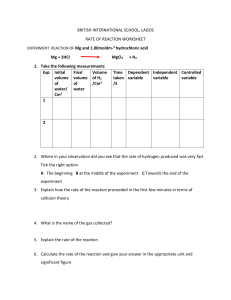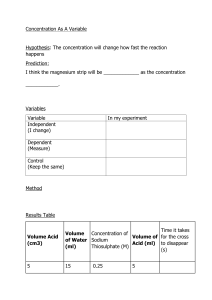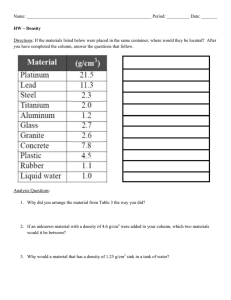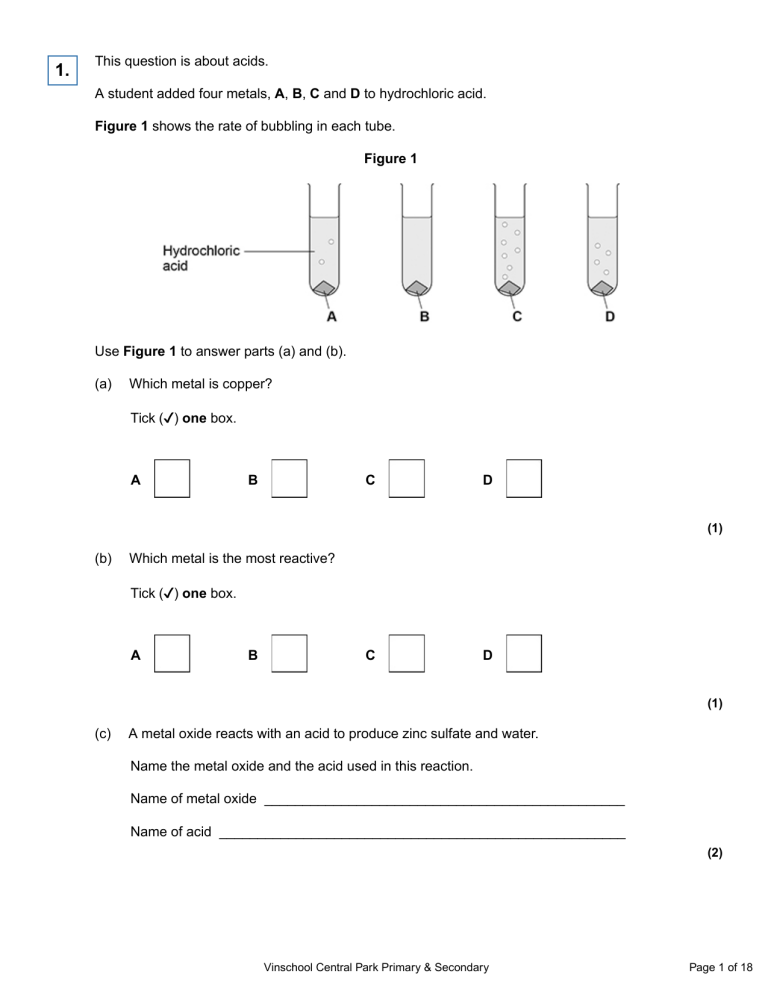
1. This question is about acids. A student added four metals, A, B, C and D to hydrochloric acid. Figure 1 shows the rate of bubbling in each tube. Figure 1 Use Figure 1 to answer parts (a) and (b). (a) Which metal is copper? Tick (✓ ✓) one box. A C B D (1) (b) Which metal is the most reactive? Tick (✓ ✓) one box. A B C D (1) (c) A metal oxide reacts with an acid to produce zinc sulfate and water. Name the metal oxide and the acid used in this reaction. Name of metal oxide _______________________________________________ Name of acid _____________________________________________________ (2) Vinschool Central Park Primary & Secondary Page 1 of 18 (d) Universal indicator is used to measure the pH of a solution. Draw one line from each pH to the colour of universal indicator in a solution with that pH. pH Colour of universal indicator Blue 1 Green Purple 7 Red Yellow (2) A student reacts an acid with an alkali in a titration. (e) What is the type of reaction when an acid reacts with an alkali? Tick (✓ ✓) one box. Combustion Decomposition Neutralisation (1) Vinschool Central Park Primary & Secondary Page 2 of 18 (f) Figure 2 shows a piece of equipment used to measure the volume of the acid in the titration. Figure 2 What is the name of this piece of equipment? Tick (✓ ✓) one box. Burette Pipette Syringe Tube (1) (Total 8 marks) Vinschool Central Park Primary & Secondary Page 3 of 18 2. A student investigated the reaction of magnesium with hydrochloric acid. Figure 1 shows the apparatus used. Figure 1 This is the method used. 1. Set up the apparatus as shown in Figure 1. 2. Cut 10 mm of magnesium ribbon. 3. Remove the stopper. 4. Add the magnesium ribbon to the conical flask. 5. Replace the stopper as quickly as possible. 6. Record the final reading on the gas syringe when the reaction has stopped. 7. Repeat steps 1 to 6 three more times. 8. Repeat steps 1 to 7 with different lengths of magnesium ribbon. (a) Which gas is produced when magnesium reacts with hydrochloric acid? Tick (✓ ✓) one box. Carbon dioxide Chlorine Hydrogen Oxygen (1) Vinschool Central Park Primary & Secondary Page 4 of 18 (b) What was the independent variable in the investigation? ___________________________________________________________________ (1) (c) Give one control variable in the investigation. ___________________________________________________________________ (1) Table 1 shows the results for one length of magnesium ribbon. Table 1 Volume of gas produced in cm3 Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3 Trial 4 19 36 37 32 One of the results was anomalous. (d) Which trial in Table 1 gave an anomalous result? Trial _______________ (1) (e) Suggest one reason for the anomalous result in Table 1. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (1) (f) Table 2 shows the mean volume of gas produced for each length of magnesium ribbon. Table 2 Length of magnesium ribbon in mm 10 20 30 40 50 60 Mean volume of gas produced in cm3 7 14 21 28 35 42 Vinschool Central Park Primary & Secondary Page 5 of 18 Plot the data from Table 2 on Figure 2. Draw a line of best fit. Figure 2 (3) (g) Complete the sentence. As the length of the magnesium ribbon increases, the mean volume of gas produced ______________________. (1) (Total 9 marks) 3. This question is about acids and alkalis. Vinschool Central Park Primary & Secondary Page 6 of 18 (a) Explain why the pH of an acid depends on: • the strength of the acid • the concentration of the acid. