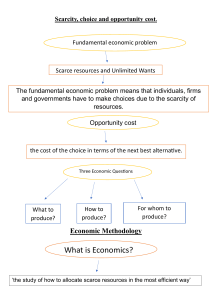
ECON 1900 Principles of Microeconomics TOPIC 1.1: WHAT IS ECONOMICS? SLIDES BY LAURA LAMB 1 What is Economics? Economics is about decision making. By studying economics, you'll gain a deep understanding of how individuals, businesses, and governments make decisions. SLIDES BY LAURA LAMB 2 What type of decisions involve economics? SLIDES BY LAURA LAMB 3 A definition of economics The social science concerned with how individuals, institutions, and society make best choices under conditions of scarcity. SLIDES BY LAURA LAMB 4 Scarcity & Choice 1. Most decisions involve scarcity and choice 2. What is scarce? 3. Scarcity → Choice SLIDES BY LAURA LAMB 5 In economics, we say these 4 categories of resources are scarce Land • Real estate, forests, water, minerals, etc. Labour • Quantity & quality of labour • Includes education, experience, skillsets Capital • Physical capital • Used for production Entrepreneurship • A human characteristic SLIDES BY LAURA LAMB 6 The concept of Opportunity cost The concept of opportunity cost: the next best alternative foregone. What is the opportunity cost of attending this class today? Illustrates that there is no free lunch! SLIDES BY LAURA LAMB 7 How does economics apply to your personal decisions? Unlimited wants (humans want lots!) Scarcity Choice ($, time) (opportunity cost) SLIDES BY LAURA LAMB 8 Microeconomics looks at specific economic units Microeconomics vs. Macroeconomics Macroeconomics examines the economy as a whole SLIDES BY LAURA LAMB 9 Practice: for each headline, state whether it is microeconomics or macroeconomics? P 1. The total revenue of Ford Motor Company have risen over the past 2 years. - Micro 2. The unemployment rate remains low at the beginning of 2023. - Macro 3. The price of gasoline continues to be volatile. - Macro 4. There is a shortage of Taylor Swift concert tickets. - Micro 5. Inflation rates are relatively high. Macro SLIDES BY LAURA LAMB 10 Economics topics can be categorized as positive or normative Positive economics describes the economy as it actually is. Normative economics involves value judgments about what the economy should be like and the desirability of the policy. SLIDES BY LAURA LAMB 11 Practice: for each statement, is it normative or positive? 1. The unemployment rate is 5.2%. - positive 2. The government should spend more on alleviating climate change. - normative 3. The unemployment rate is lowest in Manitoba. - positive 4. The price of Taylor Swift concert tickets are too high. - normative SLIDES BY LAURA LAMB 12 Analyze data Analytical tools What are some skills you will gain from studying economics? Critical thinking Problemsolving SLIDES BY LAURA LAMB finance, policy, international trade, research Navigate complex issues such as climate change, inequality, the impact of AI, etc Make informed decisions Propose solutions to realworld challenges 13 Economics uses models In economics, models are used to illustrate how an aspect of the economy works. an economic model is a simplified version of the real world Why a simplified version? The real world is messy, so models have simplifying assumptions. Models allow us to observe, understand and make predictions SLIDES BY LAURA LAMB 14 Key concepts 1. Scarcity, Choice 2. Resources 3. Opportunity Cost 4. Micro vs Macroeconomics 5. Normative vs Positive economics SLIDES BY LAURA LAMB 15