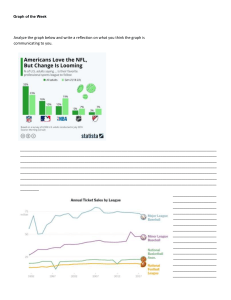
1 Issues and Trends in Professional Communication Communicating for Change in the New Economy • Communication: a transactional and relational process involving the meaningful exchange of information (p. 4) • Why is communication important? o What is the importance of communication in the current and future workplace? (p. 4) o How is communication important for you personally or for your career? (p. 4) Communicating for Change in the New Economy The new, evolving workplace requires: • Every member of the team to be a skilled communicator • Ability to communication in a variety of ways – both verbal and written • Communication across numerous channels and media • Proficiency in using various Information and Communication technologies (ICTs) (p. 3) Communicating for Change in the New Economy Contemporary workplaces also emphasize: - Team work and collaboration - Collaboration across space and time (geographic distance and different time zones) - Ability to work effectively work from home and other unconventional locations - Creativity and flexibility - Critical thinking skills (p. 3) Communicating for Change in the New Economy Soft Skill: a social, interpersonal, selfmanagement, or language skill that complements a person’s technical skills. Hard Skill: a technical skill (know-how and abilities) that a person requires for a specific job. *We need both skill sets – they complement each other. (p. 4) Communicating for Change in the New Economy, cont’d • Effective workplace communication o Designed for a particular purpose o Makes difficult concepts easy to understand o Tailored to the audience o Flexible in different situations (p. 4) Communicating for Change in the New Economy The two most important factors to consider before delivering your message – either in writing, verbally, or as a presentation: 1. Purpose or goal 2. Audience Communicating for Change in the New Economy, cont’d • Communicators: Key skills o Read and understand information o Speak and write effectively o Listen actively* (we’ll go into this in more detail in a future lesson) o Share and manage information via technologies o Apply knowledge from other disciplines (p. 5) Communicating in the Current Workplace Teams: A team is a group whose members have complimentary skills and work toward a common mission or goal • Teamwork involves group collaboration • Technology facilitates communication across locations and time constraints • Good communication skills minimize conflict in decision-making There are different types of teams for different functions (pp. 10, 20-21) Communicating in the Current Workplace Advantages of teamwork: 1. Accomplishing tasks or projects too large or too complex for individuals 2. Forming bonds and a sense of community 3. Different perspectives are effective for evaluating and solving problems 4. Teams facilitate innovation. Disadvantages of teamwork: Personality/style conflicts. Specialized communication training helps overcome challenges and boosts team performance. (p. 21) Communicating in the Current Workplace Types of Teams: 1. Project teams – formed for a time-limited basis to perform a specific task or project 2. Cross-functional teams – bring together members from different departments, sectors, areas of expertise 3. Intact standing teams – exist as ongoing organization units (example: committees) 4. Virtual teams – collaborate across time and space barriers in online / virtual environments (pp. 21-26) Communicating in the Current Workplace - Globalization - The changing landscape of work - The Canadian economy, Canadian business, and contemporary Canadian work environments - Shift from manufacturing and resource-based economies to a knowledge-based economy - Risk society and manufactured risks (piracy, hacking, cyberwarfare, ransomware, identity theft, scams) - Risk communication (pp. 5-7) The Knowledge Economy • Disruptive technologies and digital connectivity • Disruptive technologies are accessible, affordable products that begin at the bottom of the market and move up to displace existing technologies. This impacts competition and makes some existing products and services obsolete • Digital connectivity has changed the way we communicate across our personal and business relationships through social networking, interactive internet (Web 3.0), open source software, and apps.(pp. 11-12) New Economies • Attention economy o Value in seeking and receiving attention, particularly from consumers • Distraction economy o Draw attention away from one source and to another • Share (peer) economy o Collaborative consumption, sharing rather than owning • Gig economy o Short-term contracts, casual and temporary work, self-employment, etc. Lack job security, stable income, and benefits such as health care and retirement plans. (pp. 12-13) Indigenous Economic Empowerment Canadians live, work, go to school, play, and enjoy their lives on unceded traditional territories of First Peoples. In order to practice reconciliation, it’s important (and has become standard practice) to acknowledge the indigenous territory we’re on. (p. 14) Thompson Rivers University’s Kamloops campus is located on the Tk’emlúps te Secwepemc territory within the unceded traditional lands of Secwepemcúl’ecw (Secwepemc Nation). Professionalism and Employee Engagement Professional A professional is a practitioner in whom others place their trust. Professionalism o Requires demonstration of the level of competences or skill expected from a professional o “An ongoing process of social learning that involves thinking about and carrying out your duties according to a set of shared values, objectives, norms, and expectations important to you, your organization, and its stakeholders.” (p. 13) Why Professionalism Is Important • Act professionally o Put clients first o Maintain confidentiality o Use knowledge for honest, legal, and ethical purposes • Follow company and industry guidelines (pp. 15-16) Professional Boundaries and Behaviours • Personal boundaries o “The emotional, physical and mental limits individuals establish to protect themselves from harm and to set their thoughts and feelings apart from those of other people.” (p. 17) Professional Boundaries and Behaviours, cont’d • Professional boundaries o Define the roles and responsibilities of employees o Help employees work safely, comfortably and productively o Show employees where they stand and what is expected of them o Help to minimize conflict with customers or colleagues o Know your job and role. Do your own job. (pp. 17-20) Ethics and Legal Responsibilities of Business Communication Business ethics o “Socially accepted moral principles and rules of business conduct” for businesses in general.” Company code of ethics o Upholds important company values o Sensitizes managers and staff to how to behave (pp. 26-29) Tips for Ethical Communication • • • • • • Tell the truth Accept responsibility Don’t suppress or de-emphasize important information Offer value for money Back up your claims Avoid libel. Libel is printed or recorded defamation characterized by false negative comments about an individual or organization • Don’t claim authorship of documents you haven’t written – always cite sources • Exercise caution when communicating online. Everything online creates a permanent record (pp. 28-29)