Clinical Parasitology Lab Manual: Nematoda
advertisement

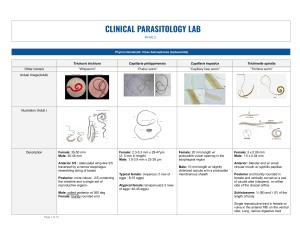
CLINICAL PARASITOLOGY LAB FINALS Phylum Nematoda: Class Adenophorea (Aphasmidia) Other name/s Trichuris trichiura Capillaria philippinensis Capillaria hepatica Trichinella spiralis “Whipworm” “Pudoc worm” “Capillary liver worm” “Trichina worm” Actual Image(Adult) Illustration (Adult ) Description Female: 35-50 mm Male: 30-45 mm Female: 2.3-5.3 mm x 29-47μm (2- 5 mm in length) Male: 1.5-3.9 mm x 23-28 μm Anterior 3/5 : attenuated whip-like 3/5 traversed by a narrow esophagus resembling string of beads Posterior: more robust , 2/5 containing the intestine and a single set of reproductive organsMale: coiled posterior at 360 deg Female: bluntly rounded end Typical female: oviparous (1 row of eggs : 8-10 eggs) Atypical female: larviparous(2-3 rows of eggs: 40-45 eggs) Female: 20 mm length w/ protrusible vulvar opening in the esophageal region Male: 10 mm length w/ slightly chitinized spicule w/in a protrusible membranous sheath Female: 3 x 0.06 mm Male: 1.5 x 0.04 mm Anterior: Slender end w/ small, circular mouth w/ syphilis papillae Posterior end bluntly rounded in female and ventrally curved w/ a pair of caudal alae (claspers), on either side of the cloacal orifice Schistosome: ½ (M) and ⅕ (F) of the length of body Single reproductive tract in female w/ vulva in the anterior fifth on the ventral side; Long, narrow digestive tract Page 1 of 13 Clinical Parasitology Lab_ ANGELES, Q.A -2-2-0 Actual Image (Egg/Ova/Larva) Illustration (Egg/Ova/Larva) Larva Description (Egg/Ova/Larva) Size: 50 x 22 μ “Lemon-shaped”/ “Barrel-shaped”/ “Japanese lantern” ; with hyaline plugs / plug-like translucent polar prominence; yellowish outer shell and translucent inner shell. Distinct Feature (Egg/Ova/Larva) - Japanese lantern Very prominent bipolar plugs Size: 20 x 40 μ “Peanut- shaped” w/ flattened bipolar plugs; moderately thick-shelled; has striations; shows straw color. - Peanut-shaped Striations Size: 50-65 μm x 30-35 μm “Lemon-shaped” outer shells are pitted like a golf ball w/ minute pores - Not striated Bipolar plugs are more prominent Larva : Size: 90-100 x 6.0 µm - Seen in muscles Life Cycle Lab DIagnosis Demonstration of parasite 1. DFS 2. Concentration techniques 3. KTS 4. Kato Katz - utilizes premeasured volume of sample (quantitative) Demonstration of parasite 1. DFS 2. Concentration techniques 3. KTS Demonstration of parasites 1. liver biopsy 1. Demonstration of parasites a. muscle biopsy (encysted larvae) (diagnostic stage: larva) b. xenodiagnosis (using albino rats fed w/ infected muscles obtained from patient w/ infection 2. Bachman intradermal test (a skin test; Ag is prepared from the larva) (+) blanched wheal 5mm or > diameter surrounded by an area of erythema 3. serological test: a. bentonite flocculation b. latex agglutination other laboratory findings: Increased CPK and LDH Increased myokinase Page 2 of 13 Clinical Parasitology Lab_ ANGELES, Q.A -0-22--0--06 LECTURE NOTES: Parasite Infective stage Trichinella spiralis Trichina worm *smallest nematode infecting man Encysted larva Trichuris trichiura MOT Host Ingestion of undercooked Vertebrate pork *domestic cycle *sylvatic cycle Ingestion of ova (STH) Primarily human Habitat Ingestion of ova Embryonated ova Capillaria philippinensis Larvae Dioctophyme/ Dioctophyma renale L3 larvae *giant kidney worm largest nematode infecting man Page 3 of 13 Zoonotic (low host specificity) Primarily rodent & carnivore *true & spurious infection Diagnostic tool/ feature Small intestine Trichinosis Trichinelliasis Trichiniasis *myocarditis, encephalitis Large intestine; cecum and ascending colon Trichuriasis Trichocephaliasis