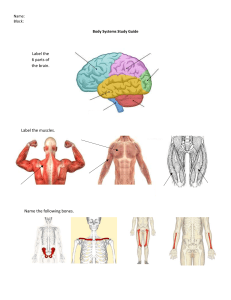
Leah Anne V. Lorenzo Doc. Daisy Mae Bialba PSY204 – 3rd Year November 01, 2022 NERVOUS SYSTEM ACTIVITY Reflection: 1. What is paralysis and how does it affect the body? Paralysis is when we lose control of our muscle functions, leading us into an immobile or immovable state. It can be either temporary or permanent, depending on the type of paralysis such as: complete, partial or incomplete, localized, generalized, and sleep paralysis. The most common causes of paralysis are damage to the brain and spinal cord, stroke, hereditary disorders that can affect the brain. Depending on the severity of the paralysis, it can be detrimental to the person’s health as it affects the body’s primary functions such as blood flow, breathing, organ function, speaking, and swallowing. 2. What is brain death and what happens when life support is switched off? Brain death simply means that the brain has no longer the capacity to function anymore due to critical brain damage and the person declared as brain-dead can only survive with artificial life or with the help of support machine; if switched off, the brain-dead person will eventually die within minutes as they permanently lost function of their entire brain that neither regaining consciousness nor breathing is possible again, albeit the heart remained beating due to life support machine. It’s a irreversible state. 3. Which memory processing is affected by amnesia? Amnesia is an umbrella term for memory loss. It can be cause problems for person to form new memories or recall past events. Short-term memory processing is known to be the most common affected on people with amnesia as they are not able to retain new memories but older memories that are ingrained deeply within their brain and oftentimes knowledge on their own identity are spared. Do You Remember? 1. The three main parts of the brain are Cerebrum, Cerebellum, and Brain Stem. 2. Cerebellum 3. The brain stem is responsible for some vital functions that supports our life such as breathing, consciousness, blood pressure, heart rate, and sleep. It also contains some parts of both the gray and white matters. 4. Hippocampus 5. Cerebellum 6. Spinal cord is a cylindrical structure that runs from our brain stem extending downwards to the center of the spine. 7. Neurons 8. Sensory Nerves 9. The parts of the nervous system that were discussed in our lecture were the following: Brain, Spinal Cord, Nerves, and different parts and classification of neurons. REFERENCES: Barclay, R., & Goldman, L. (2021, November 21). Understanding Amnesia. Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/amnesia Brain Death. (n.d.). Agency for Clinical Innovation. Accessed https://aci.health.nsw.gov.au/networks/icnsw/patients-andfamilies/patient-conditions/brain-death at Huang, J. (n.d.). Amnesias. In MSD Manual Professional Version. Retrieved November 1, 2022, from https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/neurologicdisorders/function-and-dysfunction-of-the-cerebral-lobes/amnesias Slivinski, N. (n.d). Types of Paralysis. WedMD. https://www.webmd.com/brain/paralysis-types Accessed at