Uploaded by
The_WisconsinGamer NC
AP Microeconomics: Production, Cost, and Competition Objectives
advertisement

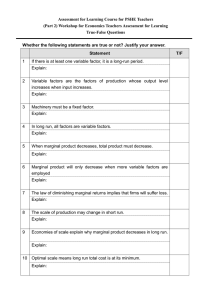
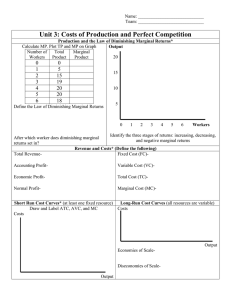
AP Microeconomics Production, Cost, and the Perfect Competition Model Module Objectives 03.01 The Production Function Describe the production function and how it explains the relationship between inputs and outputs in the short run and the long run. Using a graph or table, describe the impact of an input usage change on marginal product, average product, and total product. Calculate marginal product using data from a graph or table. Describe the law of diminishing marginal returns and identify its effects using a graph or table. 03.02 Short-Run Production Costs Define terms related to short-run production costs and explain the relationships between them using a graph or table. Illustrate how production functions with diminishing marginal returns yield an upwardsloping marginal cost curve. Illustrate and explain the impacts of specialization, division of labor, and shifts in cost curves. 03.03 Long-Run Production Costs Explain how in the long run, all of a firm's costs are variable, and there are no diminishing marginal returns. Define and distinguish between increasing, decreasing, and constant returns to scale and the relationship to average total costs in the long run using a graph. Identify and describe the significance of minimum efficient scale using a graph. 03.04 Types of Profit Define and distinguish between economic and accounting profit using the concepts of implicit costs, explicit costs, and normal profit. Recognize that if implicit costs are fully compensated, this results in normal profit. Explain how firms respond to profit opportunities. Calculate a firm's economic profit or loss. 03.05 Profit Maximization Define the profit-maximizing rule using a graph or data. Explain how firms are assumed to produce output to maximize their profits by comparing marginal revenue and marginal cost. Explain the profit-maximizing level of production using a graph or data. 03.06 Firms’ Short-Run and Long-Run Decisions Explain why in the short run firms decide to operate or shut down by comparing total revenue to total variable cost or price to average variable cost using a graph or data. Explain why in the long run firms will decide to enter a market when there are profitmaking opportunities and will decide to exit a market when they anticipate economic losses. 03.07 Perfect Competition Define and describe the characteristics of perfectly competitive markets, using a graph to distinguish between perfectly competitive markets in the short run and in the long run. Define and distinguish between productive and allocative efficiency, as well as between constant, increasing, or decreasing cost industry. Draw an accurately labeled graph of a perfectly competitive market and explain how prices lead to efficient outcomes in perfectly competitive markets. Calculate economic profit or loss in perfectly competitive markets using data from a table or graph.