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (4) (b) A student titrated 25.00 cm3 of hydrochloric acid with 0.100 mol/dm3 barium hydroxide solution. The table below shows the results. Titration number 1 Volume of barium hydroxide solution used in cm3 2 3 4 5 23.90 23.45 23.55 23.55 23.45 The student calculated the volume of barium hydroxide solution to be used in the titration calculation as 23.50 cm3. Explain why the student used a volume of 23.50 cm3 of barium hydroxide solution in the titration calculation. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (2) Vinschool Central Park Primary & Secondary Page 7 of 18 (c) 25.00 cm3 of the hydrochloric acid reacted with 23.50 cm3 of the 0.100 mol/dm3 barium hydroxide solution. The equation for the reaction is: 2 HCl(aq) + Ba(OH)2(aq) → BaCl2(aq) + 2 H2O(l) Calculate the concentration of the hydrochloric acid in mol/dm3. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ Concentration of the hydrochloric acid = _______________mol/dm3 (4) Vinschool Central Park Primary & Secondary Page 8 of 18 Another student titrated sulfuric acid with barium hydroxide solution. The equation for the reaction is: H2SO4(aq) + Ba(OH)2(aq) → BaSO4(s) + 2 H2O(l) The student measured the electrical conductivity of the mixture during the titration. The better a conductor, the higher the electrical conductivity value. The figure below shows the results. (d) Explain why the electrical conductivity of the mixture was zero when the sulfuric acid had just been neutralised. Use the equation for the reaction. Refer to ions in your answer. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (3) Vinschool Central Park Primary & Secondary Page 9 of 18 (e) The student then added a further 10 cm3 of barium hydroxide solution. The electrical conductivity of the mixture increased. Give one reason why. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (1) (Total 14 marks) 4. This question is about acids, bases and salts. Zinc nitrate is a salt. A student produces zinc nitrate using an acid and a base. (a) Which acid should the student use to produce zinc nitrate? Tick (✓ ✓) one box. Hydrochloric acid Nitric acid Sulfuric acid (1) (b) Which is a base the student could use to produce zinc nitrate? Tick (✓ ✓) one box. Zinc chloride Zinc oxide Zinc sulfate (1) Vinschool Central Park Primary & Secondary Page 10 of 18 (c) Name the salt with the formula MgBr2 ___________________________________________________________________ (1) A student investigated how pH changes during a titration. This is the method used. 1. Pour 25.0 cm3 of hydrochloric acid into a beaker. 2. Measure the pH of the hydrochloric acid with a pH probe. 3. Add 1.0 cm3 of sodium hydroxide solution from a burette. 4. Swirl the mixture. 5. Measure the pH of the mixture. 6. Repeat steps 3 to 5 until a total of 30.0 cm3 of sodium hydroxide solution has been added. The graph below shows the student’s results. Vinschool Central Park Primary & Secondary Page 11 of 18 (d) Describe how the pH of the mixture changes as sodium hydroxide solution is added to hydrochloric acid. Use the data from the graph above in your answer. