CHN 2: Herbal Meds, Vaccines, Epidemiology, COPAR Notes
advertisement

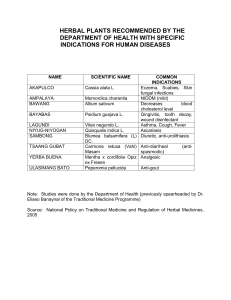
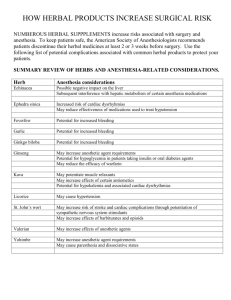
COMMUNITY HEALTH NURSING 2: FINALS NRG 302 CHN LECTURE COPAR, HERBAL MEDS, EPIDEMIOLOGY Table of Contents I. Herbal Medicines II. Vaccines ❖ Headache – Crush leaves may be applied on the forehead ❖ Rheumatism, sprain, contusions, insect bites – Pound the leaves and apply on affected area III. Epidemiology IV. COPAR I. Herbal Medicines ACRONYM: LUBBY SANTA These are the list of the ten (10) medicinal plants that the Philippine Department of Health (DOH) through its “Traditional Health Program'' has endorsed. All ten (10) herbs have been thoroughly tested and have been clinically proven to have medicinal value in the relief and treatment of various ailments: Herbal Med: LAGUNDI Scientific Name: VITEX NEGUNDO Uses: ❖ Asthma, Cough & Fever – Decoction ( Boil raw fruits or leaves in 2 glasses of water for 15 minutes) ❖ Dysentery, Colds & Pain – Decoction ( Boil a handful of leaves & flowers in water to produce a glass, three times a day) ❖ Skin diseases (dermatitis, scabies, ulcer, eczema) -Wash & clean the skin/wound with the decoction Herbal Med: ULASIMANG BATO Scientific Name: PEPEROMIA PELLUCIDA Uses: ❖ Lowers uric acid (rheumatism and gout): One and a half cup leaves are boiled in two glasses of water over low fire. Do not cover the pot. Divide into 3 parts and drink one part 3 times a day. Herbal Med: BAWANG Scientific Name: ALLIUM SATIVUM Uses: ❖ Lowers cholesterols levels in the blood Prepared by: Jubaira Aiko L. Biñas BSN 3 - 13G ❖ Hypertension: Maybe fried, roasted, soaked in vinegar for 30 minutes, or blanched in boiled water for 15 minutes. Take 2 pieces 3 times a day after meals. ❖ Toothache: Pound a small piece and apply to affected area Herbal Med: BAYABAS Scientific Name: PSIDIUM GUAJAVA Uses: ❖ For washing wounds twice a day ❖ Diarrhea - May be taken 3-4 times a day ❖ As gargle and for toothache – Warm decoction is used for gargle. Freshly pounded leaves are used for toothache. Boil chopped leaves for 15 minutes at low fire. Do not cover and then let it cool and strain. Herbal Med: YERBA (HIERBA) BUENA Scientific Name: MENTHA CORDIFOLIA; CLINOPODIUM DOUGLASSI Uses: ❖ For pain, headache, stomachache, toothache ❖ Rheumatism, arthritis, coughs, colds, swollen gums, menstrual, gas pain, nausea, fainting, insect bites, pruritus ❖ Pain (headache, stomachache) – Boil chopped leaves in 2 glasses of water for 15 minutes. Divide decoction into 2 parts, drink one part every 3 hours. ❖ Rheumatism, arthritis and headache – Crush the fresh leaves and squeeze sap. Massage sap on painful parts with eucalyptus ❖ Cough & Cold – Soak 10 fresh leaves in a glass of hot water, drink as tea. (expectorant) ❖ Swollen gums – Steep 6 g. of fresh plant in a glass of boiling water for 30 minutes. Use as a gargle solution ❖ Toothache – Cut fresh plant and squeeze sap. Soak a piece of cotton in the sap and insert this in aching tooth cavity ❖ Menstrual & gas pain – Soak a handful of leaves in a glass of boiling water. Drink infusion. ❖ Nausea & Fainting – Crush leaves and apply at nostrils of patients ❖ Insect bites – Crush leaves and apply juice on affected area or pound leaves until like a paste, rub on affected area ❖ Pruritus – Boil plants alone or with eucalyptus in water. Use decoction as a wash on the affected area. Herbal Med: SAMBONG Scientific Name: BLUMEA BALSAMIFERA Uses: anti-urolithiasis, anti-edema, diuretic ❖ Anti-edema, diuretic, anti-urolithiasis – Boil chopped leaves in a glass of water for 15 minutes until one glassful remains. Divide decoction into 3 parts, drink one part 3 times a day. Prepared by: Jubaira Aiko L. Biñas BSN 3 - 13G ❖ Diarrhea – Chopped leaves and boil in a glass of water for 15 minutes. Drink one part every 3 hours Herbal Med: ACAPULCO Scientific Name: CASSIA ALATA Uses: anti-fungal ❖ Tinea flava ❖ Ringworm ❖ Athletes foot ❖ Scabies ❖ Anti-fungal (tinea flava, ringworm, athlete’s foot and scabies) – Fresh, matured leaves are pounded. Apply soap to the affected area 1-2 times a day Herbal Med: NIYOG-NIYOGAN Scientific Name: QUISQUALIS INDICA Uses: anti-helminthic ❖ Anthelmintic – The seeds are taken 2 hours after supper. If no worms are expelled, the dose may be repeated after one week. ❖ Caution not to be given to children below 4 years old Herbal Med: TSAANG GUBAT Scientific Name: CARMONA RETUSA Uses: ❖ For diarrhea and stomachache ❖ Diarrhea – Boil chopped leaves into 2 glasses of water for 15 minutes. Divide decoction into 4 parts. Drink 1 part every 3 hours ❖ Stomach Ache – Boil chopped leaves in 1 glass of water for 15 minutes. Cool and strain. Herbal Med: AMPALAYA Scientific Name: MOMORDICA CHARANTIA Uses: ❖ For diabetes mellitus (mild non insulin dependent) ❖ Note: Young leaves may be blanched/steamed and eaten ½ glassful BID Prepared by: Jubaira Aiko L. Biñas BSN 3 - 13G II. Vaccines (EPI) Expanded Program on Immunization Vaccines A. Characteristics of EPI Vaccines ❖ ❖ ❖ ❖ ❖ ❖ ❖ BCG = freeze-dried HBV= RNA recombinant Diphtheria = weakened toxin Pertussis = killed bacteria Tetanus = weakened toxin OPV= live attenuated AMV/Measles = freeze-dried YELLOW: These vaccines are most sensitive to freezing and least sensitive to heat. It is important to store them in the body of a refrigerator (+2 to +8C). BLUE: These vaccines are most sensitive to heat so store them in the freezer for (-15 to -25C). Side notes: Especially the OPV vaccine which contains live attenuated virus, very sensitive siya to heat kung kaya e lagay talaga siya sa loob ng bioref. ★ COMPLETELY IMMUNIZED CHILD= if BCG, HBV, DPT, OPV & AMV are taken after 1 year. ★ FULLY IMMUNIZED CHILD= if BCG, HBV, DPT, OPV & AMV are taken before 1 year. Prepared by: Jubaira Aiko L. Biñas BSN 3 - 13G III. Epidemiology ❖ It is the study of the occurrence and distribution of the disease, as well as the determinants of events in a specific population. It is also the application of study to control health problems. ❖ It is regarded as the backbone of disease prevention. A. Uses of Epidemiology - Genetic, age, sex, ethnic group, physiologic, immunologic, pre-existing disease, and human behavior. ★ Environmental Factors - Physiologic environments and biologic D. DIsease Distribution It is the relationship of epidemiologic variables that includes; time, person, and place. E. Patterns of Occurrence and Distribution B. 3 Components of the Epidemiologic Triangle ★ Host: any organisms that harbors and provides nourishment for another organisms. ★ Agent: intrinsic property of microorganisms to survive and multiply in the environment to produce disease. ★ Environment: all external conditions that affects the development of an organism that can be biological, social, and physical. C. Occurrences of Disease in Human Population ★ Agent of Disease: - Nutritive elements - Chemical agents - Physical agents - Infectious agents ❖ SPORADIC - Intermittent occurrence of a few isolated and unrelated cases in a given locality. - Cases are few and scattered - They occur