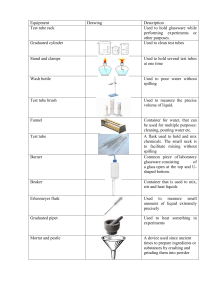
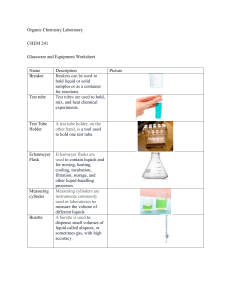
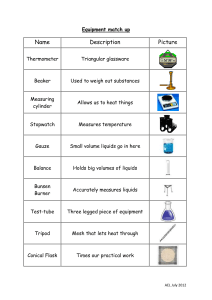
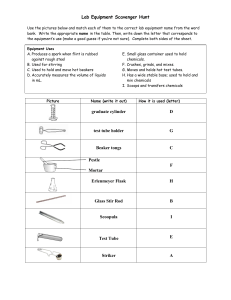
NAME: Marigold Yvette C. Cubero SECTION: CAS-06-102P SUBJECT: General Chemistry Lab SUBJECT TEACHER: Ms. Jamielou D. Bustarde DATE: September 2, 2022 ASSIGNMENT #1: Laboratory Glassware, Equipment, and Materials Laboratory Glassware, Equipment, and Materials Ammeter An ammeter is a device that measures the amount of current flowing through a circuit. It's also very handful through electrolysis reactions. Balance It is used to weigh chemical reagents or other objects. It is used to store, heat, or mix substances, hold samples and reagents and Beakers measure liquids. Beakers are cylindrical with a flat base, have a spout, and do not have rounded bottoms. Boiling Tube Boiling tubes are used to boil chemicals. Brushes are used to clean test tubes as they are the only things that can fit Brushes into the narrow-mouthed test tubes and other cylindrical and narrow objects. Buchner Flask It is frequently used for vacuum filtration or solution distillation. Bulb and Graduated These transport specific amounts of fluid from one place to another. Pipettes Bunsen Burner It is used to sterilize objects, heat and expose them to flames. Natural gas or liquified petroleum gas, such as methane, could be used. It is used to deliver and measure the volumes of any substance dispensed Burette to other equipment. It is frequently used in titration reactions. It's a long graduated tube with a stopcock at the bottom. The 50ml, 25ml, and 10ml burettes are the most popular. Burette Clamp It's used to keep burettes in place on a ring stand. It is used to determine the melting point of chemical substances. They Capillary Tube are used to keep a sample of the chemical substance whose melting point is being determined inside the melting point apparatus, also known as a Thiele tube. A centrifuge is a laboratory device that separates fluids, either gaseous or Centrifuge liquid, based on density. Centrifuge machines are also useful for Machine collecting cells, precipitating DNA, purifying viral particles, and detecting minor changes in molecular conformation. Centrifuge Tube A centrifuge vessel is a cylindrical vessel with a cap that is used to separate the components of a solution in a centrifuge machine. Column chromatography is a technique used to purify chemicals based Chromatography on their polarity or hydrophobicity. In column chromatography, a Column mixture of molecules is separated based on their differential partitioning between a mobile phase and a stationary phase. Clay Triangle It is used to hold crucibles when they are being heated. It measures the absorbance of a specific wavelength of light by a given solution to determine the concentration of a known solute. The principle of Beer-law Lambart's Digital Colorimeter states that the absorbance of Colorimeter light by a solution is directly proportional to the concentration of the solution. A photoresistor in this device monitors light transmittance or absorbance through the sample, which is then used to calculate concentration. Condensers It is used to cool down hot gases or liquids. They are long borosilicate glass tubes with a coiled inner tube to keep the distillation process cool. Crucibles are laboratory containers that can be used to melt substances. Crucible They are made to withstand high temperatures to melt or change the substance. It is used to hold chemicals while they are heated to extremely high temperatures. Crystallization Dish These containers cross between a Petri dish and a watch glass. They are frequently used to store liquids like water, oil, or acid for a brief period yet provide large surface areas for liquid evaporation. Desiccators A vessel made to absorb moisture from a substance. Also known as the Pasteur pipette, is a short glass or plastic pipe with Dropper rubber on one side. It is a piece of necessary equipment when any reagent is required in an extremely small amount in a solution. It is used to deliver small amounts of liquids, a single drop at a time. Drying Pistols A more direct way of extracting moisture from a sample. Evaporating Dish It is used to heat liquids or evaporate dissolved solids. It is employed in the evaporation of liquids. Erlenmeyer It is used to heat, mix, and store liquids. The Erlenmeyer flask has the Flasks advantage of having a wider bottom than a narrower top, which allows it to heat up faster due to the larger surface area exposed to the heat. A semi-permeable sheet of paper is used to separate solid impurities or Filter Paper components from a liquid solution. They are frequently made of cellulose, which has a capillary function that is useful when separating fine solid impurities. Also known as a boiling flask, is used to heat substances that must be Florence Flask heated evenly. The bulbed bottom allows heat to distribute more evenly through the liquid. The Florence Flask is most commonly found in distillation experiments. Forceps It is used for picking up and holding small objects. They are used to pour substances into small-mouthed vessels and to separate liquids without the risk of spillage. Filter, thistle, and dropping Funnels funnels are among the various types, each with a distinct function. The funnels of Büchner and Hirsch are excellent examples of organic chemistry laboratory apparatus. It