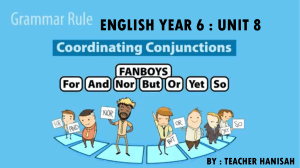
Master : Analytical Sciences and Instrumentation Prepositions and Conjunctions Supervised by: Présented by : KHADIJA ELHAMIDI Pr. SANAE SAOIBI FAYCEL BENDIDI ASMA AHARTAF 2023-2024 OUTLINE I .General Introduction II .Introduction to Prepositions III .Advanced Prepositions IV .Introduction to Conjunctions V .Advanced Conjunctions VI .General Conclusion General Introduction Prepositions and conjunctions are fundamental components of the English language that help convey relationships between words and phrases. Prepositions indicate location, time, direction, or relationships, while conjunctions connect words, phrases, or clauses. Understanding how to use these parts of speech correctly is essential for constructing coherent and meaningful sentences. In this presentation, we will explore the functions and examples of prepositions and conjunctions, providing a solid foundation for accurate usage in written and spoken English. Introduction to Prepositions What are Prepositions? • • Prepositions are essential parts of speech that help establish relationships between other words in a sentence. They often indicate location, time, direction, manner, or other relationships. Some common prepositions include "in," "on," "at," "by," "for," and "with." Let's take a closer look at their usage. Prepositional Phrases • A prepositional phrase consists of a preposition and its object, which is usually a noun or pronoun that the preposition relates to. • The preposition indicates the relationship between the object and another element in the sentence. • For example, in the sentence "The book is on the table," the prepositional phrase is "on the table," where "on" is the preposition, and "table" is the object. • Examples : o o Example 1: "She walked through the park." ▪ Prepositional phrase: "through the park" ▪ Preposition: "through" ▪ Object: "park" Example 2: "I have a meeting at 3 PM." ▪ Prepositional phrase: "at 3 PM" ▪ Preposition: "at" ▪ Object: "3 PM" Advanced Prepositions Compound Prepositions • Compound prepositions are formed by combining two or more prepositions or a preposition with another word. • They provide more specific meanings and allow us to express complex relationships. • Examples of common compound prepositions include "according to," "in front of," "instead of," and "because of." Prepositions of Time and Place • Prepositions can indicate time and place relationships. • Prepositions used to indicate time include "during," "throughout," and "until." o • Example: "She studied throughout the night." Prepositions used to indicate place include "above," "below," "between," and "among." o Example: "The bird is flying above the clouds." Introduction to Conjunctions What are Conjunctions? • Conjunctions are words that connect words, phrases, or clauses within a sentence. • They play a crucial role in creating cohesive and structured writing. • There are three types of conjunctions: o coordinating, o subordinating, o correlative. Coordinating Conjunctions • Coordinating conjunctions connect words, phrases, or independent clauses of equal importance.They are used to create compound sentences. • The most common coordinating conjunctions are "for," "and," "nor," "but," "or," "yet," and "so." • Remember the acronym FANBOYS to help you remember them. • Examples of Compound Sentences: o Example 1: "I love to read, and she enjoys painting." o Example 2: "He studied hard, so he passed the exam." o Example 3: "She wanted to go, but he stayed at home." Advanced Conjunctions Subordinating Conjunctions • Subordinating conjunctions connect independent clauses to dependent clauses, indicating a subordinate relationship. They are used to create complex sentences. • They introduce adverbial clauses, which provide additional information about time, place, reason, condition, or concession. • Examples of subordinating conjunctions include "although," "because," "if," "since," and "while." • Examples of Complex Sentences: o Example 1: "Although it was raining, they went for a walk." o Example 2: "Because he studied, he scored well on the test." o Example 3: "She couldn't attend the party since she had to work." Correlative Conjunctions • Correlative conjunctions are used in pairs to connect similar elements in a sentence. • They provide balance and emphasize equality or contrast. • Examples of correlative conjunctions include "either...or," "neither...nor," and "both...and." • Examples : o Example 1: "Either you come with me, or I'll go alone." o Example 2: "Neither John nor Mary could solve the puzzle." o Example 3: "Both the cat and the dog are adorable." General Conclusion In conclusion, prepositions and conjunctions play vital roles in English grammar and communication. Prepositions establish connections between nouns, pronouns, and other elements, providing important details about location, time, and relationships. Conjunctions, on the other hand, join words, phrases, or clauses, allowing for smooth transitions and logical connections within sentences. By mastering the usage of prepositions and conjunctions, one can effectively communicate ideas and thoughts in a precise and articulate manner.