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (3) (e) What volume of sodium hydroxide solution is needed to neutralise 25.0 cm3 of hydrochloric acid? Use the graph above. Volume = _______________ cm3 (1) (f) Figure 1 shows the colour of universal indicator at different pH values. Figure 1 The student could have used universal indicator instead of a pH probe. Determine the colour of universal indicator when 10.0 cm3 of sodium hydroxide solution has been added to 25.0 cm3 of hydrochloric acid. Use the graph above and Figure 1. Colour = _______________ (1) Vinschool Central Park Primary & Secondary Page 12 of 18 (g) The student used a pipette to measure 25.0 cm3 of hydrochloric acid. Figure 2 shows a pipette. Figure 2 The pipette is labelled 25.0 ± 0.06 cm3 Calculate the percentage uncertainty in the volume measured using this pipette. Use the equation: ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ Percentage uncertainty = _______________ % (2) (h) Give one advantage of using a pipette rather than using a measuring cylinder to measure the volume of hydrochloric acid. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (1) (Total 11 marks) Vinschool Central Park Primary & Secondary Page 13 of 18 5. Lithium carbonate reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid. A group of students investigated the volume of gas produced. This is the method used. 1. 2. 3. 4. Place a known mass of lithium carbonate in a conical flask. Measure 10 cm3 of dilute hydrochloric acid using a measuring cylinder. Pour the acid into the conical flask. Place a bung in the flask and collect the gas as shown in Figure 1. Figure 1 (a) Figure 2 shows the measuring cylinder. Figure 2 What volume of gas has been collected? Vinschool Central Park Primary & Secondary Page 14 of 18 Volume = __________________ cm3 (1) Vinschool Central Park Primary & Secondary Page 15 of 18 (b) The table below shows the students’ results. Volume of gas in cm3 Mass of lithium carbonate in g 0.0 0 0.1 22 0.2 44 0.3 50 0.4 88 0.5 96 0.6 96 0.7 96 On Figure 3: • Plot these results on the grid. • Complete the graph by drawing two straight lines of best fit. Figure 3 (4) Vinschool Central Park Primary & Secondary Page 16 of 18 (c) What are two possible reasons for the anomalous result? Tick two boxes. Too much lithium carbonate was added. The bung was not pushed in firmly enough. There was too much water in the trough. The measuring cylinder was not completely over the delivery The conical flask was too small. (2) (d) Describe the pattern the graph shows up to 0.4 g of lithium carbonate added. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (2) Vinschool Central Park Primary & Secondary Page 17 of 18 (e) Lithium carbonate decomposes when heated. The equation shows the decomposition of lithium carbonate. Li2CO3 (s) → Li2O (s) + CO2 (g) Figure 4 shows the apparatus a student used to decompose lithium carbonate. Figure 4 Why does the limewater bubble? ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (1) (f) The student repeated the experiment with potassium carbonate. The limewater did not bubble. Suggest why there were no bubbles in the limewater. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (1) (Total 11 marks) Vinschool Central Park Primary & Secondary Page 18 of 18