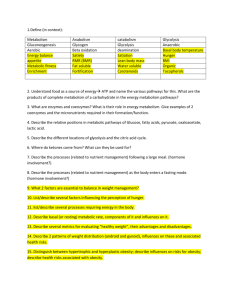
1 - Metabolism What is metabolism? • All chemical reaction that take place in an organism • These rxns extract energy from nutrients • Synthesize or breakdown macromolecules • What is the goal of metabolism? Metabolic pathways we will look at • ATP-PC system • Glycolytic (anerobic glycolysis) • Gluconeogenesis • Glycogenolysis • Aerobic respiration (krebs and ETC) • Beta oxidation What nutrients we use depends on activity….. Which nutrients (carbs or fats) would you predict to be used…… • At rest • Low to moderate exercise (25-65% of max intensity) • High intensity (above 70% of max intensity) • What are some different sports/activities or exercises? ATP-PC System Anerobic Glycolysis What happens to lactic acid? Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness (DOMS) • Peaks 24-72 hours after exercise ends • Lasts 5-7 days • Lactic acid? Metabolic Pathways • ATP-PC system • Glycolytic (anerobic glycolysis) • Gluconeogenesis • Glycogenolysis • Aerobic Respiration • Beta Oxidation Aerobic Respiration Glycogenolysis ATP production from Glucose Effects of dieting on metabolism • Weight cycling – repeated cycles of weight loss followed by weight gain induced by dieting • Potential risks of weight cycling: • Insulin resistance and type II diabetes • Dyslipidemia • Weight loss is accompanied by a larger than normal reduction in resting metabolic rate (RMR) -> metabolic adaptation • RMR remained lowered 6 years after competition