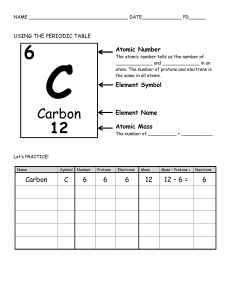
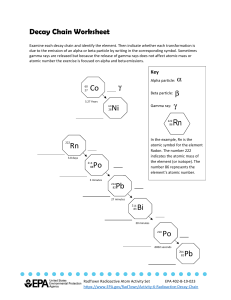
Quarter 1: Week 1 Exploring the Formation of Elements During Stellar Formation and Evolution ATTHEENDOFTHESESSION, THELEARNERS SHOULDBEABLETO: Give evidence for and describe the formation of heavier elements during star formation and evolution. Explain how the concept of atomic number led to the synthesis of new elements in the laboratory. A. Big Bang Theory 1. WHICH OF THE FOLLOWING IS THE MOST ACCEPTED THEORY ABOUT THE FORMATION OF THE UNIVERSE THAT EXPLAINS WHY IT CONTINUES TO EXPAND? B. Divine Creation Theory C. Steady State Theory D. Oscillating Theory The Big Bang theory is an effort to explain what happened at the very beginning of our universe. Our universe sprang into existence as "singularity" around 13.7 billion years ago. 2. ARRANGE THE FOLLOWING EVENTS TO FORM THE RIGHT SEQUENCES OF THE EVENTS OF THE BIG BANG THEORY. According to the Big Bang Theory, the temperatures in the early universe were so high that fusion reactions could take place. This resulted in the formation of light elements: hydrogen, deuterium, tritium , helium (two isotopes), lithium and trace amounts of beryllium. Definition of Terms: Atom - is the smallest unit of ordinary matter that forms a chemical element. Every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. Isotopes - Each of two or more forms of the same element that contain equal numbers of protons but different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei, and hence differ in relative atomic mass but not in chemical properties; in particular, a radioactive form of an element. Definition of Terms: Atomic number is usually the number of protons present in an element’s nucleus. It is also the value found associated with an element on the periodic table because it is the key to the element's identity. Atomic mass is associated with the number of neutrons and protons that are present in a particular nucleus of an element. The word “stellar” means star and the formation of elements in the center of the star is called stellar nucleosynthesis. During this Stellar evolution, nuclear reactions continued, which produced elements heavier than lithium/beryllium to iron. Produced elements Produced elements from Hydrogen to heavier than Beryllium. Beryllium to Iron. Produced elements Produced elements such as Beryllium, such as Neon , Silicon Carbon up to up to Iron. Oxygen. The star can keep growing into supergiant as it accumulates m Apha fusion processes continue the core via the alpha ladder. M and more alpha particles are fu to create heavier elements all t way to iron, making the core a star itself more massive. The star can keep growing into supergiant as it accumulates m Apha fusion processes continue the core via the alpha ladder. M and more alpha particles are fu to create heavier elements all t way to iron, making the core a star itself more massive. The star can keep growing into supergiant as it accumulates m Apha fusion processes continue the core via the alpha ladder. M and more alpha particles are fu to create heavier elements all t way to iron, making the core a star itself more massive. Radio active decay is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is considered radioactive. Three of the most common types of decay: 1.alpha decay (훼-decay) 2. beta decay (훽-decay) 3. gamma decay (훾-decay) Alpha Decay: two protons and two neutrons are immitted resulting to a lighter new element. Beta Decay: a neutron becomes a proton and an electron will be ejected resulting to a new element with the same mass. Gamma Decay: gamma ray will be emitted when a radioactive nuclide leaves a nucleus in an excited state. Henry Gwyn-Jeffreys Moseley was an English physicist who demonstrated that the atomic number, the number of protons in an atom, determines most of the properties of an element The atomic number is the number of protons (positively charged particles) in an atom. In 1919, Ernest Rutherford successfully carried out a nuclear transmutation reaction a process of transforming one element or isotope into another element. James Chadwick discovered the neutron in 1932, as a previously unknown neutral particle produced along with 12C by the nuclear reaction between 9Be and 4He: In 1925, there were four vacancies in the periodic table corresponding to the atomic numbers 43, 61, 85, and 87. Elements with atomic numbers 43 and 85 were synthesized using particle accelerators. Elements with atomic numbers greater than 92 (atomic number of uranium) are called transuranium elements They were discovered in the laboratory using nuclear reactors or particle accelerators.