Provide rescue breathing using bag-mask device with filter and tight seal. • 1 breath every 5-6 seconds, or about 10-12 breaths/min. • Activate emergency response system (if not already done) after 2 minutes. • Continue rescue breathing; check pulse about every 2 minutes. If no pulse, begin CPR (go to “CPR” box). • If possible opioid overdose, administer naloxone if available per protocol. By this time in all scenarios, emergency response system or backup is activated, and AED and emergency equipment are retrieved or someone is retrieving them. CPR Begin cycles of 30 compressions and 2 breaths using bag-mask device with filter and tight seal OR continuous compressions with passive oxygenation using face mask. Use AED as soon as it is available. AED arrives. Yes, shockable Check rhythm. Shockable rhythm? Give 1 shock. Resume CPR immediately for about 2 minutes (until prompted by AED to allow rhythm check). Continue until ALS providers take over or victim starts to move. © 2020 American Heart Association No, nonshockable Resume CPR immediately for about 2 minutes (until prompted by AED to allow rhythm check). Continue until ALS providers take over or victim starts to move.