Iron deficiency anemia Appendicitis Rectal prolapse Stichocytes in adult Male: coiled ventrally at 360 deg “Japanese lantern ova” Liver parenchyma Hepatic capillariasis (liver cirrhosis)- rare Adult resembles T. trichiura “Lemon-shaped ova” Mystery disease Internal capillariasis Malabsorption syndrome (CHON losing enteropathy) -borborygmi Adult resembles T. trichiura Larviparous (autoinfection) “Peanut-shaped ova” Dioctophymiasis (hematuria, abdominal, pain, fever, and eosinophilia) Egg in urine, sometime adult Embryonated egg Capillaria hepatica Disease Ingestion of uncooked fish with infective larvae “internal autoinfection” IH: glassfish “bagsit”, “bagsang”, “ipon”, DH: Primarily humans Small intestine mucosa Ingestion of undercooked paratenic host with L3 larvae IH: aquatic oligochaete worms (blackworms) DH: mustelids, canids, otters, martens, racoons, *rare in human Paratenic: freshwater fish and amphibian Kidney *larva migrate in the subcutaneous nodules Muscle biopsy: larva (tigtly coiled & enclosed w/in fibrous capsule Beckman Intradermal test (hypersensitivity test) Beck’s Xenodiagnosis ELISA (reco) Western blot & LA (conform ELISA) Clinical Parasitology Lab_ ANGELES, Q.A foodie Phylum Nematoda: Class Secernentea (Phasmidia) Other name/s Ascaris lumbricoides Enterobius vermicularis Strongyloides stercoralis Toxocara canis Toxocara cati “Giant intestinal roundworm” “Pinworm” / “Seatworm” Old name: Oxyuris vermicularis “Threadworm” “Dog ascaria”’ / “dog roundworm” “Cat ascaria” / “cat roundworm” Actual Image(Adult) Illustration Rhabditiform and Filariform larva Description Female: 200-350 x 4-6 mm Male: 150-200 x 2-4 mm Female : 8-13 x 0.3- 0.5 mm Male: 2-5 x 0.1 mm Smooth cuticle, unstriated , nonsegmented. - Trilobite lips Distinctive feature: - Cephalic alae - Esophageal bulb Female: 2.5 mm x -.05 mm Male: not seen in human infections Similar to Ascaris lumbricoides in appearance but only a quarter to half its size. Toxocara : body is bent ventrally Female: thin, colorless. Semitransparent, finely striated cuticle, slender tapering anterior and short conical pointed tail. Cylindrical esophagus: occupies ⅓ of the body and the intestines in the posterior. W/ paired uteri, vagina, vulva. Actual Image (Egg/Ova/Larva) Immature egg Page 4 of 13 mature egg containing larva Clinical Parasitology Lab_ ANGELES, Q.A f f f Illustration (Egg/Ova/Larva) Description (Egg/Ova/Larva) Fertilized: Corticated-Thick Shelled 60x 45 μm Broadly ovoid; golden brown in color; unembryonated at oviposition. Thick-shelled Inner: non-permeable , lipoidal vitelline membrane Middle: thick, transparent, glycogen membrane Outer: coarsely mammilated, albuminous layer Size: 50-60 x20-30 μm - Thick-walled ; colorless shell; - shell flattened on one side - coiled larva developing in egg - “D”-shaped - embryonated Unfertilized: Decorticated Thinner shell 88-94 x 39-44 μm Longer and narrower than fertilized egg; completely filled with disorganized, highly refractile granules Thinner shell and irregular mammilated, albuminous layer Egg: Size: 50-60 µm x 30-35 µm segmented in 2-4 cell stage at oviposition Rhabditiform larva (L1): Size: 250µm (with rhabditiform-type esophagus), has a short buccal canal about 4 µm in length that appears as long as wide. A conspicuous genital primordium measuring about 22 µm can be seen about two-thirds of the way back from the anterior end. Size: 85 x75 μ Superficially pitted Resemble those of Ascaris, but are larger, less elongate and have thinner shell and albuminoid outer covering Size: 65-70 μ in diameter Resemble those of Ascaris, but are larger, less elongate and have thinner shell and albuminoid outer covering Filariform larva (L3): Size: 