Electrical Engineering Fundamentals: Ohm's, Kirchhoff's, Op-Amps
advertisement

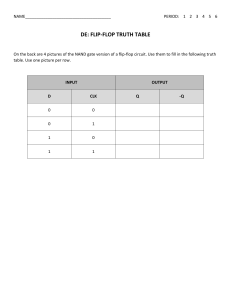
Question 1: Ohm's Law Question: State Ohm's Law and provide the mathematical equation associated with it. Solution: Ohm's Law states that the current passing through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points, provided the temperature remains constant. Mathematically, Ohm's Law is represented as V=I⋅RV=I⋅R, where VV is the voltage across the conductor, II is the current passing through the conductor, and RR is the resistance of the conductor. Question 2: Kirchhoff's Laws Question: Briefly explain Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL) and Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL). Solution: Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL) states that the total voltage around any closed loop in a circuit is equal to the sum of the voltages across all the elements in that loop. Mathematically, it can be expressed as ∑Vloop=0∑Vloop=0. Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) states that the total current entering any junction in a circuit is equal to the total current leaving that junction. Mathematically, it can be expressed as ∑Iin=∑Iout∑Iin=∑Iout. Question 3: Operational Amplifiers (Op-Amps) Question: What is the significance of the open-loop and closed-loop configurations in operational amplifiers (op-amps)? Solution: In an open-loop configuration, an operational amplifier operates without any feedback. It has a very high voltage gain but is not practically useful due to lack of stability. Closed-loop configurations involve providing feedback, and they are commonly used in practical applications. The closed-loop configuration determines the overall characteristics of the op-amp circuit, such as gain, bandwidth, and stability. Question 4: Digital Logic Gates Question: Explain the operation of an AND gate and provide its truth table. Solution: An AND gate produces a high output (1) only when both of its inputs are high (1). The truth table for an AND gate is as follows: Input A Input B Output 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 Question 5: Flip-Flops Question: What is the purpose of a D flip-flop, and how does it differ from a JK flip-flop? Solution: A D flip-flop (Data or Delay flip-flop) is a digital circuit that stores and outputs the value of its data input. It captures the input at the rising or falling edge of the clock signal. A JK flip-flop, on the other hand, has the ability to toggle its output based on certain input conditions. It has J (set) and K (reset) inputs, and its behavior is more versatile compared to a D flip-flop.