is used to conduct experiments such as the sodium fusion test Fusion Tube (Lassaigne's test) or to determine the melting or boiling point of a substance by overheating a small sample. This glassware is used in laboratories to inject or remove a volume of gas Gas Syringe from a closed system, as well as to measure the volume of gas generated by a chemical reaction. Graduated Volumetric markings on these cylindrical vessels allow them to precisely Cylinders measure the volume of a liquid. Hot Plate It is used to heat substances and liquids in beakers and flasks. Also known as Kipp’s generator is a chemistry lab device used to prepare Kipp’s Apparatus gases such as hydrogen sulfide gas, carbon dioxide gas, and hydrogen gas. It is used to determine the nitrogen concentration in organic compounds Kjeldahl Flask via Kjeldahl digestion. The flask's extra-long neck acts as an air condenser during the digestion stage, reducing vapor entrapment. The lab coat serves a specific purpose in addition to being a general uniform for medical and chemical professionals. The knee-length coat Lab Coat protects the body and clothing from accidental chemical spills and splashes. Furthermore, in case of an emergency, such as a fire or contamination, a lab coat can be removed more easily and quickly than regular clothing. Latex or Nitrile Latex or nitrile gloves act as a barrier between human skin and hazardous Gloves chemicals, protecting it from burns, infections, and contamination. Litmus and Filter The litmus paper changes colors to indicate the pH of any solution, Papers whereas the filter paper aids in the filtration process. It is a device that uses electromagnetic force to stir chemical solutions. Magnetic Stirrer This method of stirring is more efficient, quick, and sanitary than the traditional stirring glass rod. Magnifying Glass It creates a magnified image of an object. It consists of a convex lens in a frame with a handle. Measuring It is used to measure the volume of a liquid. It is graduated, and each Cylinder marking indicates the amount of reagent. Mechanical It is a laboratory device that shakes chemical compounds to mix, blend, Shaker or stir them. It has an oscillating board on which test tubes or flasks filled with chemical compounds are held. Melting Point A device for determining the melting points of chemical compounds. Apparatus Micropipette It is used to precisely measure and delivers very small volumes of liquid, typically 1 ml or less. Microscope It is used to observe objects that are too small to be seen with the naked human eye. Mortar and It is used in experiments that crush and grind materials into powders. Pestle Nuclear Magnetic It is an imaging technique used in both chemistry and physics to analyze Resonance Tube the magnetic behavior of atomic nuclei. Pear-Shaped It is commonly used in organic chemistry for a variety of heating Flask applications, including evaporating solutions to dryness post-synthesis with a rotary evaporator and removing concentrated samples. Petri dishes Shallow dishes are used to culture living cells. Petri dishes are designed to withstand thermal shock. These are also measuring volumetric glassware that is used to dispense liquids and are regarded as some of the most precise measuring labware. Pipette It measures liquids and allows liquids to be transferred from bottles with small necks into new containers. It is used to deliver small amounts of liquid as well as draw liquids into a pipe. Pipette with It is used to precisely measure and delivers small volumes of liquid, pump typically 0.1-10 ml. Also referred to as media bottles, are specially designed containers or vessels for holding liquid or powder chemicals. They come in a variety Reagent Bottles of sizes and shapes and are typically made of glass or plastic. While the majority of reagent bottles are clear glass, some are colored amber (actinic), brown, or red to protect light-sensitive chemical compounds from visible light, ultraviolet, and infrared radiation. Retort Flask These are used for distillation purposes. Ring Clamp Attached to a ring stand and equipped with wire gauze, this device is used to hold beakers or flasks while they are heated by a gas burner. A ring stand is a piece of auxiliary equipment used to support other Ring Stand laboratory apparatuses such as beakers, flasks, burets, and so on. It is used to hold heated items. Clamps or rings can be used to elevate items above the lab table for heating with Bunsen burners or other items. The flask's round bottom provides an adequate surface area for even heat distribution throughout the vessel. As a result, it is frequently used in experiments requiring uniform heating or boiling of the chemical Round Bottom contents. Furthermore, the cylindrical neck can support funnels and glass Flask stoppers. Round Bottom flasks are frequently used in conjunction with other heating apparatus such as a sand bath, water bath, rotary evaporator, and so on. It is commonly used in the laboratory-scale synthesis of other chemicals. Safety Goggles It protects our eyes from harm. They are essential safety equipment because the eyes are the most vulnerable part of the human body. Schlenk Flask A Schlenk flask is a piece of laboratory glassware used for anaerobic reactions. Scoopula It is used to take small or large amounts of chemicals from bottles. Separatory funnel Slides It is used for separating layers of immiscible