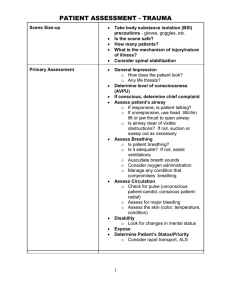
SKILL: ASSESSING THE CARDIOVASCULAR AND PERIPHERAL VASCULAR SYSTEMS Performance Criteria Assemble equipment: Stethoscope Introduce yourself and verify the client’s identity. Explain to the client what you are going to do, why it is necessary, and how the client can cooperate. Perform hand hygiene and observe other appropriate infection control procedures. Survey the Scene and note any hazards or informative signs Raise the bed and Provide for client privacy. Inquire if the client has any history of the following: Focused review of symptoms, such as chest pain, dyspnea, palpitations, lightheadedness, fatigue, edema, extremity changes/pain Childhood illness such as rheumatic fever or frequent streptococcal infections, congenital heart defects, trauma, or radiation to the chest. Family history of early onset CAD, familial hyperlipidemia, or genetic disorders. Medications or chemotherapy Cardiac testing such as ECG, echocardiogram, stress testing, cardiac catheterization Risk factors for coronary CAD, such as diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, tobacco, inactivity, and obesity Inspect and palpate the precordium for the presence of abnormal pulsations, lifts, or heaves. Inspect and palpate the aortic and pulmonic areas Inspect and palpate the tricuspid area Inspect and palpate the apical area for pulsation, noting its location Inspect and palpate the epigastric area at the base of the sternum for abdominal aortic pulsations. Auscultate the heart in all five anatomic sites: Aortic: 2nd intercostal space, right sternal border Pulmonic: 2nd intercostal space, left sternal border Erb’s point: 3rd intercostal space, left sternal border Tricuspid: 4th intercostal space, left sternal border Mitral: 5th intercostal space, mid-clavicular line (MCL). Location of PMI. Auscultate Apical heart rate. Location: 5th intercostal space, mid-clavicular line (MCL) Yes No Performance Criteria Palpate peripheral pulses for rate, rhythm, strength (bounding, non-bounding) and symmetry of pulse volume Carotid pulse, one side at a time. (Auscultate with bell for bruits) Brachial Radial Femoral Popliteal Dorsalis Pedis Posterior Tibial Assess related body structures Skin for presence of cyanosis, xanthelasma or xanthomas Extremities for edema and hair distribution Nails for clubbing and capillary refill Eyes for arcus senilus Neck for jugular venous pulsations or distension Document findings in the client record Comments: Yes No Pulse Sites Rate: A normal rate for an adult is between 60-100 beats per minute. However, depending on patient history this may differ. Therefore, it is important to watch a pulse rate trend over time. Rhythm: Patients without underlying arrhythmias should have a regular pulse. Symmetry: Pulse strength should be equal bilaterally. Strength: Normal pulses should be easily felt with gentle palpation. 4+ (bounding), 3+ (increased), 2+ (normal), 1 + (weak), or 0 (absent). Xanthelasma or Xanthomas: Xanthomas are depositions of yellowish cholesterol-rich material that can appear anywhere in the body in various disease states. They are cutaneous manifestations of lipidosis in which lipids accumulate in foam cells within the skin. Cholesterol deposits. Arcus senilis (cornea senilis) are lipid deposits that appear as rings on the outer region of the cornea. They are usually gray or white and are usually opaque. Nail Clubbing Jugular Vein Distention Pitting Edema Heart Sound Location