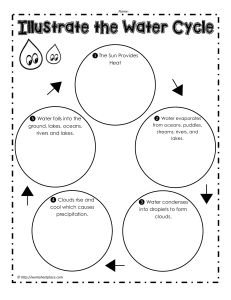
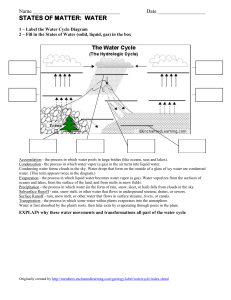
"Water is a substance formed by two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom, with H2O being its chemical formula. Found mainly in the liquid state, it is the most abundant substance in the Earth's crust. It is estimated that 70% of the planet is covered by water, and the vast majority of it is in the oceans. After the oceans, the second largest reservoir of water on the planet are glaciers. On the continents, this substance is found mainly in groundwater. We realize, therefore, that the Water is a chemical compound that can be found simultaneously in solid (glaciers), liquid (rivers, seas and oceans) and gaseous (water vapor) forms." "The water cycle is a biogeochemical cycle that ensures that water circulates through the physical environment and living beings. This process depends on sunlight, which ensures that the water evaporates, starting the cycle. The water vapor rises to higher layers high in the atmosphere and condenses, forming clouds, which are small droplets of water in the liquid state. When these clouds become charged, precipitation (rain) occurs, which can occur in liquid form or in the forms of hail and snow. Water The rain then returns to the Earth and can follow different paths, such as returning to lakes and rivers or infiltrating the soil. Read also: Cerrado: Brazil's water tank Biogeochemical cycles We call biogeochemical cycles those cycles in which a certain substance passes from the abiotic environment (air, water, soil) to living beings and passes from them back to the environment. Therefore, biogeochemical cycles are processes in which elements are cycled. The water cycle stands out as one of the main biogeochemical cycles, since this substance is found in absolutely every environment." "The Sun is responsible for providing energy for the cycle to happen. Its light causes the evaporation of water present on the Earth's surface. In some places, however, snow and ice sublimate, going from solid to vapor, jumping the melting (solid to liquid) and evaporation phases. The water, now in a gaseous state, rises to higher layers of the atmosphere, where the temperature is lower. Upon reaching a certain altitude, this substance goes from vapor to liquid (condensation) and forms clouds, which are, in reality, a large quantity of water droplets. In cold places, these droplets can solidify and form snow or hail. When rain begins, a process also called precipitation, water begins to return to the Earth's surface and is directly influenced by gravity. At that moment, it can reach rivers, lakes and oceans, infiltrate the soil and rocks or can be prevented from returning to the Earth's surface by vegetation."