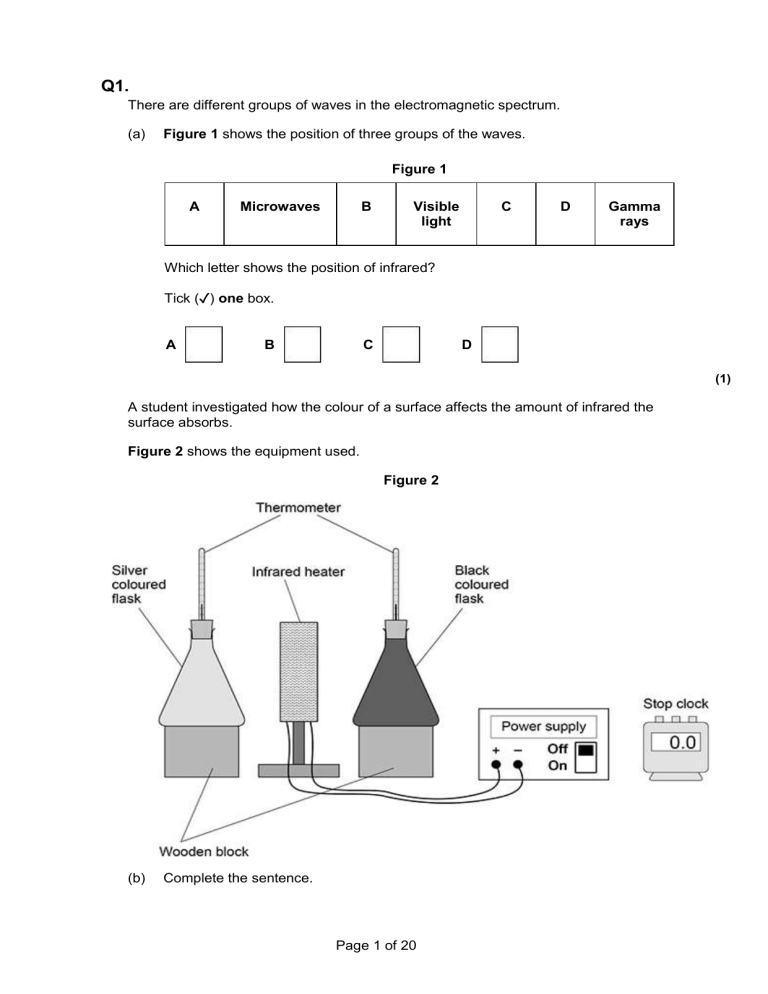
Q1. There are different groups of waves in the electromagnetic spectrum. (a) Figure 1 shows the position of three groups of the waves. Figure 1 A Microwaves B Visible light C D Gamma rays Which letter shows the position of infrared? Tick (✓) one box. A B C D (1) A student investigated how the colour of a surface affects the amount of infrared the surface absorbs. Figure 2 shows the equipment used. Figure 2 (b) Complete the sentence. Page 1 of 20 Choose the answer from the box. a control the dependent the independent In this investigation the distance between each flask and the infrared heater is ____________________ variable. (1) (c) The student wrote the hypothesis: ‘Surface colour of the flask affects the amount of infrared absorbed when the heater is switched on for five minutes.’ Describe how the equipment in Figure 2 could be used to test this hypothesis. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (4) The table below shows the results. Colour of flask Temperature increase in °C Test 1 Test 2 Test 3 Black 19 17 27 Silver 10 12 11 (d) Which one of the results for the black flask is anomalous? ___________________________________________________________________ (1) (e) The anomalous result was caused by reading the thermometer incorrectly. Page 2 of 20 What should the student do with the anomalous result? ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (1) (f) Calculate the mean temperature increase for the silver flask. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ Mean temperature increase = ____________________ °C (1) (g) What conclusion can be made from the table above? Tick (✓) one box. Both flasks absorbed the same amount of infrared during the five minutes. The black flask absorbed the most infrared during the five minutes. The silver flask absorbed the most infrared during the five minutes. (1) (Total 10 marks) Q2. (a) The diagram below shows the position of three types of wave in the electromagnetic spectrum. Which letter represents the position of X-rays in the electromagnetic spectrum? Tick (✓) one box. A B C D (1) A doctor needs to obtain an image of a bone in a patient’s injured arm. The doctor takes an X-ray of the arm. (b) Give one possible harmful consequence of receiving a dose of X-ray radiation. Page 3 of 20 ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (1) The table below gives information about two methods of bone imaging. Method Radiation dose in millisieverts X-ray of arm 0.1 CT scan of arm 6.0 (c) Compare the risk of harm to the patient of having an X-ray rather than a CT scan. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (2) (d) Which of the following is the same as 6.0 millisieverts? Tick (✓) one box. 0.60 sieverts 0.060 sieverts 0.0060 sieverts 0.00060 sieverts (1) (e) The patient received a total radiation dose of 2.5 millisieverts during one year. Calculate the percentage of this dose that came from one X-ray of the arm. Use the data in the table above. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ Percentage = _______________ % Page 4 of 20 (2) (Total 7 marks) Q3. (a) Figure 1 shows the position of three types of wave in the electromagnetic spectrum. Figure 1 A Microwaves B Visible light C D Gamma rays Which letter represents infrared in the electromagnetic spectrum? Tick (✓) one box. A B C D (1) (b) What is infrared used for? Tick (✓) one box. Electrical heating Energy efficient lamps Satellite communications Sun tanning (1) An infrared camera produces a colour image. Different colours show different temperatures. People emit infrared radiation. Figure 2 shows how the colour of the image of a person on an infrared camera depends on the person’s body temperature. Figure 2 (c) Complete the sentence. Choose the answer from the box. Page 5 of 20 orange red yellow The image produced by an infrared camera of a person with a body temperature of 37 °C is mainly _________________________ . (1) (d) Rescue workers use infrared cameras to search for people trapped under rubble after an earthquake. How does the image of a trapped person change if the person’s body temperature drops from 37 °C to 33 °C? ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (1) A student investigated how the type of surface affects the amount of infrared the surface radiates. Figure 3 shows the equipment used. Figure 3 (e) Complete the sentence. Choose the answer from the box. a control the dependent the independent In this investigation the type of surface is ___________________________ variable. (1) (f) Describe how the equipment shown in Figure 3 would be used to compare the infrared radiation emitted from the vertical surfaces of the cube. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ Page 6 of 20 ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (3) The table below shows the results. Type of surface (g) Temperature in °C Matt black 68.0 Matt white 65.5 Shiny black 66.3 Shiny silver 28.0 What is the resolution of the infrared detector? Tick (✓) one box. 0.1 °C 1.0 °C 1.7 °C 68.0 °C (1) The bar chart in Figure 4 shows two of the results. Figure 4 Page 7 of 20 (h) Complete the bar chart to show all of the results. (3) (i) Give one conclusion that can be made from the results. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (1) (Total 13 marks) Q4. The diagram below shows the position of three types of wave in the electromagnetic spectrum. Radio waves (a) A B C Ultraviolet X-rays D Which position shows where visible light is in the spectrum? Tick one box. A B C D (1) (b) Which one of the statements about electromagnetic waves is correct? Tick one box. Page 8 of 20 Radio waves have a higher frequency than X-rays. Radio waves have a longer wavelength than ultraviolet. X-rays have a longer wavelength than radio waves. X-rays travel faster through the air than ultraviolet. (1) (c) Give one possible danger of exposing your skin to ultraviolet radiation. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (1) (d) Having an X-ray taken exposes a person to ionising radiation. The table below gives the average radiation dose for an X-ray of the chest and an X-ray of the upper digestive system. Part of the body Upper digestive system Chest Radiation dose in millisieverts (mSv) 5.0 0.1 The risk of an X-ray causing cancer is about 1 in 20 000 for each mSv of radiation received. Compare the risk of developing cancer from having an X-ray of the upper digestive system with the risk from having an X-ray of the chest. Use the data in the table. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (2) (Total 5 marks) Q5. (a) Which one of the following is not an electromagnetic wave? Tick one box. Page 9 of 20 Gamma rays Sound Ultraviolet X-rays (1) (b) What type of electromagnetic wave do our eyes detect? ___________________________________________________________________ (1) (c) What is a practical use for infrared waves? Tick one box. Cooking food Energy efficient lamps Medical imaging Satellite communications (1) Scientists have detected radio waves emitted from a distant galaxy. Some of the radio waves from the distant galaxy have a frequency of 1 200 000 000 hertz. (d) Which is the same as 1 200 000 000 hertz? Tick one box. 1.2 gigahertz 1.2 kilohertz 1.2 megahertz Page 10 of 20 1.2 millihertz (1) (e) Radio waves travel through space at 300 000 kilometres per second (km/s). How is 300 000 km/s converted to metres per second (m/s)? Tick one box. 300 000 ÷ 1000 = 300 m/s 300 000 × 1000 = 300 000 000 m/s 300 000 + 1000 = 301 000 m/s 300 000 – 1000 = 299 000 m/s (1) (f) Write the equation which links frequency, wavelength and wave speed. ___________________________________________________________________ (1) (g) Calculate the wavelength of the radio waves emitted from the distant galaxy. Give your answer in metres. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ wavelength = ____________________ m (3) (Total 9 marks) Q6. The figure below shows an incomplete electromagnetic spectrum. A (a) microwaves B C ultraviolet D gamma What name is given to the group of waves at the position labelled A in the figure above? Tick one box. Page 11 of 20 infrared radio visible light X-ray (1) (b) Electromagnetic waves have many practical uses. Draw one line from each type of electromagnetic wave to its use. Electromagnetic wave Use For fibre optic communications Gamma rays For communicating with a satellite Microwaves To see security markings Ultraviolet To sterilise surgical instruments (3) (c) Complete the sentence. Use an answer from the box. black body ionising Page 12 of 20 nuclear X-rays can be dangerous to people because X-rays are _____________________ radiation. (1) (Total 5 marks) Q7. (a) On the wave drawn below, mark the amplitude and wavelength. (2) (b) A wave is said to have a frequency of 25 Hz. Explain what the term frequency means. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (1) (c) From the electromagnetic spectrum, give the name and use of a radiation of lower frequency than light. Name _____________________________________________________________ Use _______________________________________________________________ (2) (Total 5 marks) Q8. Waves may be longitudinal or transverse. (a) Describe the differences between longitudinal waves and transverse waves. