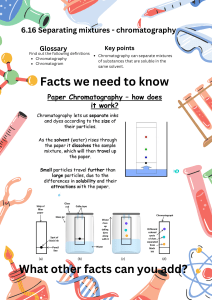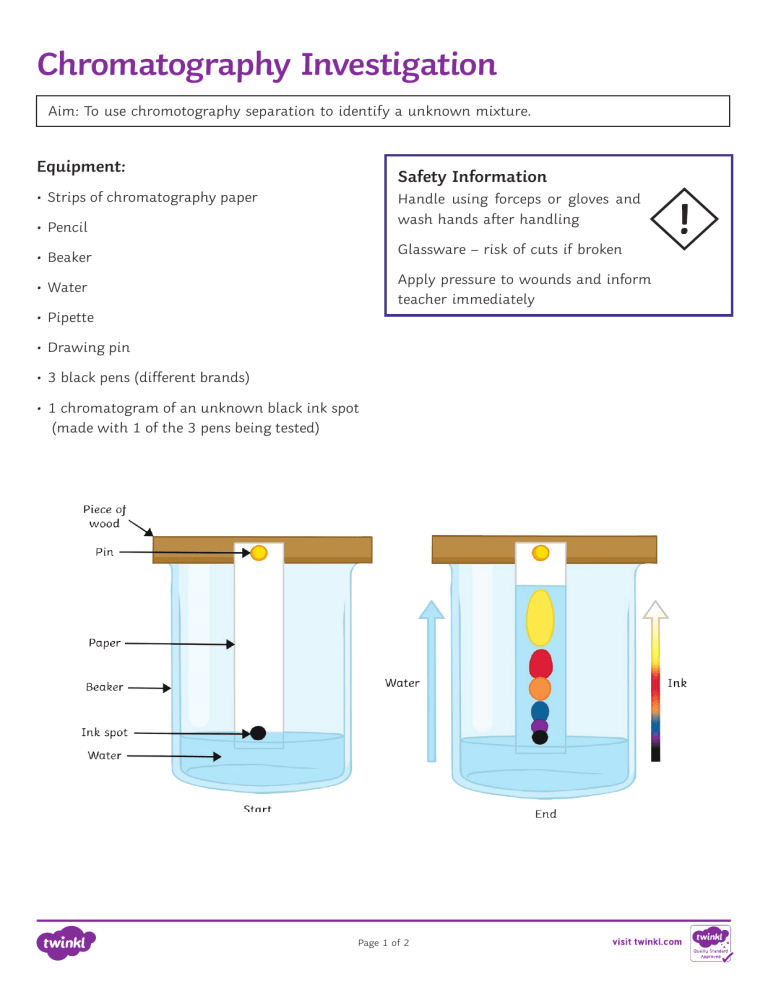
Chromatography Investigation Aim: To use chromotography separation to identify a unknown mixture. Equipment: Safety Information • Strips of chromatography paper Handle using forceps or gloves and wash hands after handling • Pencil Glassware – risk of cuts if broken • Beaker Apply pressure to wounds and inform teacher immediately • Water • Pipette • Drawing pin • 3 black pens (different brands) • 1 chromatogram of an unknown black ink spot (made with 1 of the 3 pens being tested) Page 1 of 2 Chromatography Investigation Method: Step 1: Using the first pen, make a small spot at one end, about 1 cm from the edge. Make sure you know which pen this chromatogram relates to. Step 2: With the drawing pin, secure the other end of the strip to the middle of a wooden pencil and balance across the top of the beaker. Step 3: Using the pipette, add water to the bottom of the beaker so that the paper is submerged but the black ink spot remained above the water line. Ensure you do not splash the paper, or allow it to touch the sides of the beaker. Step 4: Observe as the water is drawn up the paper. When it has reached the top, carefully lift out the paper using the pencil and lie flat to dry. Step 5: Repeat steps 1 to 4 again for each of the other pens. Step 6: Once dry, compare your chromatograms to the unknown and identify the pen used. Questions 1. What is a mixture? 2. The ink is soluble in water. What does this mean? 3. What is the solvent that is being used in this investigation? 4. Describe how chromatography is used to separate the dyes in the ink. Page 2 of 2 Chromatography Investigation Answers 1. What is a mixture? A mixture is made up of two or more different compounds, not chemically joined. 2. The ink is soluble in water. What does this mean? The ink can be dissolved in the water. 3. What is the solvent that is being used in this investigation? Water. 4. Describe how chromatography is used to separate the dyes in the ink. The dyes in the ink will dissolve into the water and are pulled through the paper at different rates. Some dyes are more soluble and will travel through the paper further. The different dyes will form spots at different distances depending on their solubility; the dyes become separated. Page 3 of 3