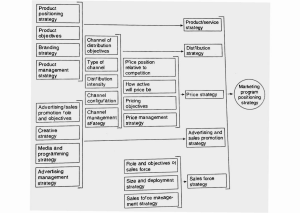
Practice test 1: Question 1: Advertising works in isolation from other parts of communications mix, is the statement true or false? A. True B. False Question 2: The two key drivers of engagement include: A. information and disregard response B. Thinking/feeling and behavioural responses C. WOM and detach response D. Purchase and refund response Question 3: What is the key criticism of Schramm’s core model of communication? A. It is not clear who the ‘sender’ and ‘receiver’ are referring to B. It does not include a feedback loop C. It does not refer to the message transfer process D. It ignores the effects of personal sources and influencers on the communication process Question 4: According to Fill and Turnbull (2019) professional industry bloggers (for example a cat blogger who is not part of your interpersonal network) is an example of opinion leaders. Is this statement true or false? A. True B. False Question 5: The attitude construct model refers to________, feelings and behaviour? A. Purschase intention B. People C. Pesuasion D. Knowledge Question 6: Most of the early advertising models were developed on the principle that individuals move through a series of sequential stages, those stages link to_________ A. Advertising triggers and touchpoints B. Superior recall and engagement C. Cognitive, affective, conative D. Information, involvement and emotional processing Question 7: The major criticism of Hierarchy of Effects model is that they assume that consumers move through the decision making stages in a logical, rational manner. Is this statement true or false? A. True B. False Question 8: What is the purpose of a ‘profile’ advertising strategy? A. To develop stakeholder relationships, corporate image and reputation B. To take a B2B approach to advertising C. To influence end users by pulling them through the channel network D. To influence marketing channel buyers by pushing themthrough the channel network towards the end users Question 9: A Pull positioning strategy targets____________ A. End users B. Retailers C. Stakeholders D. Suppliers Question 10: Advertising strategic balance considers the relation between______________ A. Audience strategies B. Push, pull and profile strategies C. Business Strategies D. Marketing Strategies Question 11: Examples of brand positioning strategies include? A. Price B. Quality C. Nationality D. All of these Question 12: Brand personality is a set of human characteristics that are attributed to a brand name. Is this staement true or false? A. True B. False Question 13: Which statement below is true about brand positioning? A. Brand positioning is an operations task B. Brand positioning is making an organisation branding similar to its competitors C. Brand positioning is related to an organisation’s market share D. Brand positioning makes a brand different or stand out from the rest Question 14: Advertising is used to reach large audiences with detailed and complex messages A. True B. False Question 15: Which of the eclectric models of advertising places the greatest emphasis on shared values? A. The persuasion/go to model B. The involvement/play model C. The salience/talked-about model D. The sales promotion/do model Question 16: The principle role of adbertising isdirected towards____________ with the target audience. A. Generating a sale B. Measuring the reaction C. Changing the perception D. Engaging Question 17: Which of the following quotes is not directly related or a definition of advertising? A. “… the capacity to reach huge audiences with simple messages.” (Fill and Turnbull 2019) B. “… the prime goals are to build awareness of a product or an organisation in the mind of the audience and engage them” (Fill and Turnbull 2019) C. “… paid, mediated form of communication from an identifiable source designed to persuade the receiver to take some action, now or in the future.” (Richard and Curran 2002) D. “… the plannes and sustained effort to establish and maintain goodwill and mutual understanding between an organisation and its publics.” (CIPR, 2018) Question 18: Advertising that uses emtional appeals, such as fear, rather than those that use rational, information based messages, are better at motivating a change in behaviour? A. True B. False Question 19: Fill and Turnbull (2019) state that classifying media by traditional and new is broad, vague and misleading A. True B. False Question 20: Media by form can be broken down into Class, Type and_____ A. Tools B. Media Channels C. Vehicles D. POEM Question 21: The acronym used to classify media by source is? A. DRIP B. POEM C. SMART D. MCPF Practice test 2: Question 1: What would be a deontological reason for an advertisement being classified as 'unethical'? A. The end result does not warrant the approach taken B. The end result is classed as sexist by some feminists C. The end result has unresolvable consequences D. The end result is culturally specific Question 2: What is the purpose of a 'profile' advertising strategy? A.To develop stakeholder relationships, corporate image and reputation B. To take a B2B approach to advertising C. To influence end users by pulling them through the channel network D. To influence marketing channel buyers by pushing them through the channel network towards the end users Question 3: What is a key criticism of Schramm's core model of communication? A. It is not clear who the 'sender' and 'receiver' are referring to B. It does not include a feedback loop C. It does not refer to the message transfer process D. It ignores the effects of personal sources and influencers on the communication process Question 4: Shrimp's CAN model (2010) refers to advertising campaigns being 'connected', 'appropriate' and ? A. Newsworthy B. Never-ending C. Novel D. Niche Question 5: Creativity is only relevant to TV advertising A. True B. False Question 6: The major criticism of Hierarchy of Effects models is that they assume that consumers move through the decision making stages in a logical, rational manner A. True B. False Question 7: AIDA stands for _______________ A. Awareness, Involvement, Desire and Attention