AB2O4 Spinel Structures: Valence, Cation Sites, and Lattice
advertisement

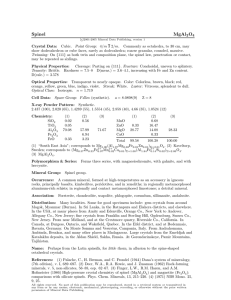
Another Complex Oxide, AB2O4 Spinel • Valence Requirement: A+2B=8 • A+2B=2+2x3, 1+7, or 1+2x3.5? • Spinel consists of an CCP array of ions with cations occupying 1/8 of T-site and ½ of Osites; Normal Spinel, AB2O4 • Normal Spinel: Divalent A ions occupy T-sites; trivalent B ions occupy O-sites; general formula is AtB2oO4c; unit cell (a0=8.0~8.5) contains 32 O= + 8A2+ +16B3+; • Typical Example for Normal Spine: • How Mg2+ and Al3+ are located in MgAl2O4 lattice? • To Determine lattice parameter based on Tetrahedral and Octahedral Coordination; • Check RMg+2, RAl+3 (for desired CN) based on Shannon’s Paper; • To understand the site compression of spinel lattice; • To calculate the theoretical density of spinel; HW for Normal/Inverse Spinel • For MgAl2O4 (Normal Spinel) • • • • Check RMg+2, RAl+3 (for desired CN); (i) Determine Lattice Parameter based on (T site-O ); (ii) Determine Lattice Parameter based on (O site-O); (iii) If it is known lattice parameter from MgAl2O4 Crystal is 8.02Å, please discuss (a) the observed lattice is determine by Al-O or Mg-O coordination; (b) what site (T or O) is compressed apparently; • Calculate the theoretical density based on (i) and (ii); Inverse Spinel, AB2O4 • Normal Spinel: Divalent A ions occupy T-sites; trivalent B ions occupy O-sites; general formula is AtB2oO4c; unit cell (a0=8.0~8.5) contains 32 O= + 8A2+ +16B3+; • Inverse Spinel: A2+ ions switch places with ½ of B3+ ions; general formula is Bt [AB]oO4c; • Fe3O4 is good example for Inverse Spinel; • Why Fe3O4 is a good example for inverse spinel? • Size dependence for Fe2+, Fe3+ under different coordination;