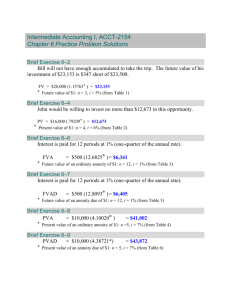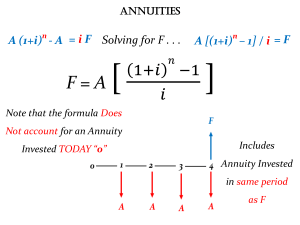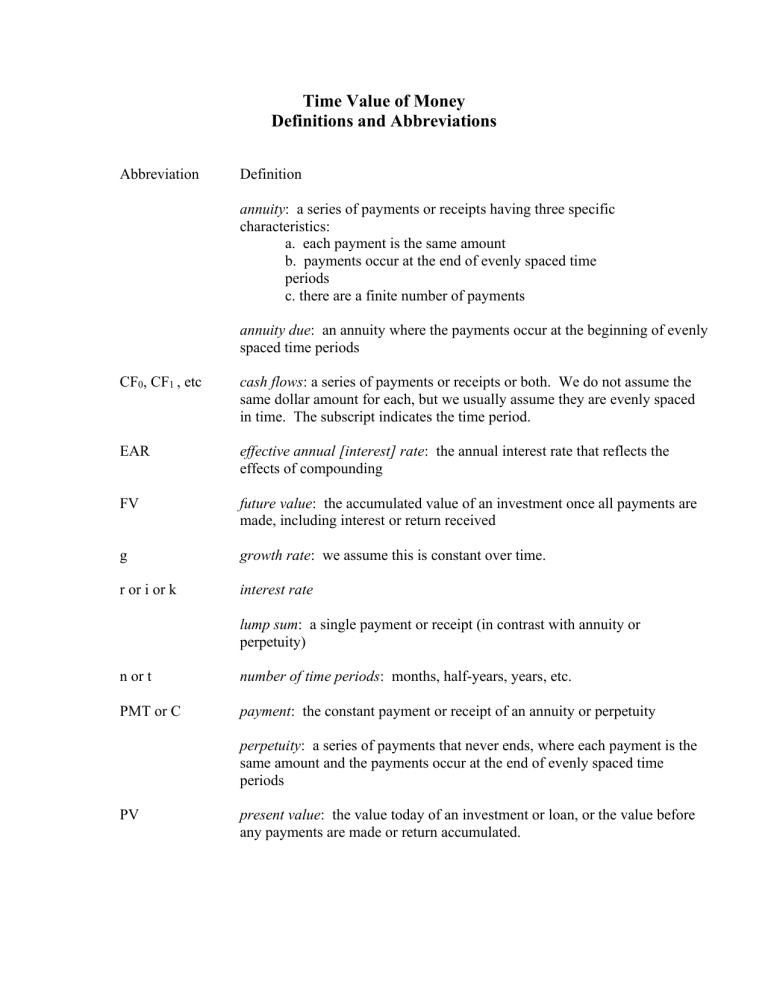
Time Value of Money Definitions and Abbreviations Abbreviation Definition annuity: a series of payments or receipts having three specific characteristics: a. each payment is the same amount b. payments occur at the end of evenly spaced time periods c. there are a finite number of payments annuity due: an annuity where the payments occur at the beginning of evenly spaced time periods CF0, CF1 , etc cash flows: a series of payments or receipts or both. We do not assume the same dollar amount for each, but we usually assume they are evenly spaced in time. The subscript indicates the time period. EAR effective annual [interest] rate: the annual interest rate that reflects the effects of compounding FV future value: the accumulated value of an investment once all payments are made, including interest or return received g growth rate: we assume this is constant over time. r or i or k interest rate lump sum: a single payment or receipt (in contrast with annuity or perpetuity) n or t number of time periods: months, half-years, years, etc. PMT or C payment: the constant payment or receipt of an annuity or perpetuity perpetuity: a series of payments that never ends, where each payment is the same amount and the payments occur at the end of evenly spaced time periods PV present value: the value today of an investment or loan, or the value before any payments are made or return accumulated. Time Value of Money Formulae Future value of a lump sum: FV = PV (1 + r ) n Present value of a lump sum: PV = *Present value of a perpetuity: FV (1 + r ) n PV = PMT r Present Value of an annuity: 1 1 PVA = PMT − r r( 1 + r ) n Future Value of an annuity: ( 1 + r )n − 1 FVA = PMT r Present Value of an annuity due: 1 1 PVA = PMT − ( 1 + r ) r r( 1 + r ) n Future Value of an annuity due: ( 1 + r )n − 1 FVA = PMT ( 1 + r ) r *Present value of a perpetuity with constant growth: PMT1 PMT0 (1 + g ) PV = = r−g r−g Present Value of an annuity with constant growth: n PMT1 1 + g PVA = 1 − r − g 1 + r Future Value of an annuity with constant growth: (1 + r ) n − (1 + g ) n FVA = PMT1 (r − g ) m Effective Annual Interest Rate: APR EAR = 1 + −1 m