on and off through a period of time - Ex: rabies occurs sporadically in the Philippines ❖ ENDEMIC - Continuous occurrence throughout a period of time in a given locality - Always occurring in a locality - Always identifiable within the locality - Ex: schistosomiasis is endemic in samar and leyte, while filariasis is endemic in sorsogon. ❖ EPIDEMIC - Unusually large number of cases in a short period of time - Not the absolute largeness compared to pandemic - Ex: bird flu ★ Host Factor (Intrinsic Factor) Prepared by: Jubaira Aiko L. Biñas BSN 3 - 13G ❖ PANDEMIC - Simultaneous occurrence of epidemic disease in several countries. - Ex: AIDS IV. COPAR Community Organizing Participatory Action Research A social development approach that aims to transform the apathetic, individualistic and voiceless poor into a dynamic, participatory and politically responsive community. Group centered and not leader centered F. DOPES ➢ ➢ ➢ ➢ ➢ Deprived Oppressed Poor Exploited Struggling G. OMG (Continuous/Sustained) ➢ Organizing ➢ Mobilizing ➢ Guiding H. Community Organizing The people in the community are brought on together to play APIE. A - ask/identify the problem P - plan activity I - implement activities E - evaluate activities ➢ ➢ ➢ ➢ I. Strengthening Community member Problem solving Decision making Self reliant J. Participatory Research Investigate the problem DOPES are participated in actual research Seek the social transportation DOPES deprive the community problem Recommendations are made by the community K. Phases of COPAR The Three (3) Phases of COPAR ➢ Pre-entry phase - Site selection: the most important during this phase - Criteria: MDA M - must have 100-200 family members D - dopes and virgin community A - area must not have serious problems. Should be safe - Initial Phase: search the community to serve and help. It is important to formulate Goals, Objectives, Target (GOT) - This phase is also where events like: train the staff, curriculum revision, and community dialog (mayor) happens. PSI (Preliminary Social Investigation): poverty, 30 minutes from the hospital, and identify the contact person. ➢ Entry Phase - Social participation phase - INTEGRATION is the most important in this phase. 6 Tasks of Entry Phase 1. Conduct courtesy call to the barangay captain 2. Establish rapport to the community members 3. Check the lifestyle 4. Immerse yourself in the community 5. Live with the people 6. Reside in the designated area Prepared by: Jubaira Aiko L. Biñas BSN 3 - 13G DSI (Deep Social Investigation) - in a core group, select a leader. SALT training (Self Awareness Leadership Training). COMMUNITY DIAGNOSIS 9 Key Elements 1. Selection of Research Team 2. Training of data collection 3. Planning for data gathering 4. Training for data validation 5. Community validation 6. Analyzing data 7. Presenting community study and diagnosis and recommendation 8. Prioritizing community needs/problems COMMUNITY ORGANIZING ➢ Phase Out ❖ After 5 years, gradual endorsement ❖ Transfer roles and responsibilities ❖ Follow up 6 Key Elements 1. Organization (Formal) 2. Name of Organization (Made) 3. Vision and Mission (Made) 4. Objectives and Goals (Made) 5. Election of Officers (made) 6. Deliberation of Roles (function and task) ARAS: Action, Reflection, Action, Session COMMUNITY ACTION ❖ Identify first ❖ Organization of barangay health worker TWO TYPES OF BHW ❖ Doctors and Nurses ❖ Intermediate health care (professional groups) ❖ Villages/Grassroot health worker worker Prepared by: Jubaira Aiko L. Biñas BSN 3 - 13G