B. Attention, Interest, Desire and Action C. Action, Interest, Desire and Attention D. Acquisition, Interest, Desire and Action Question 8: When processing advertising messages, an individual’s intention to behave in a certain way is the A. Cognitive Component B. Conative Component C.Affective Component D. Attitude Construct Question 9: Which two key audiences are missing from the following communication model A. b-2-b and b-2-c B. marketing manager and sales manager C. opinion leader and opinion former D. customer and consumer Question 10: What does 'CPM' stand for? A. Cost per million B. Cost per impression C. Cost per thousand D. Cost for mobile Question 11: The missing label in Fills planning framework diagram below is? A. Fill Plan B. Strategic analysis C. Business analysis D. Context analysis E. Evaluation analysis Question 12: A communication model that ignores the effects of personal sources and influencers on the communication process is? A. Influencer model of communication B. Schramms Linear Model C. Interactional model of communication D. Multi-step variation Question 13: Successful creativity leads from identifying a client’s ____________ A. History B. Budget C. Location D. Needs Question 14: An advertising appeal used to change people’s behaviour? A. Rational Appeal: product content B. Emotional Appeal: Fear C. Rational Appeal: Information based on product D. None of these Question 15: The missing facet from the brand identity prism is? A. Relationship B. Advertising C. Profits D. PEST Question 16: Fame campaigns work by _____________________ A. Featuring popular celebrities and being likeable B. Featuring strong product attributes C. Being easily remembered for its creative content D. Getting talked about and making the campaign famous Question 17: Egan (2007) identifies five main tools of marketing communication, there are __________ A. Product, Price, Place, People and Physical evidence B. Advertising, Sales Promotion, Personal Selling, Public Relations, Direct Marketing C. Selling, Buying, Distribution, Manufacture, Marketing D. Advertising Strategy, Segmentation, Targeting, Positioning Question 18: It is difficult to measure the effectiveness of outdoor advertising? True or false? A. True B. False Question 19: Strategic balance considers the relation between ______________ A. Advertising strategies B. Push, pull and profile strategies C. Business strategies D. Marketing strategies Question 20: Successful brands might be considered to encapsulate the three Brand Ps (3BPs). These are: A. positioning, preconditions, and preference B. promises, processes and payback C. performance, processes, and preferences D. promises, positioning and performance Question 21: The primary role of media is to enable _________ and ______messages to be channelled to, from, and among audiences A. Brand and Product B. Creative and Engaging C. Planned and Unplanned D. Product and Service Question 22: What is a key strength of digital advertising media? A. It is free B. Everyone will watch your digital ads C. Everyone has a Smartphone D. It can be easily measured Question 23: Which of the three P’s of marketing communication positioning strategy is illustrated in this diagram? A.Positioning Strategy B. Push C. Pull D. Profile E. Positioning Question 24: What label is missing from Schramm’s (1955) model of communication? A. Listener B. Medium C. Decoding D. Feedback Question 25: Which of these is not a marketing communication tool? A. Advertising B. Sales Promotion C. Public Relations D. Social Media Question 26: Advertising messages using rational appeals include the presentation of… A. Factual product or service information B. Emotional situations with the product or service C. Humorous situations with the product or service D. Consumer behaviour product or service habits Question 27: A great deal of advertising is directed towards __________ of the target audience A. Generating a response B. Measuring the reaction C. Changing the perception D. Getting the attention Question 28: Fill et al (2013) identifies three models of communication. Which one of the following is not one of these mode A. Schramm’s core model of communication B. The influencer model C. The interactional model D. The communication innovation model Question 29: Music is used frequently in advertising as ___________ A. a mood setter B. a standout feature C. background D. an executional cue Question 30: Advertising works in isolation from other parts of the communications mix A. True B. False Question 31: The body that regulates advertising in the UK is: A. ASA B. ASI C. AAR D. ASS Question 32: When processing advertising messages, the level of knowledge and belief an individual hold about a product/service is the A. Conative Component B. Cognitive Component C. Affective Component D. Attitude Construct Question 33: Which framework is used to determine campaign objectives for advertising? A. RING B. ROUTE C. DRIP D. SPLAT Question 34: Advertising that uses emotional appeals, such as fear, rather than those that use rational, information based messages, are better at motivating a change in behaviour A. True B. False Question 35: The attitude construct model refers to knowledge, feelings and ? A. Behaviour B. Purchase intention C. People D. Persuasion Question 36: Which of the three P’s of marketing communication positioning strategy is illustrated in this diagram? A. Positioning Strategy B. Push C. Pull D. Profile E. Positioning Question 37: What is the name of the model below? A. The Reinforcement Model B. The Central Route Model C. The Elaboration Likelihood Model D. The Message Persuasion Model Question 38: Advertising messages can be positive and negative. A. True B. False Question 39: Which of the following is not a school of art to have been represented in advertising A. Symbolism B. Corkism C. Impressionism D. Art Deco Question 40: Effective strategic development at all levels needs to be based on the setting of clear and detailed: A. Targets B. Plans C. Analysis D. Objectives Question 41: A Pull positioning strategy targets __________________ A. End users B. Retailers C. Stakeholders D. Suppliers