600 µm The esophagus of uniform length is long, about one-half the length of the body. The posterior is characterized by a notched or bifurcated tail. Life Cycle IS: Embryonated ova Lab Diagnosis Demonstration of parasite 1. DFS 2. Concentration techniques 3. KTS 4. Kato Katz 5. Sputum sample : larvae x-ray examination ( bolus) Page 5 of 13 Demonstration of parasite: 1. perianal swab : Graham’s scotch tape method (adult female) 2. beneath the nail bed swabs DFS Morphologic larva - Short buccal cavity (as long as wide) - Genital primordium (cluster stage) : described as conspicuous, large/long -Isolated by SCT -Coproculture technique -- Baermann Technique: a culture technique, w/c uses a funnel apparatus/method - A fresh stool is placed in a wire mesh, then wrapped w/ cloth (several layer of the gauze / cloth) -Placed in a container w/ water w/ the funnel, the rhabditiform will pass through the wire gauze -Enterotest -Sputum/ Urine - eosinophilia - concentration techniques - serology: 1. Ab detection – ELISA on serum Clinical Parasitology Lab_ ANGELES, Q.A fighters LECTURE NOTES: Parasite Infective stage MOT Host Habitat Ascaris lumbricoides Embryonated ova Ingestion of embryonated ova Primarily human Monkeys/ apes *dog: spurious Small intestine Giant/ large intestinal roundworm *largest nematode parasite in the intestine Disease Diagnostic tool/ feature *wandering Adult mouth: 3 finely Larva: lungs- ascaris denticulated lips (hence, the Pneumonia (Loefller’s triangular part) syndrome) *migrating adult: occlusion Adult male posterior end: of biliary tract, appendicitis curved ventrally to form a nasopharyngeal expulsion hook with 2 copulatory spicules *A suum: swine Ova: unfertilized, fertilized, decorticated Enterobius vermicularis Embryonated ova Oxyuris vermicularis, Pinworm, seatworm, threadworm Ingestion of embryonated ova Inhalation or swallowing or embryonated ova in dust *retroinfection Only human: high host specificity *occasional infection in captive Large intestine *larvae are often found in the appendix but role in appendicitis controversial Enterobiasis *Perianal pruritus *vulvovaginitis *pelvic or peritoneal granulomas Chimpanzee *school age *crowding Adule: 3 cephalic ale Esophagus with double bulb structure D-shaped ova Scotch tape method Parasite Infective stage MOT Host Habitat Disease Diagnostic tool/ feature Necator americanus Filiform larvae Skin penetration Human Small intestine (jejunum) Ground itch Ovoidal, thin shelled, colorless, 2-8 cell stage ova *transpulmonary migration phase Ancylostoma duodenale Filiform larvae Skin penetration Oral and transmammary route Human Small intestine (jejunum Ground itch or coolie itch Pneumonitis Iron deficiency Anemia (microcytic, hypochromic) Ovoidal, thin-shelled, colorless, 2-8 cell-stage ova Zoonotic; canids and felids Small intestine (jejunum Cutaneous larva Migrans / creeping eruption Ovoidal, thin-shelled, colorless, 2-8 cell-stage ova Zoonotic; dogs, wolves, coyotes, and foxes Small intestine (jejunum Cutaneous larva Migrans / creeping eruption Ovoidal, thin-shelled, colorless, 2-8 cell-stage ova Primarily Human Small intestine (jejunum Strongyloidiasis Larva currens: ‘racing larva’ Bronchopneumonia Chronic bronchitis Ovoidal, thin-shelled, colorless, 2-4 cell-stage ova Larva in sputum 3 small lips partenogenic *hypobiosis in the intestine or muscle Ancylostoma braziliense Filiform larvae Skin penetration Ancylostoma caninum Filiform larvae Skin penetration Oral ingestion Strongyloides stercoralis Filiform larvae Page 6 of 13 Skin penetration Clinical Parasitology Lab_ ANGELES, Q.A _fh②t② LECTURE NOTES Parasite Infective stage MOT Host Habitat Disease Diagnostic tool/ feature Toxocara