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ Page 13 of 20 ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (3) (b) Radio waves are electromagnetic waves. Describe how radio waves are different from sound waves. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (4) (Total 7 marks) Page 14 of 20 Mark schemes Q1. (a) B 1 (b) a control 1 (c) record the initial temperature of the two thermometers in each flask allow initial temperature is a control variable or ensure initial temperature is the same in both flasks 1 switch the infrared heater on and start the stop clock (at the same time) allow switch on the power supply for switch on the heater 1 after five minutes record the (final) temperature from both flasks allow calculate the temperature increase / change after five minutes 1 see / check if the temperature inside the flasks had increased by different amounts 1 (d) 27 (°C) allow 27 (°C) identified on the table allow test 3 1 (e) ignore (the result) allow repeat (the result) 1 (f) (33/3 = ) 11 1 (g) the black flask absorbed the most infrared during the five minutes 1 [10] Q2. (a) D 1 (b) Any one from: • mutation (of genes/DNA/chromosomes) allow can damage OR destroy genes/DNA/chromosomes ignore damage/destroy cells/tissues/organs Page 15 of 20 ignore mutates cells • cancer/tumour • cell death allow kills cells 1 (c) the risk of harm is lower from the X-ray 1 by a factor of 60 1 (d) 0.0060 sieverts 1 × 100 (e) 1 4 (%) allow 0.04 for 1 mark 1 [7] Q3. (a) B 1 (b) electrical heating 1 (c) orange allow a correct answer indicated in the box provided the answer space is blank 1 (d) becomes (more) red allow changes from mainly orange to mainly red 1 (e) the independent allow a correct answer indicated in the box provided the answer space is blank 1 (f) pour (hot) water into the (hollow metal) cube 1 point the IR detector at each / a side and take a reading allow point the IR detector at the cube and take a reading allow IR detector touching the surface and take a reading allow take the temperature for take a reading Page 16 of 20 1 keep the detector the same distance from each surface 1 (g) 0.1°C 1 (h) one bar drawn to 68.0 (°C) ignore the position of the bars on the x-axis 1 one bar drawn to 28.0 (°C) 1 tallest bar labelled Matt black and shortest bar labelled Shiny silver 1 (i) any one from: • (matt) black is the best emitter • shiny silver is the worst emitter allow matt white and shiny black are (almost) the same at emitting allow black is a good emitter allow silver is a poor emitter allow an answer in terms of highest / lowest temperature ignore any reference to absorption / reflection 1 [13] Q4. (a) C 1 (b) radio waves have a longer wavelength than ultraviolet 1 (c) (risk of) skin cancer cancer is insufficient or (prematurely) ageing skin skin damage is insufficient ignore kills skin cells 1 (d) risk is higher (for X-ray of uds than X-ray of chest) 1 by a factor of 50 or risk calculated for each type of X-ray chest X-ray = 1:200 000 (1) uds = 1:4000 (1) 1 Page 17 of 20 [5] Q5. (a) sound 1 (b) (visible) light 1 (c) cooking food 1 (d) 1.2 gigahertz 1 (e) 300 000 × 1000 = 300 000 000 m/s 1 (f) wave speed = frequency × wavelength allow v = f λ 1 (g) 300 000 000 = 1200 000 000 × λ an answer of 0.25 scores 3 marks 1 allow ecf from (e) 1 λ = 0.25 (m) 1 [10] Q6. (a) radio 1 (b) Page 18 of 20 award 1 mark for each correct line if more than one line is drawn from any em wave then none of those lines gain credit 3 (c) ionising 1 [5] Q7. (a) amplitude marked as approximately half a wave height great precision is not required 1 wavelength marked as a trough to trough distance or a peak to peak distance accept an equivalent repeat distance anywhere on the wave 1 (b) the number of waves each second accept cycles per second accept 25 waves pass each second 1 (c) any pair from microwave cooking or communication or mobile phone radio communication or entertainment infra-red cooking or heating or remote control or security or night sights or thermal imaging accept sensible specific uses 2 [5] Page 19 of 20 Q8. (a) the oscillation / vibration (causing the wave) a movement causes the wave is insufficient 1 for a transverse wave is perpendicular to the direction of energy transfer accept direction of wave travel 1 and for a longitudinal wave is parallel to the direction of energy transfer accept direction of wave travel if no marks awarded allow 1 mark for correctly linking perpendicular with transverse and parallel with longitudinal the marks may be scored by the drawing of two correctly labelled diagrams 1 (b) for radio waves: accept converse for each mark are transverse 1 travel at speed of light / higher speed 1 have greater frequencies 1 can travel through vacuum accept sound waves are not electromagnetic for 1 mark 1 [7] Page 20 of 20