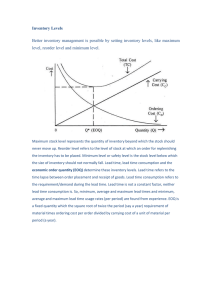
Assignment Problem: 1 Consider the following examples of an MPS record for a product built in a make- to-stock environment with inventory held. The product is built in a fixed-order quantity of 125 units, and there are110 units in beginning inventory. Table 1 is an initial MPS record showing the demand forecasts for the next 12 weeks. Week Forecast Projected available MPS 1 50 60 2 50 10 3 50 40 4 50 5 75 6 75 7 75 8 75 9 10 11 12 50 50 50 50 Problem: 2 Complete the MRP schedule for the part below: Lot size= 2,000+ Safety Stock= 400, Lead time= 1 week Allocated= 300,On hand= 1,300 Week 1 2 3 4 5 6 Gross requirements 1,100 700 1,500 900 1,850 1,400 Scheduled receipts 2,000 `Available 900 200 700 1800 1950 Planned order receipts 2000 2000 2000 Planned order releases 2000 2000 550 Net requirements 2000 Problem: 3 Assume you have a product with the following parameters: Demand 360 Holding cost per year $1.00 per unit Order cos t: $100 per order What is the EOQ? Problem: 4 Given the data from Problem 3, and assuming a 300-day work year; how many orders should be processed per year? What is the expected time between orders? Problem: 5 What is the total cost for the inventory policy used in Problem 3? Problem: 6 Assume that the demand was actually higher than estimated (i.e., 500 units instead of 360 units). What will be the actual annual total cost? Problem: 7 A manufacturer buys certain equipment form suppliers at Rs. 30 per unit. Total annual needs are 800 units. The following further data are available: Annual return on investments 10% Rent, insurance, storing per unit per year Rs. 2 Cost of placing an order Rs. 100 What is the EOQ? Problem: 8 We need 1,000 electric drills per year. The ordering cost for these is $100 per order and the carrying cost is assumed to be 40% of the per unit cost. In orders of less than 120, drills cost $78; for orders of 120 or more, the cost drops to $50 per unit. Should we take advantage of the quantity discount? Problem: 9 Litely Corp sells 1,350 of its special decorator light switch per year, and places orders for 300 of these switches at a time. Assuming no safety stocks, Litely estimates a 50% chance of no shortages in each cycle, and the probability of shortages of 5, 10, and 15 units as 0.2, 0.15, and 0.15 respectively. The carrying cost per unit per year is calculated as $5 and the stockout cost is estimated at $6 ($3 lost profit per switch and another $3 lost in goodwill, or future sales loss). What level of safety stock should Litely use for this product? (Consider safety stock of 0, 5, 10, and 15 units) Problem: 10 Presume that Litely carries a modern white kitchen ceiling lamp that is quite popular. The anticipated demand during lead time can be approximated by a normal curve having a mean of 180 units and a standard deviation of 40 units. What safety stock should Litely carry to achieve a 95% service level? Problem: 11 A local distributor for a national tire company expects to sell approximately 9600 steel-belted radical tires of a certain size and tread design next year. Annual carrying cost is $16 per tire, and ordering cost is $75 per order. The distributor operates 288 days a year. a. What is the EOQ? b. How many times per year would the store reorder if the ECQ is ordered? What is the length of an order cycle if the EOQ is ordered? What is the total cost? Problem: 12 On average, I sell 150,000 units a year, which I obtain from a wholesaler. I estimate that the cost to me of placing an order is $50 with the average inventory storage cost being 20% per year of the cost of a unit ($5). a. What would be the optimal order quantity? b. I currently order 5 times a year. How much would I save by switching to the optimal order quantity as compared with my current policy of ordering 5 times a year? Problem: 13 A carpet store has a daily demand of 30 yards of carpet with a standard deviation of 5 yards per day. The lead-time for the order is 9 days. The carpet store wants a reorder point with a 95% service level and a 5% stock-out probability. Calculate the Reorder point and the Safety stock. Problem: 14 The purchasing agent has ascertained that the usage of floppy disks in the company is approximately normally distributed, with a mean of 30 per working day and a variance of 16. The company operates 240 days per year. Floppy disks are obtained from a supplier who is very reliable, when an order is placed (on day 0), it is always received on the fifth working day. The company cannot afford to run out of floppy disks, and the purchasing agent has established a 99.5 percent service level. a. Which reorder point model is appropriate here, fixed lead time and variable lead time and fixed demand, or variable demand and variable lead time? demand, variable b. What is the mean usage during lead time? c. What is the standard deviation of the usage during lead time? d. What is the reorder point? e. What is the significance of the reorder point? f. What is the safety stock? Problem: 15 The purchasing agent has ascertained that the usage of letterhead paper has an approximately normal distribution with a mean of 200 sheets per working day and a standard deviation of 13 sheets. Letterhead paper is ordered from a printer whose deliveries are variable, with a mean of 25 working days and a variance of 4 working days. The purchasing agent has established a 99 percent service level for letterhead paper. Which reorder point model is appropriate here: variable demand and fixed lead time, fixed demand and variable lead time, or variable demand and variable lead time? b. What is the mean usage during lead time? c. What is the standard deviation of usage during lead time? d. What is the reorder point? e. What is the significance of the reorder point? f. What is the safety stock? Problem: 16 The owner of Smith's Speedy Service Station calculates that he sells about 15,000 gallons of regular unleaded gas per year. He sells gas from self-service pumps and wishes to maintain a service level of 99% per year. Although the price of gasoline fluctuates with the seasons, he estimates that it averages about $1.00 per gallon. It costs $.25 to store one gallon for one year. It costs $25.00 to place and receive one order. The lead time for an order is 1 day and the standard deviation of sales is about 5 gallons per day. a. What average number of gallons short will be consistent with the specified service level? b. What is the EOQ? c. What is the average number of gallons short per order cycle? d. What lead time service level is necessary for the 99% service level?