canis -Dog ascarid Embryonated ova with L3 larvae Ingestion of infective eggs, larva, penetration Transplacental and transmammary Dog Small intestine Visceral toxocariasis: Visceral larva migrans (VLM) Distinct cephalic alae Longer than broad (bow-like) Prominent lips Accidental: human Ocular toxocariasis: ocular larva migrans (OLM) → irreversible blindness Toxocara cati -ascarid Embryonated ova with L3 larvae Ingestion of infective eggs Larva , penetration transmammary Cat Small intestine Accidental: human Visceral toxocariasis: Visceral larva migrans (VLM) Distinct cephalic alae Broader than thin (arrow head) Prominent lips Ocular toxocariasis: ocular larva migrans (OLM) → irreversible blindness Gnathostoma spinigerum -rust colored Larvae Eating undercooked fish or poultry - larvae 1st IH: copepods 2nd: IH: aquatic animals that feed on copepod (fish, amphibians) Paratenic: snake, duck DH: Carnivorous mammal Gastric wall Cutaneous gnathostomiasis Prominent cephalic bulb and body spines Visceral gnathostomiasis/ larva migrans profundus (pulmonary, GIT, genitourinary, auricular, ocular tissues, or CNS) Accidental: human Neuro-gnathostomiasis Page 7 of 13 Clinical Parasitology Lab_ ANGELES, Q.A -0ft Phylum Nematoda: Class Secernentea (Phasmidia) —Hookworm species Other name/s Necator americanus Ancylostoma duodenale Ancylostoma caninum Ancylostoma braziliense “New world hookworm” “Old world hookworm” “Dog hookworm” “Cat hookworm” Actual image of Adult worms Description (Adult) Female: 1 cm long Male: 5-9 mm long Resembles ancylostoma but smaller; head is sharply bent in relation to the rest of the body, forming a definite hook shape at the anterior end Female: somewhat longer and stouter Male : 1 cm x 0.5mm Adult worm: grayish white / pinkish; head is slightly bent No teeth, but contains cutting plate Actual Image of Buccal Capsule Pair of semilunar cutting plates Two ventral of fused teeth Three ventral plates of fused teeth Longer than broad. Dorsal rays – deep cleft and tips bipartite Two spicules – fused and barbed. Short and broad Dorsal rays – shallow cleft and tips tripartite Two spicules – unfused and NOT barbed. Large, flame-shaped. Rays – long and slender. Two ventral plates of unfused teeth Actual Image of Copulatory Bursa Page 8 of 13 As broad as long. Rays – stunted. IIM Clinical Parasitology Lab_ ANGELES, Q.A Life Cycle Lab DIagnosis Demonstration of parasites: a. DFS b. SCT c. KTS d. Kato-katz method e. Coproculture: culture of feces (harada-mori technique – larvae; filter paper test tube method) Page 9 of 13 Clinical_ Parasitology Lab_ ANGELES, Q.A _ _ _ Phylum Nematoda: Class Secernentea (Phasmidia) —Filaria species Wuchereria bancrofti Brugia malayi Onchocerca volvulus Loa loa Mansonella pertans Mansonella streptocerca Mansonella ozzardi Size 230-320 x 10 um 170-260 x 5-6 um 150-368 x 5-9 um 250-300 x 6-8.5 um 200 x 4.5 um 180-240 x 3 um 175-240 x 4.5 um Size (width compared to RBC) Thick filariae Thick filariae Thick filariae Thick filariae Thin filariae Thin filariae Thin filariae Sheath Sheathed Sheathed Unsheathed Sheathed Unsheathed Unsheathed Unsheathed Unstained in Giemsa Stained in Giemsa Unstained in Giemsa Lightly stained in Hematoxylin Unstained in hematoxylin Stained in Hematoxylin Cephalic Space Short Long Long Short Short Short Slightly longer than wide Somatic column Nuclei dispersed regularly spaced in 2-3 rows Nuclei compact, overlapping irregularly-spaced Moderately compact Compact Compact Start in the anterior as single row of 10-12 (or more) nuclei Compact Tail Tail tapered to a point, free from nuclei Tail tapered; two discrete nuclei (terminal and subterminal) in tip of tail Tail tapered to a point, typically flexed