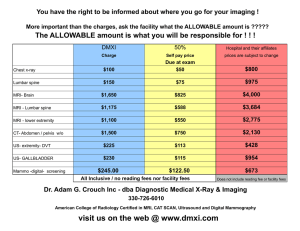
BASIS OF RADIOLOGICAL INVESTIGATION Basic methods of radiological examination ◼ ◼ ◼ ◼ ◼ ◼ US (ultrasound) Plain X-ray CT (computed tomography) MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Nuclear medicine (scintigraphy) Contrast studies RADIOLOGY TOOLS X- RAY ULTRASOUND NUCLEAR MEDICINE MAGNETIC RESONANCE COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY 3 HOW IS IMAGING DONE? ◼ ◼ ◼ IONIZING RADIATION X-ray, CT, Nuclear Medicine SOUND WAVES Ultrasound MAGNETIC FIELDS / RADIO WAVES Magnetic Resonance X-RAY ◼ ◼ DISCOVERED AND NAMED BY Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen AT UNIVERSITY OF WÜRZBURG, 1895 AWARDED FIRST NOBEL PRIZE FOR PHYSICS, 1901 X-RAYS PLAIN FILM RADIOGRAPHY ◼ ◼ ◼ ◼ ◼ ◼ CHEST MAMMOGRAPHY GIT (contrast is necessary!) SPINE EXTREMITIES, BONES & JOINTS SKULL X - RAY -- FOUR BASIC DENSITIES ▪ BONE ▪ SOFT TISSUE ▪ FAT ▪ AIR STOMACH UPPER GI – ORAL BARIUM CONTRAST (GASTRO INTESTINAL) WITHOUT CONTRASTplain or scout film COLON BARIUM ENEMA - RECTAL BARIUM CONTRAST 8 INTRAVENOUS PYELOGRAM – IVP INTRAVENOUS IODINE CONTRAST WITHOUT CONTRASTplain or scout film ARTERIOGRAM INTRAARTERIAL IODINE CONTRAST 9 Advantages of plain x-rays ◼ ◼ ◼ Quick Not expensive Relatively low radiation Disadvantages of plain x-rays ◼ ◼ ◼ Not 3 dimensional Can miss pathology May still require other imaging studies Princeples of CT imaging ◼ ◼ ◼ A CT scanner emits a series of narrow beams through the human body as it moves through an arc, unlike an X-ray machine which sends just one radiation beam. The final picture is far more detailed than an X-ray one. Inside the CT scanner there is an X-ray detector which can see hundreds of different levels of density. It can see tissues inside a solid organ. This data is transmitted to a computer, which builds up a 3-D cross-sectional picture of the part of the body and displays it on the screen. Contrast dye is used because it shows up much more clearly on the screen. CT planes CT planes AXIAL CORONAL SAGITTAL 3D-reconstruction Three-dimensional modeling of kidney on CT Projection of slice Right kidney Left kidney CT – diagnostic windows Head and neck Brain Chest Lungs Abdomen and pelvis Bones Advantages of CT scanning of the musculoskeletal system ◼ ◼ ◼ ◼ Excellent anatomic detail Will detect almost all pathology related to cortical bone injury Great for showing displacement or joint involvement Now multiplanar Disadvantages of CT ◼ ◼ ◼ Expensive More radiation Often not necessary Principles of MRI ◼ The patient is placed in a strong electromagnetic field of 0.3 to 3 teslas The magnetic field of an MRI machine is typically 3 Tesla! The Earth’s magnetic field is less that 30 microtesla (0.00003 Ts). Principles of MRI ◼ The billions of Hatoms in the body align themselves parallel with the magnetic field, either in the same direction or opposite to the direction of the field. MAGNETIC RESONANCE ◼ ◼ ◼ HYDROGEN PROTONS IN A MAGNETIC FIELD RADIO WAVE SIGNAL TRANSMISSION NO IONIZING RADIATION MAGNETIC RESONANCE EXAMPLES BRAIN SPINE KNEE Kidneys on MRI Coronal, bilateral renal ectopia Axial, norm Advantages of MRI ◼ ◼ ◼ ◼ ◼ No radiation We can slice through the body using any imaging plane Looks “inside” bone. Marrow evaluation. MRI is very good for looking at the soft tissues (muscles, ligaments, tendons and cartilage) MRI is very sensitive in detecting water Disadvantages of MRI ◼ ◼ Very expensive Not as good as CT for cortical bone Is MRI Better Than CT? MRI and CT are very different and used for different needs and reasons; both are valuable and both have specific applications; they are not interchangeable and one is not a better test than the other for all things. The decision whether to use one or the other is based according to the density of the body tissue that needs to be seen. Softer tissues that have more water molecules or hydrogen atoms in them are better seen by MRI because of the physics used. When MRI is preferable? Brain Spinal cord Soft tissues (muscles, ligaments, intervertebral discs ets.) Ultrasound ◼ ◼ ◼ ◼ SOUND WAVE-high frequency NO IONIZING RADIATION TRANSMITTER/ RECEIVER TOMOGRAPHIC DATA 28 US – EXAMPLES GALLBLADDER KIDNEY OBSTETRICS