liquids or for dropping liquids. Slides are flat, thin pieces of glass that are used to hold and display specimens for examination and study under a microscope. Soxhlet It is employed in the extraction of lipids and other desirable chemical Apparatus compounds from solid materials. Small hand-held tools for carrying, mixing, spreading, and transferring Spatula solids. They are also useful for applying paste-like treatments. Most spatulas are acid and heat-resistant, making them suitable for use with a variety of substances. It is also known as a newton meter. The tension of a spring is used to measure the weight of an object on a scale. It is made up of spring on one Spring Balance side and a hook on the other, and it functioned on the principle of Hooke's law, which states that the force applied to an object is directly proportional to its extension as long as the elastic limit is not reached. Spring Scales It measures the distance when the material gets displaced due to its weight. Stirring Rods It is used to combine chemicals, solvents, and samples, as well as to heat them. A type of lab vessel that is commonly used to collect, hold, and mix samples. It resembles a finger and opens on one end. They are made of Test Tube borosilicate glass and can be used for cold or hot applications as well as mixing, holding, and heating chemical elements. They can be warmed over an open flame. Its standard dimensions are 18 x 150 mm. Test Tube Holder It is used to hold test tubes while heating. Test Tube Rack It is used to hold test tubes while reactions are taking place or when they are not required. Thermometers used in laboratories are nearly identical in that they both Thermometer measure the temperature of substances and determine reaction conditions with a high degree of precision. Thiele Tube It is used to determine the melting point of organic compounds. Also known as the thistle funnel. These funnels make it possible to precisely place small amounts of chemicals in an existing system or Thistle Tube apparatus, making it easier to add new materials to burets and narrow neck containers. Thistle tube funnels reduce the likelihood of a reaction occurring too quickly and spilling over. Tongs are used to grasp dangerous objects as well as to hold hot vessels. Tongs They are used to hold the crucible after it has been heated, to transfer evaporating dishes, or to pick small objects out of a reaction container. Tripod A tripod is a three-legged stand that can support vessels and heat wire gauze during experiments. Utility Clamp It's used to secure test tubes and other glassware to the ring stand. Vacuum Filter It is used for vacuum filtration along with a vacuum line and a Buchner Flask funnel. Vials These small bottles are used to keep samples or reagents. Voltmeter Voltmeters are used in electrical circuits. They can be used to measure the voltage between two points. Volumetric It is a kind of glassware that has been measured to hold specific amounts Flasks of a liquid at specific temperatures. It is utilized for accurate dilutions and the preparation of standard solutions. Volumetric These can be volumetric flasks that have an etched mark on their neck Glassware that indicates the precise volume at the given temperature. It is a squeeze container with an extended nozzle. It is used for Wash Bottle sterilization and glassware rinsing. The majority of wash bottles are made of polyethylene. These typically include deionized water, ethanol, or distilled water. Watch Glass Water Bath Weigh Boat Weighing Machines Wing Top Wire Gauze It is a piece of concave glass that is typically used to hold solids, evaporate liquids, weigh, and heat small amounts of a substance. It can also be used as a beaker cover to stop condensation from escaping from the container. It is a device used for heating flammable chemical samples at a constant temperature. It is used for weighing solids on a balance. These devices assist in weighing out the precise quantity of reagents or other small units of substances in terms of weight. To produce a large, fishtail flame capable of evenly heating a large area and bending glass. Also known as wire mesh. This apparatus is intended to assist in the heating of glassware that cannot be directly heated by the burner or flame. It keeps the glass tubes from being shocked by the fire and breaking up. REFERENCES Labkafe. (2022). School science laboratory equipment list and uses. Labkafe.Com. Retrieved 2022, from https://www.labkafe.com/blog/20-common-school-science-laboratoryequipment-and-their-uses Labmate-online. (2014, December 4). What are the different types of laboratory glassware? Labmate-Online.Com. Retrieved 2022, from https://www.labmateonline.com/news/laboratory-products/3/breaking-news/what-are-the-different-types-oflaboratory-glassware/32653 LabPro. (2022). Lab glassware and glassware equipment. Labproinc.Com. Retrieved 2022, from https://labproinc.com/blogs/lab-glassware-and-glassware-equipment/the-only-glasswareequipment-list-your-high-school-chemistry-lab-needs Mbuthia, M. (2021, October 25). 20 most common lab equipment names, pictures and their uses. Legit.Ng. Retrieved 2022, from https://www.legit.ng/1222752-common-laboratoryapparatus-names-uses.html StudiousGuy. (2022). List of chemistry laboratory apparatus and their uses. Studiousguy.Com. Retrieved 2022, from https://studiousguy.com/list-of-chemistry-laboratory-apparatusand-their-uses/