free from nuclei Tail tapered and coiled within the sheath; nuclei irregularly spaced to tip of tail Tail tapered bluntly rounded; nuclei continue to tip Tail tapered and bluntly rounded; bent in shepherd's crook” shape, nuclei almost to tip Tail long and slender; tip of tail free of nuclei Addt’l Graceful appearance Kinky appearance Angular curves Rhythmical appearance/ Nocturnally periodic (mf is found in PB either at Nocturnally periodic 10pm – 2am Diurnally periodic (found at day time) None Aperiodic ( no rhythm or pattern in None Aperiodic ( no rhythm or pattern in blood; Actual Image Illustration Page 10 of 13 Clinical Parasitology Lab_ ANGELES, Q.A -fe②-II occurrence on peripheral blood day time/ the night time) Nocturnally subperiodic (peak con’c is at night) blood; found anytime) found anytime) Life Cycle LECTURE NOTES: Parasite Infective stage MOT Wuchereria bancrofti 3rd stage filarial larvae Mosquito bite Brugia malayi 3rd stage filarial larvae Mosquito bite Brugia timori 3rd stage filarial larvae Mosquito bite Loaloa -African eye worm 3rd stage filarial larvae Vector bite Onchocerca volvulus Mansonella pertans 3rd stage filarial larvae Vector bite 3rd stage filarial larvae Vector bite DH: Human IH:Midge (Culicoides) Subcutaneous tissue Mansonella ozzardi 3rd stage filarial larvae Vector bite Manzonella streptocerca Dracunculus medinensis 3rd stage filarial larvae Vector bite Peritoneal cavity or pleural cavity, less frequently in pericardium Dermis Infective larvae Drinking unfiltered water containing copepods DH: Human, monkey IH: blackfly, (simulium). Midge (Culicoides) DH: human, chimpanzee IH: midge (culicoides) IH: copepoelids Dirofilaria immitis -Dog heartworm Infective larvae Mosquito bite Some zoonotic DH: Carnivore (dogs, coyote, jackal, wolf) IH; Mosquito (Aedes, Culex, Anopheles, Mansonia) Heart Page 11 of 13 Host Habitat Disease DH: human Lymphatics Elephantiasis of the lower extremities IH: Mosquito (Culex, Aedes, “Tropical pulmonary eosinophilia” Anopheles DH: human Lymphatics Elephantiasis of the upper extremities IH: Mosquito (Mansonia, “Tropical pulmonary eosinophilia” Aeses) DH: human Lymphatics IH: Mosquito (Mansonia, Milder than bancroftian or malayan filariasis anopheles) DH: Human Subcutaneous tissue Calabar swelling (episodic angioedema), fugitive swelling, IH: Chrysops *subconjunctival migration loiasis of adult IH: blackfly (simulium) bite Subcutaneous tissue Onchocerciasis, river blindness, dermatitis Subcutaneous tissue Asymptomatic Adult migration transient subcutaneous swelling, pericarditis,pleuritic, ocular symptoms Asymptomatic Fever, pruritus, arthralgia, headache, rashes, lymphadenopathy, edema, and pulmonary symptoms Asymptomatic Pruritus, dermatitis, hyperpigmented lesion Guinea worm disease Skin infection Pulmonary disease “Coin lesion” Papule ulcers Clinical Parasitology Lab_ ANGELES, Q.A foote Phylum Nematoda: Cla Phylum Platyhelminthes: Class Cestoda–Order Pseudophyllidea and Order Cyclophyllidea Order Pseudophyllidea Diphyllobothrium latum Other name/s Fish tapeworm / broad tapeworm / broad fish tapeworm Order Cyclophyllidea Taenia solium Taenia saginata Hymenolepis nana Hymenolepis diminuta Dipylidium caninum Echinococcus granulosus Pork tapeworm Beef tapeworm Dwarf tapeworm Rat tapeworm Dog tapeworm Hydatid tapeworm Scolex (Actual image) Scolex (Illustration) Description (Scolex) Gravid Proglottids (Actual Image) Page 12 of 13 Clinical Parasitology Lab_ ANGELES, Q.A e②r②@ Gravid Proglottids (Illustration) Description (Gravid Proglottids ) Ova (Actual Image) Ova (Illustration) Description (Ova) ss Secernentea (Phasmidia) —Hookworm species Page 13 of 13 Clinical Parasitology Lab_ ANGELES, Q.A Boggs