Loneliness: A Global Issue & Its Impact on Health & Productivity
advertisement

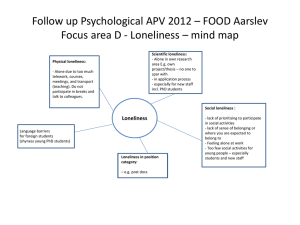
Title: Loneliness: An Urgent and Underappreciated Global Issue for the Future Introduction Loneliness, which defined as a distressing feeling that accompanies the perception that one’s social needs are not being met by the quantity or especially the quality of one’s social relationships, is an underlying issue that affects people of all ages and nations. The World Health Organization (WHO) has recognized loneliness as a public health concern, with the US Surgeon General comparing its impact on mortality to smoking 15 cigarettes per day (The Guardian, 2023), implying its devastating impact to our health. Besides, productivity is also impacted hugely so its potential harm to our academic performance is often overlooked. Delving into problems pertaining to loneliness, it is hoped that the seriousness and urgency of loneliness can be acknowledged after reading the essay. Problem 1: Impact on Physical and Mental Health The first predicament affiliated with loneliness is its deleterious influence on both physical and mental health. Loneliness has been found to increase the risk of heart disease and stroke (Valtorta et al., 2016). In addition, research has shown numerous dependencies between loneliness and conditions such as depression, anxiety, and even suicidal ideation (Hawkley & Cacioppo, 2010). Therefore, it is an appropriate derivation that countless of suicidal or sudden death for teenagers, middle-aged, elderly etc. are explicitly or implicitly caused by social isolation and the feeling of forlorn loneliness. For less extreme cases, the consequences of social isolation are interconnected with behavioral changes, entwining an Insalubrious lifestyle (such as smoking, lower physical activity, alcohol addiction, consumption of junk food) (Kobayashi and Steptoe, 2018; Leigh-Huntet al., 2017). Additionally, not only do these conundrums affect individuals, but they also place strain on healthcare systems and society at large. Millions of human resources and billions of capitals are used to provide affordable medicine for heart attack and depression, offer counselling service by psychologist, deal with crime relevant to social isolation. Furthermore, social withdrawal is associated with the detrimental effects of loneliness, exacerbating the problem and which is hard to be noticed, often occurring in elderly and some teenagers without caring parents. Problem 2: Decrease in Motivation and Productivity Loneliness precipitates diminished levels of motivation and productivity, which are paramount to all walks of life, especially us as university students. According to a study conducted by the American College Health Association in 2018, 40% of college students reported feeling so depressed that it hindered their functioning while 61% experienced anxiety. If students had been helped tackling through the loneliness obstacle, they would have been exceptional in their academic performance with great possibility, in contradistinction to struggle with procrastination. The abatement of impetus and effectiveness due to solitude is a pressing affair that necessitates advertence as it might engender curtailed life satisfaction, job performance and academic achievements. Moreover, the economic implications of shrunken productivity due to loneliness can be substantial (Harvard Economics Review, 2020). The review implied that work efficiency and activeness of employers and employees are highly lowered when they are annoyed by emptiness. As a result, under no circumstance could a company or a school stands out of the crowd while their workers or teachers are not comfortable with themselves. In the long run, it is unfavorable for the history of human development. Comparison Although both challenges hold huge significance in the foreseeable future, well-being takes precedence over productivity as the pressing concern. The physical and mental health can be deteriorated in a rapid rate owing to loneliness. On the other hand, we may take the initiative to enhance determination through substituted approaches. Undeniably, personal health is much crucial than personal value that one can provide for all human being. Solutions How can we mitigate the impact of loneliness? Individuals are encouraged to explore various hobbies or own a pet. First, engaging in activities from joining clubs, sports teams or volunteering can allow opportunities for positive interaction between similar mindsets and foster the formation of meaningful relationships. These connections brought by events can build collective memories and trust upon each other, help alleviating emotion of loneliness and establish sense of community. Second, having pets can cut back loneliness and improve health, which is proved by quantitative research (McNicholas & Collis 2000). Pets offer companionship, emotional support, and a sense of purpose which is especially beneficial for individuals living alone. Social networks might be possibly developed through either online or offline , for instance while replying on a Instagram story or walking , they also embolden icebreaking between people, acting like catalysts. Raising awareness about the issue of loneliness through implementation of policies and initiatives is the global panacea. Governments organizations and communities can collaborate to create programs in the society, targeting vulnerable groups like solitary elderly and middle-aged adults. Likewise, organizing community events in neighborhoods can construct support groups tailored for groups of people (like seniors, new parents or individuals struggling with health), or launching public campaigns. They all educate the public about the significance of being socially connected and reduce the potential risks that come with loneliness. Similarly, the fellow students in social science school can conduct more studies on loneliness and deploy more solutions over the world. (The author will greatly appreciate that.) By addressing the barrier loneliness brought and gaining policy support for nurturing social connections, the impacts of loneliness on people worldwide can be subtracted, ameliorating overall well-being for all humans. Conclusion In conclusion, loneliness is a pressing issue that warrants attention and discussion within the global community. The aforementioned problems, the impact on physical and mental health and the decline in motivation and productivity, cannot be overstated. Loneliness is the most exigent topic currently because it is right inside us to trouble anytime and anywhere, millions of people are suffering from it at the moment you are reading. However, it is invisible and seldomly expatiated. By adopting a whole-of-systems approach and developing global policy support for social connectedness, we, as global citizens, must facilitate to reconcile the adverse effects of loneliness and promote the well-being of individuals across the globe. References American College Health Association. (2018). American College Health Association-National College Health Assessment II: Reference Group Executive Summary Spring 2018. Silver Spring, MD: American College Health Association. Harvard Economics Review. (2020) https://www.economicsreview.org/post/the-cost-ofincognizance-how-loneliness-affects-productivity Hawkley, L. C., & Cacioppo, J. T. (2010). Loneliness matters: a theoretical and empirical review of consequences and mechanisms. Annals of Behavioral Medicine, 40(2), 218-227. Kobayashi, L. C. and Steptoe, A. (2018). Social isolation, loneliness, and health behaviors at older age: longitudinal cohort study. Annals of Behavioral Medicine, 52, 582–593. doi: 10.1093/abm/kax033. Leigh-Hunt, N. et al. (2017). An overview of systematic reviews on the public health consequences of social isolation and loneliness. Public Health, 152, 157–171. doi: 10.1016 /j.puhe.2017.07.035. McNicholas, J., & Collis, G. M. (2000). Dogs as catalysts for social interactions: robustness of the effect. British Journal of Psychology, 91(1), 61-70. The Guardian. (2023). https://www.theguardian.com/globaldevelopment/2023/nov/16/who-declares-loneliness-a-global-public-health-concern Valtorta, N. K., Kanaan, M., Gilbody, S., Ronzi, S., & Hanratty, B. (2016). Loneliness and social isolation as risk factors for coronary heart disease and stroke: systematic review and metaanalysis of longitudinal observational studies. Heart, 102(13), 1009-1016.