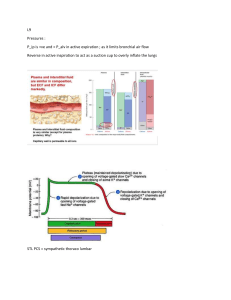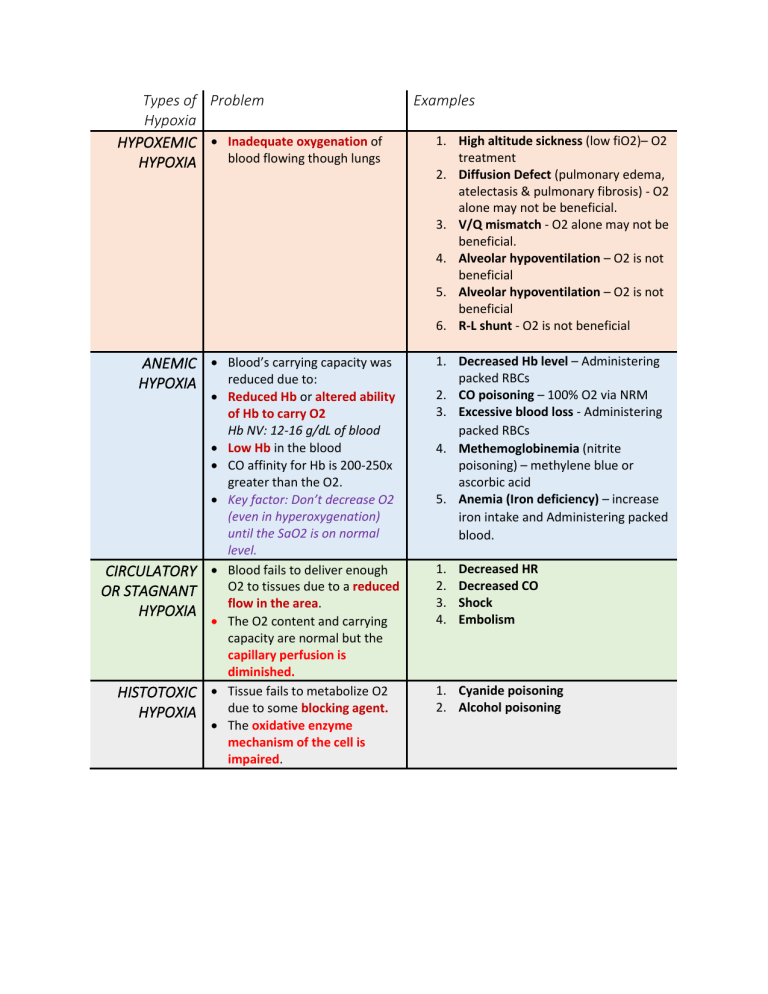
Types of Problem Hypoxia HYPOXEMIC • Inadequate oxygenation of blood flowing though lungs HYPOXIA ANEMIC • Blood’s carrying capacity was reduced due to: HYPOXIA CIRCULATORY OR STAGNANT HYPOXIA HISTOTOXIC HYPOXIA • Reduced Hb or altered ability of Hb to carry O2 Hb NV: 12-16 g/dL of blood • Low Hb in the blood • CO affinity for Hb is 200-250x greater than the O2. • Key factor: Don’t decrease O2 (even in hyperoxygenation) until the SaO2 is on normal level. • Blood fails to deliver enough O2 to tissues due to a reduced flow in the area. • The O2 content and carrying capacity are normal but the capillary perfusion is diminished. • Tissue fails to metabolize O2 due to some blocking agent. • The oxidative enzyme mechanism of the cell is impaired. Examples 1. High altitude sickness (low fiO2)– O2 treatment 2. Diffusion Defect (pulmonary edema, atelectasis & pulmonary fibrosis) - O2 alone may not be beneficial. 3. V/Q mismatch - O2 alone may not be beneficial. 4. Alveolar hypoventilation – O2 is not beneficial 5. Alveolar hypoventilation – O2 is not beneficial 6. R-L shunt - O2 is not beneficial 1. Decreased Hb level – Administering packed RBCs 2. CO poisoning – 100% O2 via NRM 3. Excessive blood loss - Administering packed RBCs 4. Methemoglobinemia (nitrite poisoning) – methylene blue or ascorbic acid 5. Anemia (Iron deficiency) – increase iron intake and Administering packed blood. 1. 2. 3. 4. Decreased HR Decreased CO Shock Embolism 1. Cyanide poisoning 2. Alcohol poisoning