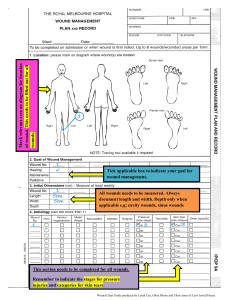
FIRST AID AND MATERIALS OBJECTIVES: At the end of this lesson, student should be able to: a) b) c) d) e) Define first aid and first aid box State reasons for administering First Aid List materials required for administering first aid Identify medicinal materials and non-medical materials and their uses in first aid administration Explain steps to take when administering first aid to an accident victim Definition: First aid treatment can be defined as the immediate and temporary care given to an accident victim or sick person before taking the victim to the hospital. REASONS FOR FIRST AID i. ii. iii. iv. v. First aid is administered to reduce pain. Arrests bleeding. First aid prevents injuries from getting worse. To save lives First aid can be a source of information to the doctor. FIRST AID NON-MEDICINAL MATERIALS The materials used in administering first aid are as follows: (i). Bandages: This material is used to wrap wounds and protect wounds from infection. (ii). Forceps: This material is used for holding cotton wool when dressing wounds. (iii). Cotton Wool: Cotton wool is used in dressing wounds and cuts. (iv). Plasters: The plaster is used to cover wounds and cuts directly, while holding the cotton wool in place. (v). Safety Pins: These are pins used to fasten the bandage in place on wounds. (vi). Razor Blade: In first aid administration, the razor blade is used for cutting plaster and bandages where there are no scissors. (vii). Sterile Gauze: It is used for sterilizing wounds so as to avoid germs and infections (viii). Record Book and Pen: With this, the name, sex, age, class of the student, the nature of injury and the type of treatment given can be recorded. (ix). Disposable Hand Gloves: This material can protect against direct contact with blood and dirt. FIRST AID MEDICINAL MATERIALS (i). Analgesics: These are pain relievers like paracetamol, Panadol, aspirin and any other pain reliever or pain killers. (ii). Antiseptics: These are cleansers like Dettol, TCP, Izal, etc. They are used against germs. (iii). Gentian violet(GV): This is a chemical substance used on burns as a coolant. It is in the form of blue ink. (iv). Iodine: Iodine is used to stop blood flow or bleeding in minor wounds. (v). Methylated spirit: The methylated spirit is used to disinfect wounds and skin before administering injections. (vi). Smelling salt: The name does not indicate that this substance has an offensive odour. It is a substance used for reviving fainting victims. (vii). Hydrogen peroxide: It is sometimes used in the place of the methylated spirit, to disinfect wounds. (viii). Embrocation: Embrocation is used as balm on sprains. STEPS IN ADMINISTERING FIRST AID (i). Check the injury and the extent of damage (is the injury a burn, cut, fracture, electric shock, loss of breath or fainting?). (ii). No matter the gravity of the injury, be cool and calm. (iii). Immobilize the injured part. i.e. hold the affected part firmly so as to avoid movement by that part. (iv). Prevent the victim from seeing his blood. (v). Give the victim the urgent needed help. (vi). Never give fluid (any fluid). (vii). Carry out the first aid treatment with utmost care. (viii). Do not allow too many people around as fresh air is very essential. (ix). Arrange for medical personnel. ABC IN FIRST AID i. A = Airways: Make sure the patient’s airways are clear, that the patient is breathing. Check if the breathing is normal. ii. B = Breathing: Ensure that the patient is breathing. If the person is conscious, sitting will be better else put the person in a recovery position. iii. C = Circulation: Check for pulse to know if the heart is circulating blood. If an adult is unconscious and not breathing, commence cardiopulmonary resuscitation(CPR). STEPS INVOLVED IN RESCUE OPERATIONS 1. Work with time: try to assess the victim as quickly as possible, if they are unconscious and immobile, then administer ABC of first aid. 2. Secure the victim: use signage to prevent more injuries from affecting victims in road accidents. In a scenario where no signage can be found in an accident scene, we use grasses or tree branches to slow down incoming vehicle 3. Transfer(Evacuate) the victim: Immediately, the rescue team should start making contacts on how to transfer the accident victims to the hospital especially when they are unconscious or badly injured. KEYWORDS 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Resuscitate Recuperate Rescue Revive Recovery Emergency Refer to your google classroom for your worksheet on this topic