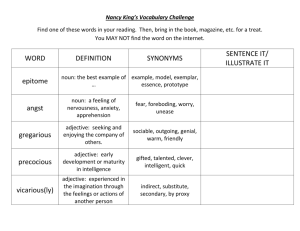
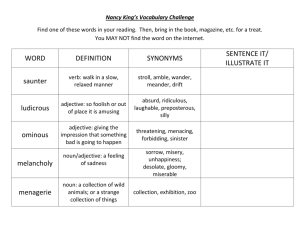
Module: Grammar Level: 1st year Date: 01-02-2021 Teacher: Siham Guibadj Adjectives (Part1) Definition: adjectives describe /modify a noun or a pronoun. We use adjectives to describe and give more information about a person, animal or thing. There are many types of adjectives, but here is something you can get started with: We can describe a noun/pronoun based on: 1. Appearance: We can describe and give information about a noun/pronoun by describing the appearance of it: Shape: square, round, triangular, rectangular, straight, flat, curved, circular...etc. Example: a round table, straight hair, curved glass. Colour: black, white, red, green, purple, pink, brown...etc. Example: black bird, red pen, brown surface. Size: small, tall, large, huge, big, short, tiny, medium...etc. Example: tall man, small house, short road, big eyes. 2. Composition: We also can describe a noun/pronoun by what is composed of: Noun wood gold leather glass silver plastic Adjective wooden golden leather glass silver plastic Example: wooden table, glass door, golden bracelet, leather jacket. 3. Measurement: We describe something using numbers, units: inches, feet, meters, kilometres, litres, pounds...etc. Example: 5 Litres of water/ 2 L of juice/ 10 inches wig 4. Age: Give information about something by indicating its age Example: a 5-year-old boy an ancient city a modern city 5. Quality: There are qualities of people, animals, things or places Example: He is a nice person. She is a mean person, respectful man, a wise woman. a big city ( we refer not only to the size of the city but also that this city is a busy city, the quality of that city), a small village(calm, quiet village) Note: the more descriptive, the clearer the picture in the listener’s mind of that thing becomes. There are different ways to use adjectives: Pure/simple adjectives: usually they are one word acting as an adjective Example: red, big, small, golden, tall, clear, clean, brilliant, calm, peaceful, easy...etc. Adjective Clause: a clause that contains information that when removed the sentence ceases to hold the same meaning. A dependent clause that functions as an adjective Examples: The angry tiger snarled at me └˃angry is a simple adjective describing the tiger The tiger that was angry snarled at me └˃ Adjective clause describing the tiger He is a wise man who speaks little (the adjective clause could mean that he is quiet, more information about the man)/ (wise is a simple adjective). Adjectival Prepositional phrases/Adjective phrases: phrases with a preposition functioning as an adjective. Example: The girl with the red hat └˃ (red describes the hat, but the prepositional phrase describes the girl) The little boy with the blue hat ate the pudding. The old schoolhouse on the hilltop is haunted └˃ which schoolhouse? The one on the hilltop Compound adjectives: generally, they are formed by combining two different words. When these two words are combined they can either be similar in meaning or have a completely different meaning. Number + noun: four-minute, one-way, ten-page, two-hour...etc. I will watch a two-hour movie. Adjective + noun: long-term, high-quality, last-minute...etc. My uncle has bought a high-quality TV. Adjective + present participle (p. continuous): easy-going, good-looking, slow-moving...etc. She is the most easy-going person in the class. Noun + present participle (p. continuous): English-speaking, time-saving, record-breaking, breath-taking...etc This is an English-speaking country. Noun + adjective: smoke-free, ice-cold, gluten-free, family-friendly...etc That cafe is a smoking-free venue. Note: adjectives can answer ‘’what kind?’’, ‘’which one?’’, ‘’how many?’’, or ‘’how much?’’ or ‘’whose?’’